Google Maps and Detailed Facts of Angola (AO). This page lets you explore Angola and its border countries (Country Location: Southern Africa, bordering the South Atlantic Ocean, between Namibia and the Democratic Republic of the Congo) through detailed Satellite imagery – fast and easy as never before Google Maps.
Find comprehensive information about this country’s diversity below: Google Maps, geography, economy, science, people, culture, environment, government, and history – All in One Wiki page.
There is also a Street View and free Driving Directions at your service. Your Google Satellite Map Sightseeing in Angola, Africa, starts here at Driving Directions and Maps.com.
Table of contents
- Background
- Overview
- Google Maps
- Climate
- Geography
- Resources and Land Use
- Population Data
- Economic Data
- Drinking Water Source
- Population, Median Age, Migration, and Citizenship
- Average Number of Childbirths
- Is this country a Safe Destination?
- Healthcare and Infectious Diseases
- Natural Hazards
- The Flag and Other Symbols
- Constitution
- Legal System
- About the Unemployment Rate, Labor Force, and Poverty Line
- About the Budget and Central Government Debt
- Inflation Rate and Prime Lending Rate
- Export/Import Partners and Data
- Renewable Energies Used
- Telecommunication Data, Calling Code
- Transport Infrastructure
- More Interesting Facts
Background
Angola’s rich history begins with the settlement of Bantu-speaking people around the 6th century A.D. Over the centuries, several Bantu kingdoms emerged, with the Kingdom of Kongo being the most prominent. The 16th century marked the arrival of the Portuguese, who established trading posts and introduced Christianity. Angola became a significant hub of the transatlantic slave trade, which led to a significant population loss. During the 1884-85 Berlin Conference, European powers formalized Angola’s current borders. After a prolonged struggle, Angola gained independence from Portugal in 1975, following the Angolan National Revolution. The post-independence era was marked by a civil war that lasted until 2002, significantly impacting the country’s development.
Overview
Angola, located in Southern Africa, is a presidential republic. Despite its vast natural resources, Angola faces socio-economic challenges, including poverty, high unemployment, and a need for diversification away from oil dependence. The country is working towards post-war reconstruction and economic reform, aiming to utilize its resources for national development.
Official Name: Republic of Angola
Date of Formation: Gained independence in 1975
Capital: Luanda
Population: Approximately 35.98 million (2023 estimate)
Total Area: N/A
Population Density: N/A
Languages: Portuguese (official), various Bantu languages
Religions: Predominantly Christian (Roman Catholic, Protestant)
Ethnic Origin: Ovimbundu, Kimbundu, Bakongo, and other African ethnic groups
Government: Presidential Republic
Currency: Angolan Kwanza (AOA)
Literacy Rate: N/A
Calorie Consumption: N/A
Google Maps
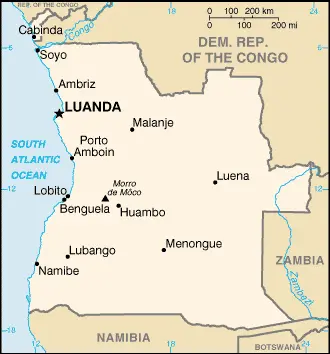
Located in southwest Africa, Angola suffered a civil war following independence from Portugal in 1975 until a 2002 peace deal. Hundreds of thousands of people died. Most of the land is hilly and grass-covered. Desert in the south. Mountains in the center and north.
From the Atlantic coastline to the interior highlands, Angola’s diverse geography can be explored through Google Maps. This tool provides an in-depth look at Angola’s urban centers, such as Luanda’s capital, and its natural landscapes.
The map below shows Angola’s cities, towns, highways, main roads, streets, and Street Views. To find a location, use the form below, type any city or place, view a simple map, and click the “show map” button.
The Google Maps above shows Angola with its location: Africa (geographic coordinates: 12 30 S, 18 30 E) and the international borders of Angola; total: 5,369 km. Border countries (total: 4): the Democratic Republic of the Congo 2,646 km (of which 225 km is the boundary of discontiguous Cabinda Province), The Republic of the Congo 231 km, Namibia 1,427 km, Zambia 1,065 km; furthermore, it’s inland counties boundaries.
The map of Angola, Africa, is for informational use only. No representation is made or warrantied given any map or content by the Driving Directions and Maps site. The user assumes all risks of using this Angola Google Maps and facts/wiki.
Climate
Angola’s climate, influenced by its location in southwestern Africa and its varied topography, exhibits significant regional variations. The country’s climate ranges from semiarid in the south and along the coast to a more tropical climate in the north. Here’s an extended overview of Angola’s climatic conditions, incorporating factual and interesting aspects:
- Semiarid Climate in the South and Coastal Regions: The southern part of Angola and the coastal strip up to Luanda experience a semiarid climate. This region, including the Namib Desert along the coast, receives limited rainfall, averaging less than 50 mm (2 inches) annually in the driest areas. The coastal fog provides much-needed moisture in these arid regions.
- Cool, Dry Season in the North (May to October): Northern Angola, which includes regions like Cabinda and the province of Uíge, experiences a cool, dry season from May to October. During this period, temperatures are relatively mild, averaging around 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F). This season is characterized by lower humidity and minimal rainfall.
- Hot, Rainy Season in the North (November to April): The same northern regions of Angola undergo a hot, rainy season from November to April. Temperatures during this season can rise above 30°C (86°F), accompanied by high humidity. Rainfall during this period is significant, with some areas receiving over 1,000 mm (39 inches) of rain, especially in the more mountainous regions.
- Central Highlands Climate: The central highlands of Angola, including cities like Huambo and Kuito, experience a more temperate climate. The elevation, averaging around 1,500 meters (4,921 feet), contributes to cooler temperatures and more moderate rainfall than the northern lowlands.
- Temperature Variations: Angola’s temperatures vary significantly between regions and seasons. Coastal regions are generally cooler due to the cold Benguela Current, while the interior highlands experience greater temperature fluctuations, with cooler nights and warm days.
- Impact of El Niño: Angola’s climate, particularly its rainfall patterns, can be influenced by El Niño events. These events can lead to variations in the usual weather patterns, sometimes causing droughts or floods.
- Agricultural Impacts: The varying climate across Angola impacts agricultural activities. With their wetter climate, the northern regions support rain-fed agriculture and various crops. In contrast, the southern and coastal regions often rely on irrigation and are suitable for drought-resistant crops.
- Biodiversity and Ecosystems: Angola’s climatic diversity supports a wide range of ecosystems, from coastal desert in the southwest to tropical rainforest in the north. This diversity contributes to Angola’s rich biodiversity, including various species of flora and fauna.
- Climate Change Concerns: Like many countries, Angola faces challenges related to climate change. These include increased risk of droughts and floods, affecting water resources, agriculture, and overall food security.
- Rainfall Variability: Rainfall in Angola is highly variable, both seasonally and annually. This variability challenges water resource management, agriculture, and hydroelectric power generation.
With its regional variations from semiarid conditions in the south and along the coast to a tropical climate in the north, Angola’s climate significantly shapes the country’s natural landscapes, biodiversity, and socio-economic activities. Understanding these climatic conditions is crucial for environmental planning, sustainable development, and adapting to the challenges posed by climate change.
Geography
Angola’s geography, characterized by its diverse terrain that transitions from a narrow coastal plain to a vast interior plateau, shapes the country’s landscape and influences its climate, biodiversity, and human settlement patterns. Here’s an extended overview of Angola’s geographical features, including more detailed statistics and information about its neighboring countries:
- Coastal Plain: Angola features a narrow coastal plain that varies in width from just a few kilometers to about 100 kilometers (62 miles). This region includes important cities like Luanda, the capital, and is characterized by its beaches and coastal lagoons.
- Interior Plateau: Most Angola is dominated by a high plateau (planalto), which rises gradually from the coast to elevations of 1,000 to 2,000 meters (3,280 to 6,560 feet). This plateau is characterized by rolling hills, wide valleys, and vast open spaces, making it a significant agricultural area.
- Highest Point – Morro de Moca: The highest point in Angola is Morro de Moca (or Mount Moco), which reaches an elevation of 2,620 meters (8,596 feet). Located in the Huambo Province, this area is known for its rich biodiversity and is part of the Angolan Central Escarpment.
- Lowest Point: The lowest point in Angola is the Atlantic Ocean, at sea level. The country has a coastline that stretches for about 1,600 kilometers (994 miles) along the South Atlantic Ocean, featuring a mix of sandy beaches and rocky cliffs.
- Mean Elevation: Angola’s mean elevation is approximately 1,112 meters (3,648 feet), reflecting its extensive plateau region. This elevation contributes to the country’s diverse ecosystems and climates.
- Rivers and Water Bodies: Angola is rich in water resources, with several major rivers, including the Cuanza, Cunene, and Cubango. These rivers are crucial to the country’s agriculture, hydroelectric power, and ecosystems. The Okavango River, in particular, is notable for its delta in neighboring Botswana.
- Surrounding Countries:
- Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC): To the northeast and north, Angola shares a long border with the DRC. This border, approximately 2,511 kilometers (1,560 miles) long, includes a significant stretch along the Congo River.
- Republic of the Congo: To the north, Angola has a smaller border with the Republic of the Congo, approximately 201 kilometers (125 miles) long.
- Namibia: To the south, the border with Namibia extends for about 1,376 kilometers (855 miles). This boundary runs through diverse landscapes, including the arid Namib Desert.
- Zambia: To the east, Angola borders Zambia. This border, around 1,110 kilometers (690 miles) long, cuts across the plateau and is marked by several rivers.
- Natural Resources: Angola is rich in natural resources, including petroleum, diamonds, iron ore, phosphates, copper, feldspar, gold, bauxite, and uranium. The country is one of the major oil producers in Sub-Saharan Africa.
- Biodiversity and Protected Areas: Angola’s varied terrain supports many habitats and biodiversity. The country has several national parks and protected areas, such as Iona National Park in the southwest and Kissama National Park near Luanda.
- Environmental Challenges: Angola faces several environmental challenges, including deforestation, soil degradation, and biodiversity loss. The country is also vulnerable to the impacts of climate change, such as changes in rainfall patterns and increased frequency of extreme weather events.
Angola’s geography, with its vast plateau, coastal plain, and significant river systems, not only defines its natural beauty and ecological richness but also influences its cultural and economic development. The country’s terrain and its borders with neighboring countries make it an important location for understanding the geography and socio-economic dynamics of this region of Africa.
Resources and Land Use
Angola is rich in natural resources like petroleum, diamonds, iron ore, phosphates, copper, feldspar, gold, bauxite, and uranium. About 45.7% of the land is agricultural, with 3.9% arable land (2018 estimate).
Population Data
As of 2023, Angola’s population is approximately 35.98 million, with a high concentration of people living in the country’s western half and urban areas, particularly Luanda.
Economic Data
Angola has a real GDP of $203.868 billion (2021 estimate), with a growth rate of 1.1% (2021 estimate). The economy is heavily reliant on its oil sector.
Drinking Water Source
About 66.5% of Angola’s population has access to improved drinking water sources.
Population, Median Age, Migration, and Citizenship
The median age in Angola is 16.2 years (estimated for 2023), with a population growth rate of 3.34% (estimated for 2023). The country has a slight negative net migration rate.
Average Number of Childbirths
The total fertility rate is high at 5.76 children born per woman (estimated for 2023).
Is this country a Safe Destination?
While Angola is making strides in stability, travelers should be aware of certain safety and health risks, especially in more remote areas.
Healthcare and Infectious Diseases
Angola has a current health expenditure of 2.9% of GDP (2020), with a low physician density of 0.21 physicians/1,000 population (2018).
Natural Hazards
The primary natural hazard in Angola is periodic flooding, particularly on the plateau.
The Flag and Other Symbols
Angola’s flag consists of two equal horizontal bands of red (top) and black with a centered yellow emblem featuring a five-pointed star within a cogwheel crossed by a machete.
Constitution
Angola’s latest constitution was adopted in 2010, transitioning from a Marxist-Leninist one-party state to a multi-party democracy.
Legal System
The legal system is based on Portuguese civil law and customary law.
About the Unemployment Rate, Labor Force, and Poverty Line
Angola’s unemployment rate was 8.53% in 2021. The country also faces a high poverty rate, with 32.3% of the population living below the poverty line (2018 estimate).
About the Budget and Central Government Debt
Angola’s public debt was around 65% of GDP in 2017, with budget revenues of $17.899 billion against expenditures of $17.244 billion (2019 estimate).
Inflation Rate and Prime Lending Rate
The inflation rate in Angola was 25.75% in 2021, reflecting ongoing economic challenges.
Export/Import Partners and Data
Key export partners include China, India, and the United Arab Emirates, with main exports being crude petroleum and diamonds. Major imports come from China, Portugal, and South Africa.
Renewable Energies Used
Angola heavily relies on hydroelectricity, with fossil fuels constituting 28.4% of total installed capacity (2020 estimate).
Telecommunication Data, Calling Code
Angola has a growing telecommunications infrastructure, with a country code of +244. The nation is increasingly focusing on expanding mobile and broadband services.
Transport Infrastructure
Angola’s transport infrastructure includes roadways, railways, airports, and ports, which are essential for its economic development and regional integration.
More Interesting Facts
Angola offers a rich cultural heritage, diverse landscapes, and significant economic potential. It is known for its vibrant music scene, unique cuisine, and rich biodiversity.
Did You Know?
- Birthplace of the Samba: While Brazil is famous for the Samba, this dance form actually has its roots in Angola. The Semba, a traditional Angolan dance, is considered a precursor to the Brazilian Samba, showcasing Angola’s cultural influence across the Atlantic.
- Rich in Natural Resources: Angola is one of Africa’s major oil producers, ranking second in Sub-Saharan Africa. Besides oil, the country is also known for its diamond mines, which are among the world’s largest.
- Unique Biodiversity: Despite its arid regions, Angola is home to a rich variety of wildlife. The country’s national animal, the giant sable antelope, is found only in Angola and is critically endangered.
- Kalandula Falls: The Kalandula Falls in Angola are among the largest waterfalls by volume in Africa. These spectacular falls are over 100 meters high and about 400 meters wide, making them a breathtaking natural wonder.
- The Tundavala Gap: One of Angola’s most stunning natural features is the Tundavala Gap, a massive escarpment that offers dramatic views of the surrounding landscape. It’s a sheer drop of about 1,000 meters and is a popular spot for hiking and sightseeing.
- A Land of Languages: Angola is a linguistically diverse country, with Portuguese as the official language. However, there are over 40 different languages spoken, reflecting the country’s rich ethnic diversity.
- Colonial History: Angola was a Portuguese colony for over 400 years, one of the longest-lasting colonial periods in Africa. This long history has left a lasting impact on the country’s culture, language, and architecture.
- Angolan Civil War: After gaining independence from Portugal in 1975, Angola endured a prolonged and devastating civil war that lasted until 2002. This conflict significantly impacted the country’s development and infrastructure.
- Music and Culture: Angolan music is a fusion of African rhythms with Portuguese influences. Genres like Kizomba and Kuduro are popular domestically and have gained international recognition.
- Luanda: The capital city, Luanda, is known for its contrasting architecture, with colonial buildings alongside modern developments. It was once considered one of the most expensive cities in the world for expatriates.
- Coffee Production: Historically, Angola was one of the world’s largest coffee producers, primarily focusing on robusta coffee. Although production declined during the civil war, the country is working to revive its coffee industry.
- Cuisine: Angolan cuisine is a rich blend of African and Portuguese influences. Dishes often feature fish, cassava products, and spices, with ‘Calulu’ – a type of fish or meat stew – being a traditional dish.
These facts about Angola reveal a country with a complex history, rich cultural heritage, and diverse natural landscapes, from its oil-rich coastlines to its vast savannas and biodiverse wildlife reserves.
Many thanks for visiting and sharing this map & country information site!