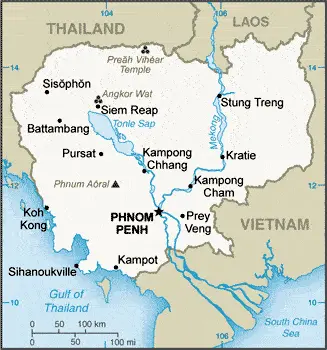
Google Maps and Detailed Facts of Cambodia (CB). This page lets you explore Cambodia and its border countries (Country Location: Southeastern Asia, bordering the Gulf of Thailand, between Thailand, Vietnam, and Laos) through detailed Satellite imagery – fast and easy as never before Google Maps.
Find comprehensive information about this country’s diversity below: Google Maps, geography, economy, science, people, culture, environment, government, and history – All in One Wiki page.
There is also a Street View and free Driving Directions at your service. Your Google Satellite Map Sightseeing in Cambodia starts at Driving Directions and Maps.com in Southeast Asia.
About Cambodia in detail
Table of contents
- Background
- Overview
- Google Maps
- Climate
- Geography
- Resources and Land Use
- Population Data
- Economic Data
- Drinking Water Source
- Population, Median Age, Migration, and Citizenship
- Average Number of Childbirths
- Is this country a Safe Destination?
- Healthcare and Infectious Diseases
- Natural Hazards
- The Flag and Other Symbols
- Constitution
- Legal System
- About the Unemployment Rate, Labor Force, and Poverty Line
- About the Budget and Central Government Debt
- Inflation Rate and Prime Lending Rate
- Export/Import Partners and Data
- Renewable Energies Used
- Telecommunication Data, Calling Code
- Transport Infrastructure
- More Interesting Facts
Background
Cambodia’s history is deeply rooted in the rich heritage of the Khmer Empire, which dominated Southeast Asia between the 10th and 13th centuries. After enduring attacks and a long decline, Cambodia became a French protectorate in 1863 and part of French Indochina in 1887. Following Japanese occupation during World War II, it gained full independence from France in 1953. The nation experienced severe turmoil under the Khmer Rouge regime led by Pol Pot, resulting in significant loss of life and devastation. Since the 1991 Paris Peace Accords and subsequent elections, Cambodia has been working towards rebuilding and stabilizing its society and political landscape.
Overview
Cambodia, a nation with a turbulent past and a resilient spirit, stands as a testament to the endurance of its people. Its journey from the glory of the ancient Khmer civilization to the shadows of the Khmer Rouge and back towards progress and development is harrowing and inspiring. The Kingdom of Cambodia, with its rich cultural heritage and natural beauty, blends historical magnificence and modern aspirations.
Official Name: Kingdom of Cambodia
Capital: Phnom Penh
Population: 16,891,245 (2023 estimate)
Total Area: 181,035 sq km
Languages: Khmer (official) 95.8%, minority languages 2.9%, Chinese 0.6%, Vietnamese 0.5%, other 0.2% (2019 estimate)
Religions: Buddhist (official) 97.1%, Muslim 2%, Christian 0.3%, other 0.5% (2019 estimate)
Ethnic Groups: Khmer 95.4%, Cham 2.4%, Chinese 1.5%, other 0.7% (2019-20 estimate)
Government: Parliamentary constitutional monarchy
Currency: Riel (KHR)
Cambodia Google Maps
Cambodia, located in Southeastern Asia, bordering the Gulf of Thailand, between Thailand, Vietnam, and Laos, offers a rich exploration experience on Google Maps. From the ancient Angkor Wat temple complex to the bustling streets of Phnom Penh, the country’s diverse landscapes and historical sites are vividly showcased.
The map below shows Cambodia’s cities, towns, highways, main roads, streets, and Street Views. To find a location, use the form below, type any city or place, view a simple map, and click the “show map” button.
The Google Maps above shows Cambodia’s location: Southeast Asia (geographic coordinates: 13 00 N, 105 00 E) and the international borders of Cambodia; total: 2,530 km. Border countries (total: 3): Laos 555 km, Thailand 817 km, Vietnam 1,158 km; furthermore, it’s inland counties boundaries.
The map of Cambodia Southeast Asia is for informational use only. No representation is made or warrantied given any map or content by the Driving Directions and Maps site. The user assumes all risks of using this Cambodia Google Maps and facts/wiki.
Climate
Cambodia, located in Southeast Asia, experiences a distinctly tropical climate characterized by a monsoon season and a dry season, with minimal temperature variation throughout the year. This climate significantly impacts the nation’s agriculture, ecology, and daily life.
- Monsoon Season (May to November): The monsoon season, also known as the wet season, is marked by heavy and frequent rainfall. This period is crucial for agriculture, as it provides the needed water for rice cultivation, the staple crop of Cambodia. The average rainfall during this season can range from 1,400 to 2,000 millimeters (55 to 79 inches), with the highest amounts typically recorded in the coastal areas.
- Dry Season (December to April): The dry season is characterized by lower rainfall and higher temperatures. During this season, the average temperature can range from 24°C to 32°C (75°F to 90°F), with March and April being the hottest months. Water scarcity can become an issue during this time, affecting agriculture and daily life.
- Little Seasonal Temperature Variation: Cambodia maintains relatively stable and warm temperatures throughout the year. The average annual temperature is about 27°C (81°F). This consistency is typical of tropical climates and is attributed to Cambodia’s location near the equator.
- Impact on Agriculture: Cambodia’s agricultural cycle relies heavily on monsoon rains. Rice is the primary crop, with the planting season beginning with the onset of the monsoon. Other crops grown include maize, cassava, sweet potatoes, and various fruits. The Mekong River and Tonle Sap Lake are crucial in providing water for irrigation.
- Flooding and Droughts: The monsoon season can sometimes lead to severe flooding, particularly along the Mekong River and the Tonle Sap. Conversely, the dry season can bring drought conditions, which have become more frequent and severe in recent years, likely due to climate change.
- Influence on Daily Life and Festivals: The climate and seasons deeply intertwine with Cambodian culture and daily life. Festivals such as the Water Festival or Bon Om Touk, celebrate the end of the rainy season and the reversal of the flow of the Tonle Sap River.
- Biodiversity and Ecosystems: The climate supports diverse ecosystems, including tropical rainforests, mangroves, and the unique flooded forests around the Tonle Sap Lake. These ecosystems are home to a rich array of wildlife, including several endangered species.
- Climate Change Concerns: Climate change poses significant challenges to Cambodia, with predictions of more erratic rainfall patterns, more intense and frequent flooding, prolonged droughts, and rising temperatures. These changes could profoundly impact agriculture, water resources, and biodiversity.
The tropical climate of Cambodia, with its distinct wet and dry seasons, plays a fundamental role in shaping the country’s environment, agriculture, culture, and overall way of life while also presenting challenges increasingly exacerbated by climate change.
Geography
Cambodia, nestled in the heart of Southeast Asia, has a diverse terrain that includes low-lying plains, mountains, and a significant river system. This geographical landscape is vital to the nation’s ecosystem, culture, and economy.
- Terrain and Topography: Most of Cambodia’s landscape consists of low, flat plains in the larger Mekong River Delta region. These plains are crucial for Cambodia’s agriculture, particularly rice cultivation. The country’s terrain becomes more rugged and mountainous towards the southwest and north.
- Highest and Lowest Points: The highest point in Cambodia is Phnum Aoral, which stands at 1,810 meters (5,938 feet) in the Cardamom Mountains. In contrast, the lowest point is at the Gulf of Thailand, at sea level. These elevations contribute to the country’s diverse habitats and climate conditions.
- Mekong River and Tonle Sap Lake: The Mekong River, one of the world’s longest rivers, flows through Cambodia and is a lifeline for the nation’s agriculture and fisheries. The Tonle Sap Lake, Southeast Asia’s largest freshwater lake, is unique for its flow pattern that changes direction with the seasons. During the rainy season, it swells to be one of the largest lakes in Asia. This lake and river system supports one of the most productive inland fisheries in the world.
- Surrounding Countries: Cambodia is bordered by Thailand to the northwest, Laos to the northeast, and Vietnam to the east and southeast. To the southwest lies the Gulf of Thailand. These borders have influenced Cambodia’s cultural and historical interactions with its neighbors.
- Population and Land Use: Cambodia has a population of around 16 million people, with a significant portion living in rural areas and relying on agriculture and fishing. The fertile plains and river basins support this lifestyle, although urbanization is increasing, particularly in cities like Phnom Penh, the capital.
- Biodiversity and Conservation Areas: The varied terrain, from coastal areas to mountains, creates habitats for diverse wildlife. Cambodia is home to numerous national parks and protected areas, including the Cardamom Mountains, which are known for their rich biodiversity.
- Climate Impact on Geography: The geographic features of Cambodia, particularly the Mekong River and Tonle Sap Lake, are highly influenced by the monsoonal climate, which dictates the agricultural calendar and affects the livelihoods of millions of Cambodians.
- Environmental Challenges: Cambodia faces environmental challenges such as deforestation, soil erosion, and pollution, impacting its diverse ecosystems. Efforts are ongoing to address these issues, including reforestation initiatives and conservation projects.
The geographical features of Cambodia, from its expansive plains to its vital river systems, not only define its physical landscape but also play a central role in the country’s cultural identity, economic activities, and ecological diversity.
Resources and Land Use
Rich in natural resources, Cambodia has oil and gas, timber, gemstones, iron ore, manganese, phosphates, hydropower potential, and arable land. The land use is predominantly agricultural, with about 32.1% (2018 est.) of the land used for agriculture.
Population Data
Cambodia’s population is concentrated in the southeast, particularly around Phnom Penh and the Tonle Sap and Mekong Rivers. The nation has a relatively young population, with a median age of 27.6 years (estimated for 2023).
Economic Data
Cambodia’s economy has been one of the fastest-growing in the region, driven by tourism, clothing exports, and a substantial manufacturing and construction sector. Despite COVID-19-related declines and challenges in rural poverty, the country has made significant strides in economic development.
Drinking Water Source
Access to improved drinking water sources in Cambodia is high, with 99.3% coverage in urban areas and 80.6% in rural areas. However, ensuring a consistent and quality water supply remains a challenge.
Population, Median Age, Migration, and Citizenship
Cambodia’s youthful population indicates potential for continued growth and development. The country experiences a negative net migration rate, highlighting the challenges of migration and urbanization.
Average Number of Childbirths
The total fertility rate in Cambodia is 2.2 children born per woman (2023 etimate), reflecting a moderate childbirth rate in line with regional trends.
Is this country a Safe Destination?
Cambodia is generally safe for tourists, with visitors advised to follow standard travel safety precautions.
Healthcare and Infectious Diseases
While healthcare facilities are improving, challenges remain, especially in rural areas. Infectious diseases such as dengue fever and malaria are prevalent.
Natural Hazards
The country faces natural hazards like monsoonal rains, flooding, and occasional droughts.
The Flag and Other Symbols
Cambodia’s flag, featuring Angkor Wat, symbolizes the nation’s cultural and historical identity. The kouprey, a wild ox, is another national symbol.
Constitution
The Constitution of Cambodia, promulgated in 1993, establishes a parliamentary constitutional monarchy and has been amended several times, most recently in 2022.
Legal System
Cambodia’s legal system combines civil law, customary law, Communist legal theory, and common law.
About the Unemployment Rate, Labor Force, and Poverty Line
Cambodia’s unemployment rate is low, but the country continues to face challenges with poverty, particularly in rural areas.
About the Budget and Central Government Debt
Managing the budget and public debt is a significant concern for the Cambodian government, with efforts focused on sustainable fiscal policies.
Inflation Rate and Prime Lending Rate
Cambodia’s inflation rate has been relatively stable, reflecting the country’s growing economic stability.
Export/Import Partners and Data
The country’s major exports include clothing, footwear, rice, and rubber, with key import partners being the United States, China, and Vietnam.
Renewable Energies Used
Cambodia relies primarily on fossil fuels for energy, with increasing efforts to develop renewable sources like hydroelectricity.
Telecommunication Data, Calling Code
Cambodia’s telecommunication sector is expanding, focusing on mobile cellular networks. The country code is +855.
Transport Infrastructure
Transport infrastructure includes a growing network of roads, railways, several airports, and waterways, primarily on the Mekong River.
More Interesting Facts
Cambodia is known for its ancient temples, rich cultural history, and the resilience of its people. The nation continues to navigate its path toward economic growth and political stability.
Did You Know?
- Angkor Wat: Cambodia is home to Angkor Wat, the largest religious monument in the world. Built in the early 12th century, this temple complex symbolizes Cambodia and appears on its national flag. It’s a masterpiece of Khmer architecture and a UNESCO World Heritage site.
- Tonle Sap’s Unique Hydrology: The Tonle Sap Lake in Cambodia is known for its unique hydrological phenomenon. During the monsoon season, the lake swells to about five times its size, reversing the flow of the Tonle Sap River, which connects it to the Mekong River.
- A Land of Festivals: Cambodia celebrates numerous festivals throughout the year, with the most famous being the Water Festival or Bon Om Touk. This festival marks the reversal of the flow of the Tonle Sap River and features boat races watched by millions of Cambodians.
- The Khmer Language: Cambodia’s official language is Khmer, written in the world’s longest alphabet with 74 characters.
- Rich Biodiversity: Despite its small size, Cambodia has a rich biodiversity. It hosts several large mammals, such as the Indochinese tiger, Asian elephant, and the Irrawaddy dolphin, which can be found in the Mekong River.
- A Young Population: Cambodia has a remarkably young population, with over 50% of its citizens under the age of 25. This demographic trend is a result of the tragic Khmer Rouge regime of the 1970s.
- Rice and Rubber: Cambodia’s economy relies heavily on agriculture, with rice being the primary crop. It’s also one of the world’s leading producers of natural rubber.
- Landmine Legacy: From the 1960s to the 1990s, Cambodia was heavily impacted by war, which left a legacy of landmines. Significant efforts have been made to clear these mines, but large areas still remain affected.
- Traditional Apsara Dance: The Apsara Dance is a classical Khmer dance characterized by intricate hand gestures and elaborate costumes. This dance form is a crucial part of Cambodia’s cultural heritage.
- The Kingdom of Wonder: Cambodia is often referred to as the “Kingdom of Wonder”, a title that reflects its rich cultural heritage, stunning landscapes, and resilience of its people.
These facts about Cambodia offer a glimpse into the country’s fascinating history, unique culture, and natural wonders, making it a remarkable place of interest in Southeast Asia.
Many thanks for visiting and sharing this map & country information site!