 |
 |
 |
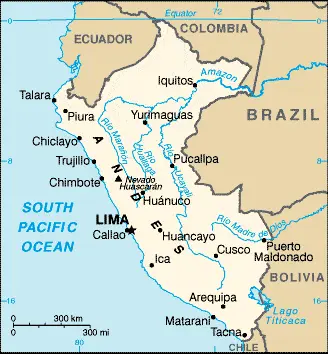
| Borderline map of Peru | Location map of Peru | Flag of Peru |
Google Maps and Detailed Facts of Peru (PE). This page lets you explore Peru and its border countries (Country Location: Western South America, bordering the South Pacific Ocean, between Chile and Ecuador) through detailed Satellite imagery – fast and easy as never before Google Maps.
Find comprehensive information about this country’s diversity below: Google Maps, geography, economy, science, people, culture, environment, government, and history – All in One Wiki page.
There is also a Street View and free Driving Directions at your service. Your Google Satellite Map Sightseeing in Peru, in South America, starts here at Driving Directions and Maps.com.
Peru Google Maps & Satellite Maps
The map below shows Peru with its cities, towns, highways, main roads, streets, and Street Views. To find a location, use the form below, type any city or place, view a simple map, and click the “show map” button.
The Google Maps above shows Peru with its location: South America (geographic coordinates: 10 00 S, 76 00 W) and the international borders of Peru; total: 7,062 km. Border countries (total: 5): Bolivia 1,212 km, Brazil 2,659 km, Chile 168 km, Colombia 1,494 km, Ecuador 1,529 km; furthermore, it’s inland counties boundaries.
Hint: Look at the Street view in Peru or South America. All you have to do is drag and pull the little yellow man (named: Pegman) on the Google Maps above the desired location. After that, whenever it is available (more than 50 countries globally), blue stripes will appear to show the photos and details from Google’s regularly updated data image base. In case if you have signed in to your Google account currently, you may have a look at the satellite map of this country/area as well.
The map of Peru, South America, is for informational use only. No representation is made or warrantied given any map or its content by Driving Directions and Maps site. The user assumes all risks of using this Peru Google Maps and facts/wiki.
About Peru in detail
Where is Peru?
Peru, in case, if you are looking on the map under the Coordinates 12 03 S 77 03 W otherwise in South America, in Western South America, bordering the South Pacific Ocean, between Chile and Ecuador.
What is the capital city of Peru?
The capital city of Peru is Lima.
What is the time in Lima?
It is the same time as Washington, D.C. during Standard Time; Lima’s timezone is UTC-5.
What is the Internet code for Peru?
The Top Level Domain (TLD) for Peru is: .pe
What is the size of Peru?
The territory of Peru is total: 1,285,216 sq km; land: 1,279,996 sq km, water: 5,220 sq km.
If we want to describe the size of Peru’s territory is almost twice the size of Texas, somewhat smaller than Alaska.
If we would like to walk around and discover Peru, we can cover a total distance: 7,062 km.
What is the water coverage of Peru?
We have already mentioned what percentage of Peru is covered by water (see below), and this includes 2,414 km coastline.
What is the climate like in Peru?
Peru’s climate varies from tropical in the east to desert in the west: temperate to frigid in the Andes.
Geographical data of Peru
Peru’s elevation; mean elevation: 1,555 m, elevation extremes; lowest point: Pacific Ocean 0 m, highest point: Nevado Huascaran 6,768 m.
The specific geographical details of Peru include western coastal plain (costa), high and rugged Andes in the center (sierra), eastern lowland jungle of Amazon Basin (selva).
Suppose we would like to describe the countries location from a different perspective. In that case, it is safe to say, and easy to read from a map, Peru is shares control of Lago Titicaca, the world’s highest navigable lake, with Bolivia; a remote slope of Nevado Mismi, a 5,316 m peak, is the ultimate source of the Amazon River.
Resources and land use of Peru
The country’s main mined products are copper, silver, gold, petroleum, timber, fish, iron ore, coal, phosphate, potash, hydropower, natural gas. The population partly uses the earlier highlighted land territory and partly left in its natural state: agricultural land: 18.8%; arable land 3.1%; permanent crops 1.1%; permanent pasture 14.6%; forest: 53%; other: 28.2% (2011 estimate).
Population data of Peru
The number of inhabitants of Peru is 30,741,062 (July 2016 estimate).
If we examine the proportion of the population distribution, it is safe to say that approximately one-third of the population resides along the desert coastal belt in the west, with a strong focus on the capital city of Lima; the Andean highlands, or sierra, which is strongly identified with the country’s Amerindian population, contains roughly half of the overall population; the eastern slopes of the Andes, and adjoining rainforest, are sparsely populated.
If we look at the proportion of the urbanized and barely populated areas, these are the figures: urban population: 78.6% of the total population (2015).
Most of the Peru population is concentrated in LIMA (capital) 9.897 million; Arequipa 850,000; Trujillo 798,000 (2015).
Ethnicity in Peru
According to ethnicity details, the ethnic groups are Amerindian 45%, mestizo (mixed Amerindian and white) 37%, white 15%, black, Japanese, Chinese, and other 3%.
The spoken languages in Peru are the following: Spanish (official language) 84.1%, Quechua (official language) 13%, Aymara (official language) 1.7%, Ashaninka 0.3%, other native languages (includes a large number of minor Amazonian languages) 0.7%, other (includes foreign languages and sign language) 0.2% (2007 estimate).
What are the most important religions in Peru?
According to this, during the general census, researchers examine the churches: Roman Catholic 81.3%, Evangelical 12.5%, other 3.3%, none 2.9% (2007 estimate).
Further population data of Peru
The proportion of gender and age tells a lot about the society as follows 0-14 years: 26.62% (male 4,164,681 / female 4,019,436) 15-24 years: 18.63% (male 2,868,743 / female 2,859,476) 25-54 years: 39.91% (male 5,892,065 / female 6,377,681) 55-64 years: 7.62% (male 1,135,938 / female 1,205,579) 65 years and over: 7.21% (male 1,049,409 / female 1,168,054) (2016 estimate). It also a significant factor in a society the population growth rate, which in the case of Peru is 0.96% (2016 estimate).
The population growth rate is based on two elements, the birth and the death rate. In Peru the birth rate is 18 births / 1,000 population (2016 estimate), the death rate 6 deaths / 1,000 population (2016 estimate).
In this day and age in developed societies, the first child borns later compared to the previous centuries and decades, so childbearing is extended. In Peru, the average age of mothers at the first childbirth is N/A.
Although the children’s birth is postponed in the best-case scenario, the parents can still see their kids grow as life expectancy also extended. In the case of Peru, these figures are. With the introduction of modern medicine, vaccinations, and the proper hygienic conditions, the infant mortality rate is in a steep decline. The infant mortality statistics in Peru are the following: N/A. Relevant data is the budget of healthcare, which is in this country’s case is 5.5% of GDP (2014).
Economic data of Peru
Suppose we would like to describe a country. We also have to mention its economy; Peru’s economy reflects its varied topography – an arid lowland coastal region, the central high sierra of the Andes, and the Amazon’s dense forest, with tropical lands bordering Colombia and Brazil. A wide range of important mineral resources is found. The Peruvian economy grew by an average of 5.6% from 2009-13 with a stable exchange rate and low inflation, which in 2013 was just below the upper limit of the Central Bank target range of 1% to 3%. This growth was partly due to high international pricesPeru’s rapid expansion, coupled with cash transfers and other programs, have helped reduce the national poverty rate by 28 percentage points since 2002. Still, inequality persists and continues to pose a challenge for the Ollanta HUMALA administration. Peru’s free trade policy has continued under the HUMALA administration; since 2006, Peru has signed trade deals with the US, Canada, Singapore, China, Korea, Mexico, Japan, the EU, the European Free Trade Association, Chile, Thailand, Costa Rica, Panama.
GDP is a prominent figure, as all the relevant calculations and statistics are based on it. GDP in Peru is $180.3 billion (2015 estimate).
Another important indicator is the rate of GDP growth, which in Peru is 3.7% (2016 estimate), 3.3% (2015 estimate) 2.4% (2014 estimate).
These statistics affect the world economy; remember, in 2015, the Chinese real GDP growth rate was worse than expected; The world markets fall, and the Chinese stock exchange was temporarily suspended.
A further major factor of a country’s economy, the GDP per capita. In Peru this is $13,000 (2016 estimate) $12,700 (2015 estimate) $12,400 (2014 estimate).
In the economy, the Trinity is in common places, such as agriculture, industry, and services.
What are the agricultural products Peru produces?
The main agricultural products of Peru are artichokes, asparagus, avocados, blueberries, coffee, cocoa, cotton, sugarcane, rice, potatoes, corn, plantains, grapes, oranges, pineapples, guavas, bananas, apples, lemons, pears, coca, tomatoes, mangoes, barley, medicinal plants, quinoa, palm oil, Mari.
Regarding the economy, the essential segments are mining and refining of minerals; steel, metal fabrication; petroleum extraction and refining, natural gas and natural gas liquefaction; fishing and fish processing, cement, glass, textiles, clothing, food processing, beer, soft drinks, rubber, machinery.
It is essential to mention that – thanks to the development of the infrastructure -, the rate of potable water improved: urban: 91.4% of the population, rural: 69.2% of the population, total: 86.7% of the population. Unimproved: urban: 8.6% of the population, rural: 30.8% of the people, total: 13.3% of the population (2015 estimate).
The average number of childbirth in Peru
In Peru, the average delivery number is 2.15 children born / woman (2016 estimate).
Population, median age, migration, and citizenship in Peru
The population’s average age is 27.7 years; male: 26.9 years, female: 28.4 years (2016 estimate). The age of adulthood varies in every country of the world in Peru; it is 18 years of age, universal and compulsory until 70.
When we are experiencing an unprecedented scale of migration and globalization, it is an important factor in the number of new immigrants. In Peru is -2.4 migrant(s) / 1,000 population (2016 estimate). It is important to know how to apply for citizenship: citizenship by birth: yes. Citizenship by descent: yes. Dual citizenship recognized: yes, the residency requirement for naturalization: 2 years.
Is Peru a safe destination? Healthcare services and infectious diseases in Peru
Many of the travelers are looking into the healthcare services and infectious diseases of their destinations. In Peru, the hospital beds’ density is 1.5 beds / 1,000 population (2012).
According to the WHO rating regarding contagious diseases in Peru, the degree of risk: very high food or waterborne diseases: bacterial diarrhea, hepatitis A, and typhoid fever vectorborne disease: dengue fever, malaria, and Bartonellosis (Oroya fever). Note: active local transmission of Zika virus by Aedes species mosquitoes has been identified in this country (as of August 2016); it poses an important risk (a large number of cases possible) among US citizens if bitten by an infective mosquito; other less common ways to get Zika are through sex, via blood transfusion, or during pregnancy, in which the pregnant woman passes Zika virus to her fetus (2016).
However, HIV is not curable but maintainable. Let’s do not forget when the disease surfaced; it was a world threatening condition. Unfortunately, in some countries, it is still very high the number of infected patients and fatalities due to the disease.
In Peru, the number of HIV/AIDS deaths: N/A.
Regarding tourism obesity, not an important issue, but we have to mention health statistics, as it is the plague of the 20th and the 21st century. The rate of obese adults in Peru is 20.4% (2014).
What are the natural hazards in Peru? Is there any?
The most known natural risk in Peru are earthquakes, tsunamis, flooding, landslides, mild volcanic activity. Volcanism: volcanic activity in the Andes Mountains; Ubinas (elevation 5,672 m), which last erupted in 2009, is the country’s most active volcano; other historically active volcanoes include El Misti, Huaynaputina, Sabancaya, and Yucamane.
More interesting facts about Peru
A few words about the past, as every country and society, are connected to its history; Ancient Peru was the seat of several prominent Andean civilizations, most notably that of the Incas, whose empire was captured by Spanish conquistadors in 1533. Peru declared its independence in 1821, and the remaining Spanish forces were defeated in 1824.
After a dozen years of military rule, Peru returned to democratic leadership in 1980 but experienced economic problems and a violent insurgency growth. President Alberto FUJIMORI’s election in 1990 ushered in a decade that saw a dramatic turnaround in the economy and significant progress in curtailing guerrilla activity. Nevertheless, the president’s increasing reliance on authoritarian measures and an economic slump in the late 1990s generated mounting dissatisfaction with his regime, which led to his resignation in 2000. A caretaker government oversaw a new election in the spring of 2001, which installed Alejandro TOLEDO Manrique as the new head of government – Peru’s first democratically elected president of indigenous ethnicity. The presidential election of 2006 saw the return of Alan GARCIA Perez, who, after a disappointing presidential term from 1985 to 1990, oversaw a robust economic rebound. Former army officer Ollanta HUMALA Tasso was elected president in June 2011 and carried on the three preceding administrations’ sound, market-oriented economic policies. Poverty and unemployment levels have fallen dramatically in the last decade, and today Peru boasts one of the best performing economies in Latin America. Pedro Pablo KUCZYNSKI Godard won a very narrow presidential runoff election in June 2016.
In every nation’s memory, some cornerstones placed the country on the timeline of history. The date of declaration of independence of Peru: 28 July 1821 (from Spain).
The flag and other symbols of Peru
The colors, symbols, and animals on the flag usually have a historical background or an important milestone or memory of the nation.
This case is not an exception either; three equal, vertical bands of red (hoist side), white, and red with the coat of arms centered in the white band; the coat of arms features a shield bearing a vicuna (representing fauna), a cinchona tree (the source of quinine, signifying flora), and a yellow cornucopia spilling out coins (denoting mineral wealth); red recalls blood shed for independence, white symbolizes peace.
Apart from the flag, the symbol of national unity is the national anthem. The anthem’s primary purpose is to share the nation’s core values, endeavors, and patriotic feelings.
National symbols of Peru: vicuna (a camelid related to the llama); national colors: red, white.
Constitution of Peru
The existence of the nation is based on the constitution. Some constitutions knew worldwide, like the U.S. Constitution that was accepted on the 17th of September 1787, in Philadelphia, the United States of America’s Constitution.
It is not related to the declaration of independence that was stolen by Nicolas Cage in the movie National Treasure 🙂
What is the legal system of Peru?
Most of the time, the legal system of a country is the focus of lawyers. It is a common fact that there are two main approaches in the world, “the law in books” and “the law in action.”
In the Anglo-Saxon world, the practice is the “law in action,” while in the rest of the world, the law is based on Roman law, the “law in books.”
The legal system of Peru is a civil law system.
It was Aristotle who founded the Theory of 3 separations of powers. In his view, these are the council of public affairs, the magistrates, and the justice system. The age of enlightenment was the time when terminologies have defined the way we still use them. In most democratic countries, the three authorities separated from each other. In dictatorships, the rules usually interweaved in one hand.
About the legislative branch of Peru, we can highlight the following structures unicameral Congress of the Republic of Peru or Congreso de la Republica del Peru (130 seats; members directly elected in multi-seat constituencies by closed party-list proportional representation vote to serve 5-year terms).
About the unemployment rate, labor force, and poverty line in Peru
One of the major problems of the 21st-century economy is unemployment. Governments are struggling to maintain a low level of the unemployment rate. Still, as a result of automation, the cheap 3rd world labor, and the outsourcing of workflow, these attempts fail. In Peru, the labor force is 17.12 million (2016 estimate). Please bear in mind that the population in Peru is total: 19 deaths / 1,000 live births; male: 21.1 deaths / 1,000 live births, female: 16.7 deaths / 1,000 live births (2016 estimate) – as we already mentioned above.
The rate of unemployment in Peru is 5.9% (2016 estimate).
Widely known that the gap between the rich and poor is widening on an enormous scale.
According to the 2017 shocking Oxfam report, the most affluent eight people’s fortune is equal to the wealth of the poorest half of the world’s population.
In Peru, the households’ income and consumption compared to the entire population: lowest 10%: 1.4% highest 10%: 36.1% (2010 estimate).
Another widely used indicator is the so-called GINI index, which measures the inequalities of statistical dispersion, but is mainly used for measuring the sharing of income and fortune.
The GINI index was named after its founder Corrado Gini, an Italian economist. Gini index has grades between 0-1, but often it is used on a percentage basis. It is 0 if the examined criteria territorial distribution is equal. It is one of the criteria concentrated on the territory. In Peru, the GINI index is .45,3 (2012).
The states usually set up a poverty line, which is more or less, is a subjective measure. It varies by country; its base is often the minimum pension, the incomes of the most deficient 20 percent, the X percent of income per capita Etc.
In Peru, the poverty line people are the lowest 10%: 1.4% highest 10%: 36.1% (2010 estimate).
About the budget and central governments debt of Peru
The available budget mainly defines the state’s economy. Peru’s budget is; revenues: $60.84 billion, expenditures: $66.46 billion (2016 estimate). Taxes and other revenues are 33.7% of GDP (2016 estimate).
The budget deficit (Budget surplus (+) or deficit (-)) is N/A.
The fiscal year in Peru is the calendar year.
In the country’s economy, we have to consider the public debt. Public debt is the consolidated sum of the state’s local, federal, and central government debt.
Inflation rate and prime lending rate in Peru
A few further interesting and relevant economic data are the following; Inflation rate: 3.4% (2016 estimate), 3.5% (2015 estimate), and the rate of the Commercial bank prime lending rate: 16.1% (31 December 2016 estimate).
Export/import partners and data of Peru
Peru, with the export of products, industrial tools, and other services, generates revenue. Peru’s export value is $38.09 billion (2016 estimate), $34.16 billion (2015 estimate). The total revenue of these activities: copper, gold, lead, zinc, tin, iron ore, molybdenum, silver; crude petroleum and petroleum products, natural gas; coffee, asparagus, and other vegetables, fruit, apparel and textiles, fishmeal, fish, chemicals, fabricated metal products, and machinery.
The most important export partners of Peru are China, 22.1%, US 15.2%, Switzerland 8.1%, Canada 7% (2015).
The most important imported products are petroleum and petroleum products, chemicals, plastics, machinery, vehicles, TV sets, power shovels, front-end loaders, telephones, and telecommunication equipment, iron and steel, wheat, corn, soybean products, paper, cotton, vaccines, and medicines, and the countries from where the import is coming: China 22.7%, US 20.7%, Brazil 5.1%, Mexico 4.5% (2015).
Renewable energies used in Peru
To suppress the pollution of the environment, renewable energies have to replace the fossil energy. The more the proportion of renewable energies in a country means more effort against pollution. Peru, the indicator of how much of the country’s produced energy is coming from the hydroelectric source, is 35.9% of total installed capacity (2012 estimate).
To indicate how much another renewable energy produced is 0.9% of total installed capacity (2012 estimate).
Telecommunication data of Peru, calling code
To maintain the economy, the development of a reliable and modern telecommunications infrastructure is crucial. We can say the following about Peru; adequate for most requirements; nationwide microwave radio relay system, and a domestic satellite system with 12 earth stations. Domestic: fixed-line teledensity is only about 10 per 100 persons; mobile-cellular teledensity, spurred by competition among multiple providers, exceeds 110 telephones per 100 persons. International: country code – 51; the South America-1 (SAM-1) and Pan American (PAN-AM) submarine cable systems provide links to parts of Central and South America, the Caribbean, and the US; satellite earth stations – 2 Intelsat (Atlantic Ocean) (2015).
Transport infrastructure in Peru
In the 21st century, we often say that the world has become small and there are no distances anymore. With widespread air travel when (sometimes) there are no visa restrictions, it is easy to reach other countries, but if the distance is not too long, we can also use railway or water transportation.
The number of airports in Peru: 191 (2013), and the number of heliports: 5 (2013).
The total length of the roadways in Peru: total: 140,672 km (18,699 km paved). Note: includes 24,593 km of national roads (14,748 km paved), 24,235 km of departmental roads (2,340 km paved), and 91,844 km of local roads (1,611 km paved) (2012).
The total length of the waterways in Peru: 8,808 km (8,600 km of navigable tributaries on the Amazon system and 208 km on Lago Titicaca) (2011).
Are you traveling to Peru?
If you plan to travel by plane to Peru, try our air ticket comparison site, where you can choose from hundreds of carriers and offers. Our application is scanning the market and shows you the best and the cheapest deals without any extra charge or commission.
Are you looking for a hotel, apartment another kind of accommodation in Peru, South America? We are here to help you to find your accommodation from budget to luxury. Our search engine is scanning, regularly updating data from hundreds of accommodation websites and more than a million offers. You can quickly and easily find your hotel stay anywhere in the world, without any extra charge or commission.
Facts & data about Peru
Name of the country: conventional long way: the Republic of Peru, traditional short form: Peru, local long form: Republica del Peru, local short state: Peru, etymology: exact meaning is obscure, but the name may derive from a native word “biru” meaning “river.”
| Abbreviation: Peru | Geographic coordinates: 10 00 S, 76 00 W |
Country Location: South America |
| Capital of Peru: Lima | GPS of the Capital: 12 03 S 77 03 W |
Position: Western South America, bordering the South Pacific Ocean, between Chile and Ecuador |
| Land area: total: 1,285,216 sq km; land: 1,279,996 sq km, water: 5,220 sq km | Terrain: western coastal plain (costa), high and rugged Andes in center (sierra), eastern lowland jungle of Amazon Basin (selva) |
Area comparative: almost twice the size of Texas; somewhat smaller than Alaska |
| Population: 30,741,062 (July 2016 estimate) | Population grow rate: 0.96% (2016 estimate) | Sex ratio: at birth: 1.05 male(s) / female, 0-14 years: 1.04 male(s) / female, 15-24 years: 1 male(s) / female, 25-54 years: 0.92 male(s) / female, 55-64 years: 0.94 male(s) / female, 65 years and over: 0.9 male(s) / female, total population: 0.97 male(s) / female (2016 estimate) |
| Exports: $38.09 billion (2016 estimate), $34.16 billion (2015 estimate) | Imports: $38.35 billion (2016 estimate), $36.99 billion (2015 estimate) | Import partners: China 22.7%, US 20.7%, Brazil 5.1%, Mexico 4.5% (2015) |
| Urbanization: urban population: 78.6% of the total population (2015) | Major urban area(s): LIMA (capital) 9.897 million; Arequipa 850,000; Trujillo 798,000 (2015) | Median age: total: 27.7 years; male: 26.9 years, female: 28.4 years (2016 estimate) |
| Internet users: total: 12.452 million. Percent of the population: 40.9% (July 2015 estimate) | Telephones (fixed-lines): total subscriptions: 2,912,316. Subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 10 (July 2015 estimate) | Telephones (mobile, cellular): total: 34.236 million. Subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 112 (July 2015 estimate) |
| Unemployment rate: 5.9% (2016 estimate) | Nationality: Peruvian(s) adjective: Peruvian | National holidays: Independence Day, 28 July (1821) |
| Life expectancy at birth: total population: 73.7 years. Male: 71.7 years, female: 75.9 years (2016 estimate) | Total fertility rate: 2.15 children born / woman (2016 estimate) | Birthrate: 18 births / 1,000 population (2016 estimate) |
| Literacy: age 15 and over can read and write. Total population: 94.5%; male: 97.3%, female: 91.7% (2015 estimate) | Legal system: civil law system | Suffrage: 18 years of age, universal and compulsory until the age of 70 |
| Industries: mining and refining of minerals; steel, metal fabrication; petroleum extraction and refining, natural gas and natural gas liquefaction; fishing and fish processing, cement, glass, textiles, clothing, food processing, beer, soft drinks, rubber, machinery, | Industrial production growth rate: 3.2% (2016 estimate) | GDP real growth rate: 3.7% (2016 estimate) 3.3% (2015 estimate) 2.4% (2014 estimate) |
Do you like this Peru Google Maps & country information page?
Please do us a favor: Share or like this page using the icons at the top of the page. We also do encourage you to visit our Facebook page for more travel and country related information.
Many thanks for visiting and sharing this map & country information site!
