Google Maps and detailed facts about American Samoa (AS). This page lets you explore American Samoa and its border countries (Country Location: Oceania, a group of islands in the South Pacific Ocean, about halfway between Hawaii and New Zealand) through detailed Satellite imagery – fast and easy as never before Google Maps.
Find comprehensive information about this country’s diversity below: Google Maps, geography, economy, science, people, culture, environment, government, and history – All in One Wiki page.
There is also a Street View and free Driving Directions at your service. Your Google Satellite Map Sightseeing in American Samoa, in Oceania, starts here at Driving Directions and Maps.com.
Table of contents
- Background
- Overview
- Google Maps
- Climate
- Geography
- Resources and Land Use
- Population Data
- Economic Data
- Drinking Water Source
- Population, Median Age, Migration, and Citizenship
- Average Number of Childbirths
- Is this country a Safe Destination?
- Healthcare and Infectious Diseases
- Natural Hazards
- The Flag and Other Symbols
- Constitution
- Legal System
- About the Unemployment Rate, Labor Force, and Poverty Line
- About the Budget and Central Government Debt
- Inflation Rate and Prime Lending Rate
- Export/Import Partners and Data
- Renewable Energies Used
- Telecommunication Data, Calling Code
- Transport Infrastructure
- More Interesting Facts
Background
American Samoa, with a history dating back to 1000 B.C., has been a strategic location in the South Pacific, serving as a refuge and trade center in ancient times. European explorers, including Dutchman Jacob Roggeveen and Frenchman Louis Antoine de Bougainville, first encountered the islands in the 18th century. American interest in the islands grew in the mid-1800s, leading to the establishment of a coaling station at Pago Pago in 1878. The Samoan archipelago was eventually divided between the US and Germany in 1899, with local chiefs ceding the Eastern islands to the US. The territory, officially named “American Samoa” in 1911, has since evolved with self-government while retaining its traditional culture and US national status.
Overview
American Samoa, an unorganized territory of the US, is located in the South Pacific Ocean. It has a republican form of government with local self-rule. The economy is based primarily on tourism, tuna, and government services. Despite its small size and remote location, American Samoa has a unique cultural heritage and a significant strategic position in the Pacific.
Official Name: American Samoa
Date of Formation: Officially named in 1911
Capital: Pago Pago
Population: 44,620 (2023 estimate)
Total Area: N/A
Population Density: N/A
Languages: English and Samoan
Religions: Primarily Christian (various denominations)
Ethnic Origin: Predominantly Samoan
Government: Unorganized territory of the US with local self-government
Currency: US Dollar (USD)
Literacy Rate: N/A
Calorie Consumption: N/A
Google Maps
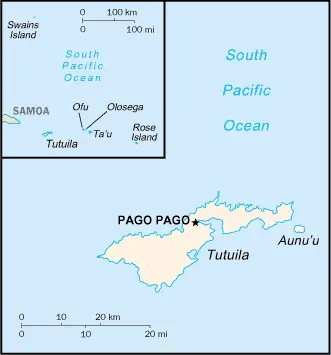
Using Google Maps, one can explore the geography and layout of American Samoa, located about halfway between Hawaii and New Zealand. This tool offers a detailed view of its islands, including Tutuila, the Manu’a Islands, Rose Atoll, and Swains Island.
The map below shows American Samoa with its cities, towns, highways, main roads, streets, and Street Views. To find a location, use the form below, type any city or place, view a simple map, and click the “show map” button.
The Google Maps above shows American Samoa with its location: Oceania (geographic coordinates: 14 20 S, 170 00 W) and the international borders of American Samoa; 0 km; furthermore, its inland counties boundaries.
The map of American Samoa, Oceania, is for informational use only. No representation is made or warrantied given any map or its content by Driving Directions and Maps site. The user assumes all risks of using this American Samoa Google Maps and facts/wiki.
Climate
American Samoa’s climate, characterized by its tropical marine nature, is significantly influenced by its geographic location in the South Pacific Ocean. This setting results in a generally warm, humid, and rainy climate throughout the year. Here’s an extended overview of American Samoa’s climatic conditions, incorporating factual and interesting aspects:
- Moderating Influence of Trade Winds: The southeast trade winds play a crucial role in moderating the climate of American Samoa. These winds, prevalent throughout the year, help to temper the heat and bring moisture, contributing to the area’s high humidity and consistent rainfall.
- High Rainfall: American Samoa is known for its substantial rainfall. The average annual rainfall can range from about 2,500 mm (98 inches) to 3,000 mm (118 inches), making it one of the wettest places in the world. The mountainous areas of the islands receive even more rainfall.
- Rainy and Dry Seasons: The wettest period typically extends from November to April, coinciding with the South Pacific’s cyclone season. During this time, the islands can experience heavy, persistent rains. From May to October, the drier season sees slightly less rainfall but remains relatively humid.
- Little Seasonal Temperature Variation: American Samoa experiences little variation in temperature throughout the year. The average temperature usually ranges between 26°C to 30°C (79°F to 86°F). The warm, tropical climate is consistent, with the oceanic setting ensuring that extreme temperatures are rare.
- Tropical Cyclones: The region is susceptible to tropical cyclones, particularly during the wet season. These cyclones can bring intense rainfall and strong winds and sometimes lead to significant damage.
- Humidity Levels: High humidity is a constant feature of American Samoa’s climate. The humidity level often exceeds 80%, contributing to the lush, tropical environment and posing challenges in heat discomfort.
- Oceanic Influence: Being a group of islands, American Samoa’s climate is heavily influenced by the surrounding Pacific Ocean. The ocean helps moderate temperatures, ensuring they do not fluctuate widely between day and night or across seasons.
- Sunshine Hours: American Samoa enjoys a fair amount of sunshine despite the high rainfall. The islands typically receive about 7 to 8 hours of sunshine daily, contributing to their vibrant and diverse ecosystems.
- Impact on Ecosystems: The warm, moist climate of American Samoa supports a rich array of tropical ecosystems, including rainforests, coral reefs, and mangroves. These ecosystems are home to various plant and animal species, some of which are unique to the region.
- Climate Change Concerns: Like many Pacific island nations, American Samoa faces challenges related to climate change. Rising sea levels, increased intensity of tropical cyclones, and changes in rainfall patterns are significant concerns that could impact the islands’ ecosystems, infrastructure, and way of life.
American Samoa’s tropical marine climate, with its consistent warmth, high humidity, and abundant rainfall, plays a vital role in shaping the natural beauty and biodiversity of the islands. Understanding these climatic conditions is crucial for the region’s environmental conservation and sustainable development.
Geography
American Samoa’s geography, characterized by its volcanic islands and coral atolls, presents a unique and diverse landscape in the South Pacific. Here’s an extended overview of American Samoa’s geographical features, including more detailed statistics and information about its surrounding regions:
- Volcanic Islands: The territory consists of five main volcanic islands: Tutuila, Aunu’u, Ofu, Olosega, and Ta‘ū. These islands are known for their rugged peaks formed through volcanic activity. The volcanic nature contributes to the islands’ fertile soil, supporting lush vegetation.
- Coral Atolls: Besides the volcanic islands, American Samoa includes two coral atolls: Swains Island and Rose Atoll. Coral atolls are formed from coral reefs and are important for their unique ecosystems. Rose Atoll, in particular, is a significant bird and marine sanctuary.
- Highest Point – Lata Mountain: Lata Mountain, on Ta‘ū Island, is the highest point in American Samoa, standing at 964 meters (3,163 feet). This mountain is part of the larger volcanic structure that forms the island and is a prominent feature of the territory’s topography.
- Coastal Plains: The coastal plains in American Samoa are limited due to the steep volcanic terrain. However, these areas are crucial for settlements and agriculture. The plains are most extensive on the island of Tutuila.
- Pago Pago Harbor: Pago Pago, located on Tutuila Island, boasts one of the finest natural deepwater harbors in the South Pacific. The surrounding high mountains protect the harbor well, making it an excellent port and a strategic location for maritime activities.
- Surrounding Ocean and Marine Life: American Samoa is surrounded by the vast Pacific Ocean, which plays a crucial role in the territory’s climate, culture, and economy. The surrounding waters are rich in marine biodiversity, including various fish species, coral reefs, and other marine organisms.
- Climate Influence: The geographical features of American Samoa, particularly its volcanic origins and oceanic location, significantly influence its climate. The islands experience a tropical marine climate with relatively consistent temperatures and high humidity.
- Natural Resources: The territory’s natural resources include its fertile land, which supports tropical vegetation, and the surrounding ocean, rich in marine life. Fishing and agriculture are important components of the local economy.
- Surrounding Regions: American Samoa is located in the South Pacific Ocean, northeast of Fiji and west of the Cook Islands. The closest significant landmass is Samoa, to the west, an independent nation that shares cultural and historical ties with American Samoa.
- Environmental Challenges: Like many Pacific islands, American Samoa faces environmental challenges such as the risk of tropical cyclones, rising sea levels due to climate change, and the preservation of its delicate marine ecosystems.
American Samoa’s geography, combining volcanic islands and coral atolls, creates a distinctive and diverse environment. This geography not only shapes the territory’s natural beauty and ecological richness but also influences its cultural and historical development. The territory’s position in the South Pacific makes it an important location for understanding Pacific island ecosystems and cultures.
Resources and Land Use
American Samoa’s natural resources are limited, primarily including pumice and pumicite. About 24.5% of the land is used for agriculture, with 15% being arable land.
Population Data
The population of American Samoa is 44,620 (estimated to be 2023), with a significant urban concentration in Pago Pago.
Economic Data
The economy is small, with a real GDP of $658 million (2016 estimate). The territory faces challenges like a vulnerable tuna canning industry and a large government sector.
Drinking Water Source
Nearly all the population (99.8%) has access to improved drinking water sources.
Population, Median Age, Migration, and Citizenship
The median age in American Samoa is 29.4 years (estimated to be 2023). The territory has a negative population growth rate of -1.74% (2023 estimate) and a very high net migration rate of -27.4 migrants/1,000 population (2023 estimate).
Average Number of Childbirths
The total fertility rate in American Samoa is 2.13 children born per woman (estimated to be 2023).
Is this country a Safe Destination?
American Samoa is generally safe for travelers. However, visitors should know about natural hazards like cyclones and limited medical facilities.
Healthcare and Infectious Diseases
N/A
Natural Hazards
The territory is prone to cyclones, especially from December to March. Limited volcanic activity is also present.
The Flag and Other Symbols
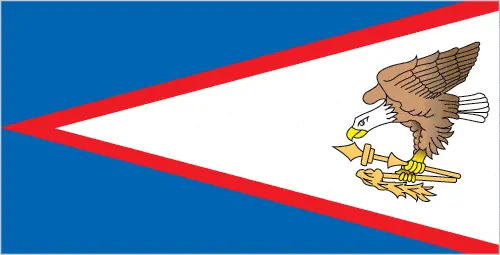
The flag of American Samoa features a white triangle edged in red, charged with an eagle on a blue field, symbolizing the territory’s relationship with the United States. Traditional Samoan symbols of authority are also included.
Constitution
American Samoa’s constitution was adopted in 1960 and revised in 1967. It protects traditional Samoan land tenure rules, language, and culture significantly.
Legal System
The legal system is a mix of US common law and customary law.
About the Unemployment Rate, Labor Force, and Poverty Line
The unemployment rate was 29.8% as of 2005. Data on the poverty line is N/A.
About the Budget and Central Government Debt
The territory had budget revenues of $249 million against expenditures of $262.5 million in 2016.
Inflation Rate and Prime Lending Rate
Data on the inflation rate N/A.
Export/Import Partners and Data
Key export partners include Australia, Ghana, Indonesia, Burma, and Portugal. Major imports come from Fiji, Singapore, New Zealand, South Korea, Samoa, Kenya, and Australia.
Renewable Energies Used
Data on renewable energies used N/A.
Telecommunication Data, Calling Code
American Samoa has a developing telecommunication system, with country code +1-684. The territory is connected to the world via fiber-optic cables and satellites.
Transport Infrastructure
The territory has three airports with paved runways and a major seaport at Pago Pago.
More Interesting Facts
American Samoa offers a unique blend of Polynesian culture and American influence. It is known for its beautiful landscapes, traditional villages, and warm hospitality.
Did You Know?
- Unincorporated U.S. Territory: American Samoa is an unincorporated territory of the United States, meaning it is under U.S. sovereignty but does not have the same status as a state. It’s the southernmost territory of the U.S. and one of only two U.S. territories located in the Southern Hemisphere.
- Unique Political Status: Unlike residents of other U.S. territories, people born in American Samoa are U.S. nationals, not citizens. This unique political status means they cannot vote in U.S. presidential elections and have limited rights to work and reside in other parts of the United States.
- Pago Pago Harbor: The harbor at Pago Pago, on the island of Tutuila, is one of the best natural deepwater harbors in the Pacific. Surrounded by steep volcanic peaks, it has played a significant strategic role throughout history, including during World War II.
- Lata Mountain: The highest point in American Samoa is Lata Mountain on Ta‘ū Island, standing at 964 meters (3,163 feet). This mountain is part of a dormant volcano and is a prominent feature of the island’s rugged landscape.
- Rainforest Cover: Much of American Samoa is covered in lush tropical rainforests. The National Park of American Samoa spread across three islands, protects some of these pristine environments, and is the only U.S. National Park south of the equator.
- Cultural Heritage: The Samoan culture, known as Fa’a Samoa, is over 3,000 years old and central to the people’s everyday life. It emphasizes communal living, family ties, and respect for traditional customs and hierarchies.
- Flying Foxes: American Samoa is home to the Samoan flying fox, a large species of bat that plays an important role in the local ecosystem as a pollinator and seed disperser. These bats are notable for their impressive wingspan, exceeding 3 feet.
- Rose Atoll Marine National Monument: Rose Atoll, an uninhabited coral atoll, is a U.S. National Monument and part of the National Wildlife Refuge system. It’s a sanctuary for rare species of birds, fish, and marine life, including giant clams and nesting sea turtles.
- Traditional Tattoos: Tattooing, or “tatau”, is important to Samoan culture. The traditional male tattoo, called “Pe’a”, covers the body from the waist to the knees and is a rite of passage symbolizing courage and societal status.
- Language: Samoan and English are the official languages. Samoan, a Polynesian language, is widely spoken and significant in daily communication, cultural practices, and local media.
- Rugby and American Football: Rugby is a popular sport in American Samoa, reflecting its Polynesian heritage. Interestingly, American Samoa also has a remarkably high number of American football players relative to its population, many of whom have played professionally in the NFL.
- Economic Activities: The economy of American Samoa is strongly linked to the United States and is primarily driven by tuna fishing and processing. The territory also receives financial aid from the U.S. government.
These facts about American Samoa highlight its unique blend of natural beauty, rich cultural heritage, and complex political relationship with the United States, making it a fascinating and distinctive part of the Pacific region.
Many thanks for visiting and sharing this map & country information site!