Google Maps and Detailed Facts of Argentina (AR). This page lets you explore Argentina and its border countries (Country Location: Southern South America, bordering the South Atlantic Ocean, Chile, and Uruguay) through detailed Satellite imagery – fast and easy as never before Google Maps.
Find comprehensive information about this country’s diversity below: Google Maps, geography, economy, science, people, culture, environment, government, and history – All in One Wiki page.
There is also a Street View and free Driving Directions at your service. Your Google Satellite Map Sightseeing in Argentina, in South America, starts here at Driving Directions and Maps.com.
About Argentina in detail
Table of contents
- Background
- Overview
- Google Maps
- Climate
- Geography
- Resources and Land Use
- Population Data
- Economic Data
- Drinking Water Source
- Population, Median Age, Migration, and Citizenship
- Average Number of Childbirths
- Is this country a Safe Destination?
- Healthcare and Infectious Diseases
- Natural Hazards
- The Flag and Other Symbols
- Constitution
- Legal System
- About the Unemployment Rate, Labor Force, and Poverty Line
- About the Budget and Central Government Debt
- Inflation Rate and Prime Lending Rate
- Export/Import Partners and Data
- Renewable Energies Used
- Telecommunication Data, Calling Code
- Transport Infrastructure
- More Interesting Facts
Background
Argentina’s journey to independence began in 1816 when the United Provinces of the Río de la Plata broke free from Spanish rule. The subsequent separation of Bolivia, Paraguay, and Uruguay led to the formation of modern-day Argentina. A significant influx of European immigrants, particularly from Italy and Spain, profoundly influenced the country’s population and culture from 1860 to 1930. Argentina’s political landscape in the 20th century was marked by internal strife and military involvement, with democracy firmly reestablished in 1983. Economic challenges have been persistent, with a severe crisis in 2001-02 leading to public upheaval and political instability. The 21st century saw varying political regimes, from Peronist rule to brief economic reforms under President Macri and a return to Peronist governance in 2019.
Overview
In Southern South America, Argentina shares borders with Chile, Bolivia, Paraguay, Brazil, and Uruguay. It’s the world’s 9th largest country, covering an area of approximately 2,780,400 sq km (1,073,518 sq miles), slightly less than three-tenths the size of the United States. The nation’s diverse geography ranges from the fertile plains of the Pampas to the rugged Andes mountains and the Patagonian plateau. Its climate varies from temperate in most of the country to arid in the southeast and subantarctic in the southwest.
Official Name: Argentine Republic
Date of Formation: 9 July 1816 (from Spain)
Capital: Buenos Aires
Population: 46,621,847 (2023 est.)
Total Area: 1,073,500 Sq. Miles / 2,780,400 Sq. Km
Population Density: N/A
Languages: Spanish (official), Italian, English, German, French, indigenous (Quechua, Guarani, Mapudungun)
Religions: Roman Catholic 62.9%, Evangelical 15.3%, Jehovah’s Witness and Church of Jesus Christ 1.4%, other 1.2%, none 18.9%, unspecified 0.3% (2019 est.)
Ethnic Origin: European (mostly Spanish and Italian descent) and Mestizo 97.2%, Amerindian 2.4%, African descent 0.4% (2010 est.)
Government: Presidential republic
Currency: Argentine peso (ARS)
Literacy Rate: 99% (2018)
Calorie Consumption: N/A
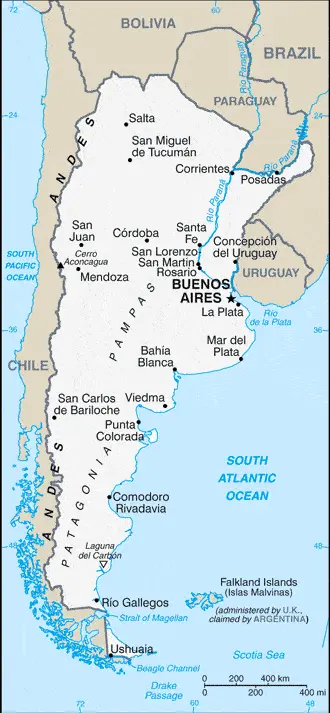
Argentina Google Maps
Argentina occupies most of southern South America. After 30 years of intermittent military rule, democracy returned in 1983. The economic crash in 2001 led to the largest-ever debt default. The Andes form a natural border with Chile in the west. East is the heavily wooded plains (Gran Chaco) and treeless but fertile Pampas plains. Bleak and arid Patagonia lies in the south.
Google Maps offers comprehensive coverage of Argentina, providing detailed mapping of its diverse landscapes, from the bustling streets of Buenos Aires to the remote regions of Patagonia. Users can explore various terrains and urban areas, making it an indispensable tool for travelers and locals alike.
The map below shows Argentina’s cities, towns, highways, main roads, streets, and Street Views. To find a location, use the form below, type any city or place, view a simple map, and click the “show map” button.
The Google Maps above shows Argentina with its location: South America (geographic coordinates: 34 00 S, 64 00 W) and the international borders of Argentina; total: 11,968 km. Border countries (total: 5): Bolivia 942 km, Brazil 1,263 km, Chile 6,691 km, Paraguay 2,531 km, Uruguay 541 km; furthermore, it’s inland counties boundaries.
The map of Argentina, South America, is for informational use only. No representation is made or warrantied given any map or its content by Driving Directions and Maps site. The user assumes all risks of using this Argentina Google Maps and facts/wiki.
Climate
Argentina, the eighth-largest country in the world, presents a diverse climate that significantly influences its varied landscapes and ecosystems:
- Predominant Temperate Climate: The most populated areas enjoy a temperate climate, including Buenos Aires and the Pampas region. Here, summers (December to February) are warm, with average temperatures around 24°C (75°F), and winters (June to August) are mild, with averages around 10°C (50°F). This climate is conducive to agriculture, making the Pampas one of the most fertile areas in Argentina.
- Arid Southeast: The southeast of Argentina, particularly towards Patagonia, experiences arid conditions. Regions like the Patagonian Desert receive minimal rainfall, averaging less than 200 mm (7.9 inches) annually. This aridity results in sparse vegetation and a landscape dominated by wind-eroded plains and plateaus.
- Subantarctic Southwest: The southwest has a subantarctic climate, especially in the Andean region. Areas like Tierra del Fuego and parts of Santa Cruz Province have cold climates with short, cool summers and long, wet winters. The average temperature in the warmest month is below 10°C (50°F). This region is known for its glaciers, ice fields, and cold-weather forests.
- Varied Landscapes and Ecosystems: Argentina’s climatic diversity is mirrored in its varied landscapes. The fertile Pampas support extensive agriculture; the Patagonian plateau is characterized by vast arid steppes, and the Andes region features alpine climates, fostering unique flora and fauna.
- Regional Variations: The northwest of Argentina experiences more extreme temperature variations with a semi-arid to arid climate characterized by hot summers and cold winters. The northeastern region, including the provinces of Misiones and Corrientes, has a subtropical climate with higher humidity and rainfall, supporting lush forests and wetlands, such as the Iguazú Falls area.
- Climate Influence on Culture and Economy: Argentina’s climate profoundly impacts its culture and economy. The temperate regions are the hub of agricultural activities, contributing significantly to the country’s economy through crops like soybeans, maize, and wheat. In contrast, the arid and subantarctic regions contribute to tourism, with attractions like Patagonia’s glaciers and Tierra del Fuego’s unique landscapes.
- Climate Change Impacts: Like many countries, Argentina faces challenges due to climate change, including glacier retreats in the Andes, changes in precipitation patterns affecting agriculture, and increased frequency of extreme weather events.
This climatic diversity not only shapes Argentina’s natural beauty but also influences its region’s lifestyle and economic activities, making it a country of rich and varied climatic experiences.
Geography
Argentina’s geography is as diverse as its climate, characterized by distinct regions, each with unique features and statistics:
- Pampas in the North: The Pampas, covering approximately 760,000 square kilometers, are fertile lowlands extending from the Atlantic coast to the Andes. This region is Argentina’s agricultural heartland, known for its rich soil and grasslands, making it ideal for cattle ranching and grain production. Buenos Aires, the capital, is located in this region, alongside other major cities like Rosario and La Plata.
- Patagonian Plateau in the South: The Patagonia region, spanning over 1 million square kilometers, is a vast area of flat to rolling plateau. Characterized by arid and semi-arid conditions, it’s home to unique landscapes like the Valdes Peninsula, famous for marine wildlife, and the Perito Moreno Glacier. Patagonia’s rugged terrain and national parks make it an outdoor and adventure tourism hub.
- Andes Mountains Along the West: Forming a natural border with Chile, the Argentine Andes stretch over 4,000 kilometers and include several subranges like the Sierras Pampeanas. Cerro Aconcagua, located in the province of Mendoza, stands at 6,962 meters (22,841 feet) and is the highest point in South America and the highest peak outside of Asia. The Andes are crucial for their biodiversity and mineral resources and as a water source for irrigation in agricultural valleys.
- Laguna del Carbón in Santa Cruz: Situated in the San Julián Great Depression, Laguna del Carbón at -105 meters (-344 feet) is the lowest point in Argentina and the Western Hemisphere. This area is part of the larger Patagonian steppe and showcases the region’s diverse topography.
- Surrounding Countries: Argentina shares borders with five countries:
- Chile to the west, separated by the Andes mountain range.
- Bolivia to the northwest, sharing a diverse border region that includes parts of the Gran Chaco and the Andes.
- Paraguay, located to the northeast, is bordered by the Pilcomayo and Paraguay rivers.
- Brazil to the northeast, with a border highlighted by the Iguazú Falls, one of the world’s most spectacular waterfalls.
- Uruguay to the east, separated by the Uruguay River and the Río de la Plata estuary.
- Significant Water Bodies: The Paraná, Uruguay, and Colorado Rivers are major waterways, with the Paraná River Delta being one of the world’s largest river deltas and an important ecological area. The country also has an extensive coastline along the Atlantic Ocean, featuring significant coastal cities like Mar del Plata and Bahía Blanca.
With its varied landscapes, Argentina’s geography plays a crucial role in its culture, economy, and biodiversity. Each region contributes uniquely to the country’s identity and livelihood, from the fertile lands of the Pampas to the rugged Andes and the arid Patagonian plateau.
Resources and Land Use
Argentina has diverse natural resources, including fertile agricultural land minerals like lead, zinc, tin, copper, iron ore, manganese, petroleum, and uranium. Agricultural land comprises 53.9% of the country’s total land area, with 13.9% arable land. Forests cover 10.7%, highlighting the nation’s rich biodiversity.
Population Data
The estimated population of Argentina in 2023 is approximately 46.62 million, making it the 33rd most populous country in the world. The ethnic composition is predominantly European and Mestizo, with a significant portion of the population residing in urban areas, particularly in and around Buenos Aires.
Economic Data
Argentina’s economy is large and diversified, facing challenges like debt obligations, rapid inflation, and reduced investor confidence. The country has a resource-rich, export-led growth model and is increasingly fostering trade relations with nations like China. It’s a member of the G20 and a significant player in the Organization of American States (OAS).
Drinking Water Source
Argentina has a high access rate to improved drinking water sources, with virtually all urban populations covered. Rural data is not fully available, but significant efforts have been made to extend these services nationwide.
Population, Median Age, Migration, and Citizenship
The median age in Argentina is 33 years. The country has experienced various migration waves, historically being a destination for European immigrants and, more recently, regional migration from neighboring countries. The net migration rate is -0.1 migrant(s)/1,000 population as of 2023.
Average Number of Childbirths
The total fertility rate in Argentina is about 2.17 children born per woman (2023 est.), reflecting a gradual decline in birth rates over recent decades.
Is this country a Safe Destination?
Argentina is generally considered a safe destination for travelers, with standard precautions advised for visitors. While certain areas may pose risks due to petty crime, the country is known for its welcoming culture and vibrant tourist attractions.
Healthcare and Infectious Diseases
Argentina’s healthcare system is fairly advanced, with a high physician density of 4.06 physicians/1,000 population. The country invests significantly in healthcare, accounting for 10% of its GDP. Infectious diseases are controlled effectively, but travelers are advised to take standard precautions.
Natural Hazards
Argentina faces several natural hazards, including earthquakes in the Andes, violent windstorms (pamperos) in the Pampas and northeast, and heavy flooding in some areas. Volcanic activity is present along the Chilean border.
The Flag and Other Symbols
The Argentine flag features three horizontal sky blue and white bands with a radiant yellow Sun of May in the center. The sun symbol commemorates the May Revolution of 1810, which led to independence. The national colors, sky blue and white, are widely recognized symbols of Argentina.
Constitution
Effective since 1853, the Argentine Constitution has undergone several amendments, the most significant in 1994. It establishes Argentina as a presidential republic, with a clear separation of powers among the executive, legislative, and judicial branches.
Legal System
Argentina’s legal system is based on West European legal traditions. A significant reform in 2015 replaced the 1871 civil code with a new one, modernizing the legal framework and aligning it more closely with contemporary societal values.
About the Unemployment Rate, Labor Force, and Poverty Line
Argentina’s unemployment rate stood at 10.9% in 2021. The labor force predominantly engages in services, with agriculture and industry also playing significant roles. However, poverty remains a challenge, with 35.5% of the population living below the poverty line as of 2019.
About the Budget and Central Government Debt
The country’s budget dynamics are complex, with revenues at $150.823 billion and expenditures at $170.725 billion (2019 est.). Public debt, amounting to 57.6% of GDP in 2017, is a concern.
Inflation Rate and Prime Lending Rate
Inflation remains a persistent issue, with rates around 25.7% in 2017. The provided data does not specify the prime lending rate details, but high inflation typically affects interest rates and lending practices.
Export/Import Partners and Data
Argentina’s main export partners include Brazil, China, the United States, and Chile. Major exports are corn, soybean products, wheat, and beef. Import partners are Brazil, China, and the US, with cars and petroleum products being significant imports.
Renewable Energies Used
The country is increasingly investing in renewable energy, focusing on wind and solar power. As of 2020, renewable sources accounted for a substantial portion of the total installed electricity capacity.
Telecommunication Data, Calling Code
Argentina’s telecommunication infrastructure is well-developed, with a high rate of mobile cellular subscriptions and a growing broadband sector. The country code is +54.
Transport Infrastructure
Argentina boasts extensive transport infrastructure, including many airports, a well-developed road network, and extensive waterways. Railways and ports play vital roles in domestic and international transport.
More Interesting Facts
Argentina’s rich cultural heritage includes tango music and dance, renowned beef cuisine, and vibrant football culture. It’s home to natural wonders like the Iguazú Falls and the Perito Moreno Glacier, making it a diverse and fascinating country to explore.
Did You Know?
- Home to Natural Wonders: Argentina boasts some of the world’s most breathtaking natural sights. The Iguazú Falls, located on the border with Brazil, is one of the largest waterfall systems globally, featuring 275 individual waterfalls spread over nearly 3 kilometers.
- Land of Extremes: Argentina houses both the highest and lowest points in the Southern Hemisphere. Cerro Aconcagua is the highest peak outside of Asia at 6,962 meters (22,841 feet), while Laguna del Carbón, at -105 meters (-344 feet), is the lowest point in the Western Hemisphere.
- Patagonian Ice Fields: The Southern Patagonian Ice Field in Argentina is the world’s third-largest reserve of fresh water and one of the largest remnants of the Last Glacial Maximum.
- Birthplace of Tango: Argentina is the birthplace of Tango, a dance that originated in the late 19th century in the suburbs of Buenos Aires. It’s not just a dance but a cultural symbol, deeply rooted in Argentine tradition and recognized by UNESCO as part of the world’s intangible cultural heritage.
- Diverse Wildlife: The Valdes Peninsula in Patagonia is a UNESCO World Heritage site and one of South America’s most important marine mammal reserves, home to whales, sea lions, and elephant seals.
- Fossil Paradise: Argentina is a hot spot for paleontology. The country’s diverse climates and landscapes have contributed to significant dinosaur discoveries, including the largest known dinosaur species, Argentinosaurus, and the largest carnivorous dinosaur, Giganotosaurus.
- Wine Country: Argentina is the fifth-largest wine producer in the world, and its Mendoza region is famous for producing high-quality Malbec wine. The region’s high altitude and dry climate create ideal conditions for vineyards.
- Colorful Buenos Aires: The capital city, Buenos Aires, is known as the “Paris of South America” for its vibrant cultural scene, European-style architecture, and bustling nightlife.
- A Haven for Scientists: Ushuaia in Tierra del Fuego is often referred to as the southernmost city in the world and serves as a key research hub and gateway for Antarctic expeditions.
- Political Milestone: In 2007, Argentina elected Cristina Fernández de Kirchner as its first female president, reflecting its progressive stance in Latin American politics.
These fascinating facts about Argentina illustrate its rich natural and cultural heritage, from its dramatic landscapes and unique biodiversity to its profound cultural and scientific contributions.
Many thanks for visiting and sharing this map & country information site!