Google Maps and Detailed Facts of Armenia (AM). This page lets you explore Armenia and its border countries (Country Location: Southwestern Asia, between Turkey (to the west) and Azerbaijan; note – Armenia views itself as part of Europe; geopolitically, it can be classified as falling within Europe, the Middle East, or both) through detailed Satellite imagery – fast and easy as never before Google Maps.
Find comprehensive information about this country’s diversity below: Google Maps, geography, economy, science, people, culture, environment, government, and history – All in One Wiki page.
There is also a Street View and free Driving Directions at your service. Your Google Satellite Map Sightseeing in Armenia, in Asia, starts here at Driving Directions and Maps.com.
About Armenia in detail
Background
Armenia, known for being the first state to adopt Christianity in the early 4th century, has a tumultuous history marked by periods of foreign domination and brief moments of independence. The impact of the Armenian Genocide during World War I, where over a million Armenians perished, is a defining aspect of its history. Armenia became part of the USSR in 1920 and regained independence with the Soviet Union’s dissolution in 1991. The country has faced ongoing conflicts with Azerbaijan over the Nagorno-Karabakh region, leading to significant territorial changes and political challenges.
Overview
Armenia, located in Southwestern Asia, is a landlocked country sharing borders with Turkey, Azerbaijan, Georgia, and Iran. It covers an area of 29,743 sq km (11,484 sq miles), making it slightly smaller than Maryland. The country’s terrain is predominantly mountainous, with fast-flowing rivers and the fertile Aras River valley. Despite its small size, Armenia has a rich cultural heritage and a complex geopolitical position, straddling Europe and the Middle East.
Official Name: Republic of Armenia
Date of Formation: 21 September 1991 (from the Soviet Union)
Capital: Yerevan
Population: 2,989,091 (2023 est.)
Total Area: 11,484 Sq. Miles / 29,743 Sq. Km
Population Density: N/A
Languages: Armenian (official) 97.9%, Kurmanji 1%, other 1.1%; note – Russian is widely spoken
Religions: Armenian Apostolic Christian 92.6%, Evangelical Christian 1%, other 2.4%, none 1.1%, unspecified 2.9% (2011 est.)
Ethnic Origin: Armenian 98.1%, Yezidi 1.2%, other 0.7%
Government: Parliamentary democracy
Currency: Armenian dram (AMD)
Literacy Rate: N/A
Calorie Consumption: N/A
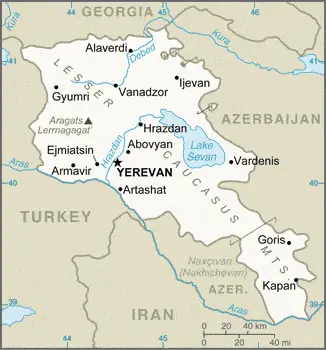
Armenia Google Maps
The smallest of the former USSR’s republics, Armenia, lies landlocked in the Lesser Caucasus Mountains. After 1988, a confrontation with Azerbaijan dominated national life. Rugged and mountainous, with expanses of semidesert and a large lake in the east: Sevana Lich.
Google Maps provides detailed and interactive maps of Armenia, showcasing its diverse landscapes, from the bustling capital of Yerevan to the scenic beauty of Lake Sevan. The tool is invaluable for exploring Armenia’s historic sites, navigating its cities, and understanding its complex geography.
The map below shows Armenia’s cities, towns, highways, main roads, streets, and Street Views. To find a location, use the form below, type any city or place, view a simple map, and click the “show map” button.
The Google Maps above shows Armenia with its location: Asia (geographic coordinates: 40 00 N, 45 00 E) and the international borders of Armenia; total: 1,570 km. Border countries (total: 4): Azerbaijan 996 km, Georgia 219 km, Iran 44 km, Turkey 311 km; furthermore, it’s inland counties boundaries.
The map of Armenia, Asia, is for informational use only. No representation is made or warrantied given any map or content by the Driving Directions and Maps site. The user assumes all risks of using this Armenia Google Maps and facts/wiki.
Climate
Armenia, nestled in the South Caucasus region, experiences a distinctive highland continental climate, which significantly influences its natural landscapes and biodiversity:
- Temperature Extremes: Due to its highland continental climate, Armenia undergoes substantial temperature variations. Summers are typically hot, with average temperatures in July reaching up to 25°C (77°F) in the lowlands. However, in the high-altitude areas, temperatures can be significantly cooler. Conversely, winters are cold, with January temperatures averaging -5 °C (23°F) in the lowlands and even colder in the mountainous regions, often dropping below 10°C (14°F).
- Precipitation Patterns: Armenia’s annual precipitation varies based on elevation and geography. The average annual rainfall is about 550 mm (21.7 inches), but it can be as high as 800 mm (31.5 inches) in the mountainous regions. The country receives most of its precipitation during the spring and early summer.
- Impact on Biodiversity and Landscapes: This climate supports diverse ecosystems, from semi-desert to alpine and even subtropical systems in the southern regions. Armenia’s landscapes are characterized by mountain meadows, forests, and grasslands, fostering a rich biodiversity that includes various endemic plant and animal species.
- Viticulture and Agriculture: The climate is particularly favorable for viticulture and agriculture. Armenia is known for its ancient wine-making traditions, with the highland climate providing ideal conditions for growing various grapes. The fertile valleys and moderate climate also support cultivating fruits, vegetables, and grains.
- Scenic Beauty and Tourism: Armenia’s climate contributes to its stunning natural beauty, making it an attractive tourist destination. The country’s picturesque landscapes, including Lake Sevan, the world’s largest high-altitude lake, and the snow-covered peaks of the Caucasus, offer a scenic backdrop for outdoor activities like hiking, skiing, and bird watching.
- Climatic Challenges: Despite the benefits, Armenia also faces climatic challenges, such as water scarcity in the arid zones and the risk of soil erosion in mountainous areas. Climate change poses additional threats, potentially altering precipitation patterns and impacting agricultural productivity.
- Microclimates: Due to its varied topography, Armenia experiences several microclimates. In the Tavush and Lori provinces, the climate is more temperate and humid, while regions like the Ararat Valley experience hot and dry conditions, creating a patchwork of climatic conditions across the country.
In summary, Armenia’s highland continental climate not only shapes its diverse ecosystems and stunning landscapes but also plays a critical role in its cultural practices and economic activities, particularly in agriculture and tourism.
Geography
Armenia’s geography, characterized by the Armenian Highland, presents a unique topography that significantly influences its landscape, ecology, and human activities:
- Armenian Highland: Dominating the country’s geography, the Armenian Highland is a region of complex mountains interspersed with high plateaus extending across Armenia, eastern Turkey, northern Iran, and the southern parts of Georgia and Azerbaijan. This highland region has numerous rivers and lakes, with elevations ranging from 1,000 to 2,500 meters (3,280 to 8,200 feet).
- Mountain Ranges and Peaks: The country is largely mountainous, with an average altitude of 1,800 meters (5,900 feet) above sea level. Mount Aragats, an isolated four-peaked volcano massif, is the highest point in Armenia at 4,090 meters (13,419 feet). Its snow-capped peak is a prominent feature of the national landscape.
- Forests and Valleys: Armenia has limited forest land, covering approximately 11.2% of the country’s territory. These forests are mainly found in the northern regions. The fertile valleys, notably the Aras River valley, which forms part of the border with Iran and Azerbaijan, are crucial for agriculture, supporting the cultivation of various crops.
- Lowest Point: The country’s lowest point is the Debed River at 400 meters (1,312 feet), which flows through some of Armenia’s major cities and is significant for hydroelectric power production.
- Surrounding Countries: Armenia shares its borders with:
- Turkey to the west: Turkey’s border is currently closed due to political tensions.
- Georgia to the north: This border area features a mix of mountains and valleys, playing a vital role in regional transport and trade.
- Azerbaijan to the east: The border is complex, especially around the Nagorno-Karabakh region, a source of longstanding conflict.
- Iran to the south: This border runs along the Aras River, an important regional water source.
- Significant Water Bodies: Apart from the Aras River, Lake Sevan is a major freshwater body, one of the largest high-altitude lakes in the world. It is crucial for Armenia’s fisheries and recreational activities.
- Climate Influence: The varied elevations result in diverse climatic conditions across the country, ranging from dry subtropical to mountainous climates.
Armenia’s geography, characterized by its rugged highlands, scarce forest cover, and fertile valleys, is crucial in its cultural identity, agricultural practices, and geopolitical relationships. The country’s landscape not only shapes its natural beauty but also poses challenges and opportunities for its development and interaction with neighboring nations.
Resources and Land Use
Armenia’s natural resources include small gold, copper, molybdenum, zinc, and bauxite deposits. Agricultural land accounts for 59.7% of the total land area, with arable land constituting 15.8%. Forests cover 9.1% of the country, highlighting its environmental diversity.
Population Data
As of 2023, Armenia’s population is estimated at 2,989,091, ranking 139th globally. The majority of the population resides in the country’s northern half, with the capital, Yerevan, being the largest and most populous city.
Economic Data
Armenia’s economy is diverse, with key sectors including mining, agriculture, and energy. It has joined the Eurasian Economic Union and has signed a Comprehensive and Enhanced Partnership Agreement with the EU, reflecting its strategic economic alliances.
Drinking Water Source
Armenia boasts 100% access to improved drinking water sources for both urban and rural populations, underscoring its commitment to public health and hygiene.
Population, Median Age, Migration, and Citizenship
The median age in Armenia is 38.3 years as of 2023. The country has experienced significant emigration, particularly since independence, contributing to a diverse and widespread diaspora. Citizenship laws allow for dual citizenship and require a three-year residency for naturalization.
Average Number of Childbirths
The total fertility rate in Armenia is 1.65 children born per woman (2023 est.), which is below the replacement level and indicative of the country’s declining birth rate.
Is this country a Safe Destination?
Armenia is generally safe for travelers, but visitors are advised to remain aware of regional tensions, particularly near the borders with Azerbaijan and Turkey.
Healthcare and Infectious Diseases
Armenia has a relatively well-developed healthcare system, with a physician density of 4.4 physicians/1,000 population (2017). It allocates 12.2% of its GDP to healthcare expenditure.
Natural Hazards
The country faces natural hazards like severe earthquakes and occasional droughts. Its location in a seismically active zone necessitates robust disaster preparedness and response mechanisms.
The Flag and Other Symbols
The Armenian flag features three equal horizontal red, blue, and orange bands. Mount Ararat, the eagle, and the lion are prominent national symbols, representing the nation’s history and culture.
Constitution
Armenia’s constitution was adopted in 1995 and has undergone several amendments, with a significant change in 2015, transitioning the government to a parliamentary system. The latest amendment occurred in 2020.
Legal System
The country operates under a civil law system, which various European legal traditions have influenced.
About the Unemployment Rate, Labor Force, and Poverty Line
Armenia’s unemployment rate stood at 20.9% in 2021, with a significant portion of the labor force engaged in agriculture. Poverty remains a challenge, with 26.4% living below the poverty line as of 2019.
About the Budget and Central Government Debt
The national budget reflects revenues of $3.258 billion and expenditures of $3.392 billion (2019 est.). Public debt amounted to 63.4% of GDP in 2020.
Inflation Rate and Prime Lending Rate
The inflation rate was 7.18% in 2021, reflecting economic challenges and market fluctuations.
Export/Import Partners and Data
Armenia’s main export partners are Russia, Switzerland, and China, with key exports including copper ore and gold. Import partners include Russia and China, with natural gas and cars being significant imports.
Renewable Energies Used
The country is working towards expanding its renewable energy sector, with hydroelectricity constituting a significant portion of its energy mix.
Telecommunication Data, Calling Code
Armenia has a well-developed telecommunications infrastructure, with a high rate of mobile phone usage. The country code is +374.
Transport Infrastructure
Armenia’s transport infrastructure includes a network of roads, railways, and several airports, despite being landlocked. The transport sector is crucial for its economic connectivity.
More Interesting Facts
Armenia is renowned for its rich cultural heritage, including its ancient monasteries, vibrant music and dance traditions, and unique Armenian cuisine. The country is also known for its significant contributions to art, literature, and science, both historically and in contemporary times.
Did You Know?
- Oldest Known Winery: Archaeologists discovered the world’s oldest known winery in Armenia, dating back to around 4100 BCE. Located in the Areni cave, this finding highlights Armenia’s ancient winemaking traditions that continue to this day.
- First Christian Nation: Armenia became the first country in the world to adopt Christianity as its state religion in 301 AD. This early adoption has profoundly influenced Armenian culture, art, and architecture.
- Unique Script and Language: The Armenian alphabet, created by Saint Mesrop Mashtots in 405 AD, is a unique feature of the Armenian identity. It consists of 39 characters and was essential in preserving the Armenian language and literature.
- Chess in Schools: Armenia takes chess seriously – it was the first country to include chess as a compulsory subject in schools. The game is considered a vital part of intellectual development.
- Land of Ancient Monasteries: The country is dotted with ancient monasteries and churches, often located in areas of stunning natural beauty. The Geghard Monastery and the Haghpat Monastery are UNESCO World Heritage sites renowned for their intricate architecture and historical significance.
- Mount Ararat’s Significance: While Mount Ararat is now in Turkey, it remains a national symbol for Armenians. It is visible from the capital, Yerevan, and is deeply rooted in Armenian culture and history.
- Lake Sevan: One of the largest high-altitude freshwater lakes in the world, Lake Sevan is situated at an altitude of about 1,900 meters (6,234 feet). It’s a major tourist attraction and an important source of fish.
- A Land of Stone: Armenia is often called a “land of stone” due to its rugged landscape. The country has a wide variety of native stones and a strong stone sculpture and architecture tradition.
- Yerevan’s Age: The capital city, Yerevan, is one of the world’s oldest continuously inhabited cities. Founded in 782 BC, it predates Rome by nearly 30 years.
- Apricots from Armenia: The apricot is a national fruit of Armenia, and the country is known for its particularly delicious varieties. The Latin name for the apricot, Prunus armeniaca, means “Armenian plum,” indicating its deep connection to the country.
These fascinating facts about Armenia provide a glimpse into its rich cultural heritage, ancient history, and unique traditions, making it a captivating and unique country in the Caucasus region.
Many thanks for visiting and sharing this map & country information site!