Google Maps and Detailed Facts of Aruba (AW). This page lets you explore Aruba and its border countries (Country Location: the Caribbean, an island in the Caribbean Sea, north of Venezuela) through detailed Satellite imagery – fast and easy as never before Google Maps.
Find comprehensive information about this country’s diversity below: Google Maps, geography, economy, science, people, culture, environment, government, and history – All in One Wiki page.
There is also a Street View and free Driving Directions at your service. Your Google Satellite Map Sightseeing in Aruba, Central America, and the Caribbean starts here at Driving Directions and Maps.com.
About Aruba in detail
Table of contents
- Background
- Overview
- Google Maps
- Climate
- Geography
- Resources and Land Use
- Population Data
- Economic Data
- Drinking Water Source
- Population, Median Age, Migration, and Citizenship
- Average Number of Childbirths
- Is this country a Safe Destination?
- Healthcare and Infectious Diseases
- Natural Hazards
- The Flag and Other Symbols
- Constitution
- Legal System
- About the Unemployment Rate, Labor Force, and Poverty Line
- About the Budget and Central Government Debt
- Inflation Rate and Prime Lending Rate
- Export/Import Partners and Data
- Renewable Energies Used
- Telecommunication Data, Calling Code
- Transport Infrastructure
- More Interesting Facts
Background
Aruba, a picturesque island nation nestled in the southern Caribbean Sea, is a unique blend of cultures and histories. As an integral part of the Kingdom of the Netherlands, Aruba boasts a diverse tapestry woven from indigenous, Spanish, and Dutch influences. This rich cultural amalgamation is evident in its architecture, languages, and customs, making Aruba a distinctive and captivating destination.
Overview
Aruba is renowned for its breathtaking beaches, crystal-clear waters, and year-round sunshine, attracting tourists from around the globe. The island’s economy primarily thrives on tourism, but it also has a growing interest in renewable energy sources. With a commitment to sustainability, Aruba is steering towards a future where environmental preservation and economic growth go hand in hand.
Official Name: Country of Aruba
Date of Formation: Full autonomy in internal affairs was obtained in 1986
Capital: Oranjestad
Population: 123,702 (2023)
Total Area: 180 sq km
Population Density: N/A
Languages: Papiamento (official) 69.4%, Spanish 13.7%, English (widely spoken) 7.1%, Dutch (official) 6.1%, Chinese 1.5%, other 1.7%, unspecified 0.4% (2010 est.)
Religions: Roman Catholic 75%
Ethnic Origin: Dutch 78.7%, Colombian 6.6%, Venezuelan 5.5%, Dominican 2.8%, Haitian 1.3%, other 5.1% (2020 est.)
Government: Parliamentary democracy; part of the Kingdom of the Netherlands
Currency: Aruban guilder/florin (AWG)
Literacy Rate Rate: 98,7%
Calorie Consumption: N/A
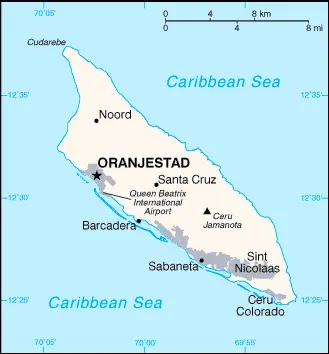
Aruba Google Maps
Google Maps is an invaluable tool for exploring Aruba’s enchanting landscape. From pinpointing the best beaches and resorts to navigating the charming streets of Oranjestad, Google Maps provides detailed and user-friendly guidance, enhancing the travel experience for visitors and locals alike.
“The map below shows Aruba’s cities, towns, highways, main roads, streets, and Street Views. To find a location, use the form below, type any city or place, view a simple map, and click the “show map” button.”The map below shows Aruba’s cities, towns, highways, main roads, streets, and Street Views. To find a location, use the form below, type any city or place, view a simple map, and click the “show map” button.
The Google Maps above shows Aruba with its location: Central America and the Caribbean (geographic coordinates: 12 30 N, 69 58 W) and the international borders of Aruba; 0 km; furthermore, its inland counties boundaries.
The Aruba, Central America, and Caribbean map is only informational. No representation is made or warrantied given any map or its content by Driving Directions and Maps site. The user assumes all risks of using this Aruba Google Maps and facts/wiki.
Climate
Aruba’s climate, classified as a tropical savannah, is one of its most appealing features, contributing significantly to its status as a popular tourist destination:
- Consistent Warm Temperatures: The island experiences a relatively stable climate year-round. The average temperature hovers around 28°C (82°F), with slight fluctuations throughout the year. The warmest months are usually from May to October when temperatures can reach up to 33°C (91°F).
- Low Rainfall and Dry Atmosphere: Aruba is notably dry compared to other Caribbean islands, receiving an average annual rainfall of less than 500 mm (20 inches). Most of this rainfall occurs during the short rainy season, from October to January, but even then, the showers are usually brief and sporadic.
- Location Outside the Hurricane Belt: One of Aruba’s key climatic advantages is its location outside the traditional hurricane belt. This factor significantly reduces the risk of hurricanes compared to other Caribbean regions, contributing to its reputation as a year-round travel destination. The island’s geographical position, just north of the Venezuelan coast, is crucial in this aspect.
- Trade Winds: Aruba enjoys cooling trade winds that blow consistently from the east. These winds provide a refreshing breeze that helps moderate the heat, especially during the hotter months. They also contribute to the island’s popularity for wind-driven water sports like windsurfing and kitesurfing.
- Sunshine Hours: The island is graced with abundant sunshine, averaging about 8 to 10 hours of sunlight per day. This consistent sunshine and warm temperatures make Aruba’s beaches particularly attractive.
- Impact on Ecosystems: The dry, sunny climate supports a unique landscape compared to typical lush, tropical Caribbean islands. Aruba features a mix of arid regions with cacti and aloe plants and beautiful white sandy beaches.
- Climate Change Considerations: Like many islands, Aruba faces challenges related to climate change, including rising sea levels and increased temperatures. These changes could have implications for its natural ecosystems and tourism-centered economy.
- UV Index: Given its location near the equator, Aruba has a high UV index year-round. Visitors are advised to take precautions against sun exposure, reinforcing the importance of sun safety in tropical climates.
In summary, Aruba’s tropical savannah climate, characterized by consistent warm temperatures, low rainfall, and its fortunate location outside the hurricane belt, plays a crucial role in shaping the island’s natural beauty and making it a favored destination for tourists seeking sun, sand, and sea.
Geography
Aruba’s geographical position and landscape offer a fascinating study of contrast and natural beauty:
- Proximity to South America: Located just 27 kilometers (about 17 miles) north of the Venezuelan coast, Aruba is part of the Lesser Antilles in the southern part of the Caribbean Sea. This proximity to the South American mainland influences both its climate and culture.
- Lesser Antilles Island Chain: As part of the Lesser Antilles, Aruba lies in a region that forms the eastern boundary of the Caribbean Sea with the Atlantic Ocean. This chain of islands stretches from the Virgin Islands in the north to Trinidad and Tobago in the south.
- Coastal Diversity: Aruba is renowned for its varied coastline. The western and southern coasts are known for their white sandy beaches, like Eagle Beach and Palm Beach, which are among the most popular and picturesque on the island. These beaches are characterized by calm, crystal-clear waters, making them ideal for swimming and water sports.
- Rugged Northern and Eastern Terrain: In contrast, the northern and eastern coasts present a more rugged and dramatic landscape. This less developed area features rocky shores, limestone cliffs, and a rougher sea, offering spectacular natural scenery. This island part is also home to natural pools and unique rock formations.
- Mount Jamanota: The island’s highest point, Mount Jamanota, stands at 188 meters (617 feet) above sea level. Although not very high in terms of absolute elevation, it provides panoramic views of the island and is a popular spot for hiking and nature observation.
- Size and Population Density: Aruba is a relatively small island, stretching about 32 kilometers (20 miles) from north to south and 10 kilometers (6 miles) at its widest point. Despite its small size, the island is densely populated, with a total population of over 100,000 residents, resulting in a unique blend of urban and natural landscapes.
- Surrounding Regions and Countries:
- To the north and east, Aruba is bordered by the open Atlantic Ocean.
- To the south, it faces the Caribbean Sea and the coast of Venezuela.
- Neighboring islands in the Caribbean include Curaçao and Bonaire to the east, forming the ABC islands of the Lesser Antilles.
- Natural Reserves: Aruba also boasts several natural reserves, including Arikok National Park, which covers approximately 18% of the island’s area. This park protects a range of native flora and fauna, caves, and indigenous rock paintings.
Aruba’s geographic location and diverse landscapes make it a unique destination in the Caribbean and contribute to its rich cultural heritage and biodiversity. The island offers many natural attractions, from serene beaches to rugged coastlines and scenic high points.
Resources and Land Use
Aruba’s natural resources are limited due to its small size and arid climate. However, the island has made significant strides in renewable energy, particularly in wind and solar power. Land use predominantly focuses on tourism development and urban areas, with limited agricultural activities.
Population Data
Aruba’s population is approximately 123,700, with a diverse ethnic mix that includes Aruban, Colombian, Dutch, Venezuelan, and other nationalities. The multicultural fabric of Aruba is one of its most charming aspects, reflected in its languages, cuisines, and traditions.
Economic Data
Tourism is the backbone of Aruba’s economy, contributing significantly to its GDP. The island has also ventured into other sectors like offshore banking, oil refining, and aloe cultivation. Aruba’s GDP per capita stands at about USD 25,000, highlighting its status as one of the more prosperous islands in the Caribbean region.
Drinking Water Source
Aruba ensures a high-quality drinking water supply, primarily derived from seawater desalination. This process is crucial due to the island’s arid climate and lack of freshwater sources.
Population, Median Age, Migration, and Citizenship
The median age in Aruba is around 39 years, indicative of a relatively young population. Migration plays a significant role in the island’s demographic dynamics, with many people moving to Aruba for work and better living conditions. Citizenship is typically granted in accordance with Dutch nationality laws, reflecting the island’s status within the Kingdom of the Netherlands.
Average Number of Childbirths
In Aruba, the average number of childbirths per woman is approximately 1.7, aligning with global trends towards smaller family sizes.
Is this country a Safe Destination?
Aruba is generally considered a safe destination for tourists. The island maintains a low crime rate and a friendly atmosphere, although standard safety precautions are advised, as in any travel destination.
Healthcare and Infectious Diseases
Aruba provides quality healthcare services with modern facilities and skilled medical professionals. Infectious diseases are relatively low, but visitors are advised to take routine vaccinations before traveling.
Natural Hazards
Being outside the hurricane belt, Aruba is largely spared from the severe storms that can affect other Caribbean islands. Occasional droughts are the most common natural hazard due to its dry climate.
The Flag and Other Symbols
Aruba’s flag features light blue, symbolizing the sea and sky, yellow stripes representing its bountiful past, and a red star with a white outline signifying the island itself, its beautiful beaches, and its position in the Caribbean Sea. Other national symbols include the Watapana tree and the Burrowing Owl (Shoco).
Constitution
Aruba’s constitution, established when it became a separate entity within the Kingdom of the Netherlands in 1986, outlines the framework of its parliamentary democracy. It ensures the rights and freedoms of its citizens and governs the island’s political and legal systems.
Legal System
The legal system in Aruba is based on Dutch civil law, with modifications to suit its Caribbean context. The judiciary is independent, and the well-established legal framework offers security and clarity for residents and businesses.
About the Unemployment Rate, Labor Force, and Poverty Line
Aruba’s unemployment rate is relatively low, reflecting its robust tourism industry and diversified economy. The labor force is mainly employed in tourism, trade, and public administration. Poverty is not a significant issue, but the government focuses on social welfare programs to ensure equitable growth.
About the Budget and Central Government Debt
Aruba’s budget primarily focuses on public services, infrastructure, and economic development, carefully managing its debt levels. The government’s fiscal policies aim to balance development needs with financial sustainability.
Inflation Rate and Prime Lending Rate
Aruba’s moderate inflation rate is managed through prudent fiscal and monetary policies. The prime lending rate is aligned with international standards, facilitating investment and economic activities.
Export/Import Partners and Data
Aruba’s main exports include machinery, transport equipment, and live animals, largely to partners like the Netherlands, the United States, and Colombia. Imports consist of machinery, fuels, and food products, reflecting the island’s reliance on external sources for these essentials.
Renewable Energies Used
Aruba is at the forefront of renewable energy use in the Caribbean, with significant wind and solar power investments. This shift towards green energy aligns with the island’s commitment to environmental sustainability and reducing its carbon footprint.
Telecommunication Data, Calling Code
Aruba has a well-developed telecommunications infrastructure, offering advanced services like high-speed internet and mobile connectivity. The international calling code for Aruba is +297.
Transport Infrastructure
Aruba’s transport infrastructure is well-maintained, facilitating easy movement around the island. Key components include a modern international airport, a cruise port, and a network of highways and roads catering to both residents and tourists.
More Interesting Facts
Aruba is often called ‘One Happy Island,’ a testament to its friendly locals and welcoming atmosphere. The island is also home to the Arikok National Park, a protected area showcasing Aruba’s native flora, fauna, and unique geological formations. Additionally, Aruba’s commitment to becoming fully reliant on renewable energy by 2020 is a notable endeavor in the global environmental landscape.
Did You Know?
- Close to South America: Aruba is one of the closest Caribbean islands to South America, lying just 27 kilometers (17 miles) north of the Venezuelan coast. This proximity influences its culture, cuisine, and even wildlife.
- Aloe Vera Capital: Known as the ‘Island of Aloe’, Aruba is one of the world’s largest producers of aloe vera. The aloe plants thrive in the island’s arid climate, and their products are renowned for their quality.
- Languages Galore: While Dutch and Papiamento, a Creole language, are the official languages, most Arubans are multilingual and can also speak English and Spanish, reflecting the island’s diverse cultural influences.
- Windswept Divi-Divi Trees: The iconic divi-divi trees, bent at 45-degree angles due to the constant trade winds, are a unique feature of Aruba’s landscape and can often be seen pointing towards the west.
- Outside the Hurricane Belt: Aruba is located outside the hurricane belt, contributing to its stable and dry climate. This makes it an ideal destination for tourists year-round, as it’s less likely to be affected by tropical storms.
- Bird-Watching Paradise: Despite its small size, Aruba is home to more than 220 species of birds, including the Shoco, a burrowing owl that is Aruba’s national symbol.
- Sustainable Energy Leader: Aruba is a leader in sustainable energy in the Caribbean. The island aims to be completely energy-independent, with extensive wind farms and solar panels contributing to its energy mix.
- Historical Gold Rush: In the 19th century, Aruba experienced its own gold rush. Remnants of this history can still be seen at various sites, including the Bushiribana Gold Mill Ruins.
- Shipwreck Diving Sites: The waters around Aruba are home to several shipwrecks, making it a popular destination for divers. The Antilla, a German cargo ship sunk during World War II, is one of the largest shipwreck dive sites in the Caribbean.
- Carnival Celebrations: Aruba hosts an annual Carnival season, which is one of the island’s largest and most colorful celebrations, featuring parades, music, and dance that showcase its vibrant culture and heritage.
These facts about Aruba reflect its unique blend of natural beauty, cultural diversity, and commitment to sustainability, making it a distinctive and intriguing destination in the Caribbean.
Many thanks for visiting and sharing this map & country information site!