Google Maps and Detailed Facts of Bahamas (BS). This page lets you explore the Bahamas and its border countries (Country Location: chain of islands in the North Atlantic Ocean, southeast of Florida, northeast of Cuba) through detailed Satellite imagery – fast and easy as never before Google Maps.
Find comprehensive information about this country’s diversity below: Google Maps, geography, economy, science, people, culture, environment, government, and history – All in One Wiki page.
There is also a Street View and free Driving Directions at your service. Your Google Satellite Map Sightseeing in the Bahamas, Central America, and the Caribbean starts at Driving Directions and Maps.com.
About the Bahamas in detail
Table of contents
- Background
- Overview
- Google Maps
- Climate
- Geography
- Resources and Land Use
- Population Data
- Economic Data
- Drinking Water Source
- Population, Median Age, Migration, and Citizenship
- Average Number of Childbirths
- Is this country a Safe Destination?
- Healthcare and Infectious Diseases
- Natural Hazards
- The Flag and Other Symbols
- Constitution
- Legal System
- About the Unemployment Rate, Labor Force, and Poverty Line
- About the Budget and Central Government Debt
- Inflation Rate and Prime Lending Rate
- Export/Import Partners and Data
- Renewable Energies Used
- Telecommunication Data, Calling Code
- Transport Infrastructure
- More Interesting Facts
Background
The Bahamas, with its history deeply rooted in the Lucayan Indian civilization, came into prominence when Christopher Columbus first landed in the New World in San Salvador in 1492. The British settled the islands in 1647, leading to their colonial status in 1783. The nation’s proximity to major shipping lanes fostered piracy in the 17th and 18th centuries. Since gaining independence from the UK in 1973, The Bahamas has thrived on tourism, international banking, and investment management, constituting up to 85% of its GDP. The country’s closeness to the US has also made it a significant point for illicit trafficking.
Overview
The Bahamas is a sovereign nation known for its robust tourism and financial services sector. It is marked by a high-income economy with notable income inequality. Strong bilateral relations with the US and several tax relief programs have been pivotal in its economic development. The nation has also targeted investments in agriculture, energy, light manufacturing, and technology industries to diversify its economy.
Official Name: Commonwealth of The Bahamas
Date of Formation: 1973
Capital: Nassau
Population: 358,508 (2023 estimate)
Total Area: 13,880 sq km
Population Density: N/A
Languages: English (official), Creole (among Haitian immigrants)
Religions: Protestant 69.9% (includes Baptist 34.9%, Anglican 13.7%, Pentecostal 8.9%, Seventh Day Adventist 4.4%, Methodist 3.6%, Church of God 1.9%, Brethren 1.6%, other Protestant .9%), Roman Catholic 12%, other Christian 13% (includes Jehovah’s Witness 1.1%), other 0.6%, none 1.9%, unspecified 2.6% (2010 estimate)
Ethnic Origin: African descent 90.6%, White 4.7%, mixed 2.1%, other 1.9%, unspecified 0.7% (2010 est.)
Government: Parliamentary democracy under a constitutional monarchy; a Commonwealth realm
Currency: N/A
Literacy Rate: N/A
Calorie Consumption: N/A
Google Maps
Google Maps is essential for exploring the stunning archipelago of The Bahamas. It provides detailed imagery and navigation of its beautiful islands, helping to plan travel and explore its rich cultural and natural landscapes. Google Maps offers a comprehensive guide to this Caribbean paradise, from the bustling streets of Nassau to the serene beaches of the Exumas.
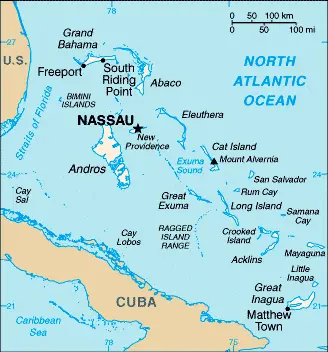
Located off the Florida coast in the western Atlantic, the Bahamas comprises an archipelago of some 700 islands and 2400 cays, with only around 30 inhabited. Long, mainly flat coral formations with a few low hills. Some islands have pine forests, lagoons, and mangrove swamps.
The map below shows the Bahamas with its cities, towns, highways, main roads, streets, and Street Views. To find a location, use the form below, type any city or place, view a simple map, and click the “show map” button.
The Google Maps above shows the Bahamas with its location: Central America and the Caribbean (geographic coordinates: 24 15 N, 76 00 W) and the international borders of the Bahamas; 0 km; furthermore, its inland counties boundaries.
The map of the Bahamas, Central America, and the Caribbean is for informational use only. No representation is made or warrantied given any map or content by the Driving Directions and Maps site. The user assumes all risks of using this Bahamas Google Maps and facts/wiki.
Climate
The Bahamas, an archipelago consisting of around 700 islands and cays, is blessed with a tropical marine climate heavily influenced by the warm currents of the Gulf Stream. This climatic influence ensures relatively stable and pleasant temperatures throughout the year, making the Bahamas a sought-after destination for tourists yearning for a tropical retreat.
Stable Temperatures: The temperature variations between summer and winter in the Bahamas are minimal compared to continental climates. Summer temperatures (June to September) average around 80°F to 85°F (27°C to 29°C), while in the winter months (December to February), the temperatures hover around a comfortable 70°F to 75°F (21°C to 24°C). The warm Gulf Stream is crucial in moderating these temperatures, ensuring they remain consistent and conducive to tourism and outdoor activities.
Rainfall and Dry Seasons: The Bahamas experiences distinct wet and dry seasons. The wet season, which coincides with the Atlantic hurricane season, runs from June to November. This period is characterized by higher humidity and more frequent rain showers, although they tend to be brief and localized. The northern islands generally receive more rainfall than the southern islands. From December to May, the dry season sees significantly less rainfall, contributing to the ideal vacation weather that the Bahamas are known for.
Hurricane Season: While the Bahamas is a paradise for most of the year, it is important to note that it lies within the Atlantic hurricane belt. This means that from June to November, hurricanes have a higher risk. However, modern forecasting techniques provide advanced warnings, allowing for ample preparation and ensuring the safety of both residents and tourists.
Sunshine Hours: The Bahamas enjoys ample sunshine throughout the year, with an average of seven to eight hours of bright sunshine per day. This abundance of sunlight, combined with the archipelago’s crystal-clear waters and pristine beaches, is a primary draw for visitors.
Water Temperatures: The surrounding waters of the Bahamas are an integral part of its climate appeal. The Gulf Stream ensures that the sea temperatures remain warm year-round, typically ranging between 73°F to 82°F (23°C to 28°C), which is ideal for a wide range of water activities, including swimming, snorkeling, and diving.
Impact on Biodiversity and Ecosystems: The stable, warm climate of the Bahamas supports a rich array of marine and terrestrial biodiversity. The warm waters are home to vibrant coral reefs, various fish species, and other marine life. At the same time, the land is covered in lush vegetation, including mangroves and tropical forests, which are home to various bird species and other wildlife.
In summary, the tropical marine climate of the Bahamas, with its warm temperatures, clear sunny skies, and inviting sea waters, not only makes it a premier destination for tourism but also plays a crucial role in supporting the rich biodiversity and natural beauty of the islands.
Geography
The Bahamas, an enchanting archipelago, is strategically positioned in the North Atlantic Ocean, southeast of Florida, USA, and northeast of Cuba. This chain of islands, often geopolitically aligned with the Caribbean region, is renowned for its breathtaking geography, which includes long, flat coral formations and some low, rounded hills.
Island Chain: The Bahamas consists of approximately 700 islands and over 2,000 rocks and cays, spread over 100,000 square miles of ocean. The archipelago extends over 500 miles (800 kilometers) from the coast of Florida to the edge of the Caribbean. The largest island is Andros Island, and the capital city, Nassau, is situated on New Providence Island.
Topography: The topography of the Bahamas is primarily flat and low-lying. The highest point in the country is Mount Alvernia (also known as Como Hill) on Cat Island, which rises to only 63 meters (207 feet) above sea level. This low elevation makes the islands particularly sensitive to sea-level rise.
Surrounding Countries and Waters: To the northwest, the Bahamas is bordered by the United States, specifically Florida, about 50 miles (80 kilometers) away at its nearest point. To the south, the Tropic of Cancer runs through the country, and further south lies Cuba, which is roughly 140 miles (225 kilometers) from the Bahamian island of Great Inagua. The Atlantic Ocean surrounds the Bahamas, providing stunningly clear waters that are a hallmark of the archipelago.
Coral Reefs and Marine Life: The Bahamas is home to one of the world’s largest barrier reefs known for its extensive underwater cave systems. These coral formations support a rich marine biodiversity, including various fish species, sharks, and rays, making it a premier destination for snorkelers and scuba divers.
Climate Influence on Geography: The tropical marine climate of the Bahamas has significantly influenced the geographical formation of the islands. The warm, clear waters have contributed to the growth of the extensive coral reef systems. Additionally, the sandy beaches found throughout the islands are primarily composed of finely ground and eroded coral due to the constant interaction between the ocean and the coral formations.
Impact of Geographical Location: The geographical location of the Bahamas has made it a key player in the region’s history and economy. The proximity to major shipping lanes has historically made the islands a strategic asset. Today, this location, combined with the islands’ natural beauty, drives the Bahamian economy, heavily reliant on tourism.
In summary, the geographical landscape of the Bahamas, characterized by its stunning coral formations, low-lying terrain, and strategic location in the North Atlantic, not only defines the natural beauty of the archipelago but also plays a significant role in its cultural, historical, and economic identity.
Resources and Land Use
The country’s natural resources include salt, aragonite, timber, and arable land. However, only a small fraction of the land is used for agriculture, with the majority being forested or other types of land.
Population Data
As of 2023, The Bahamas has an estimated population of 358,508. The country has a high rate of urbanization, with a significant majority living in urban areas, particularly on New Providence Island, where the capital, Nassau, is located.
Economic Data
The Bahamian economy is primarily driven by tourism and financial services. It has a GDP of approximately $12.323 billion as of 2021, with a notable real GDP growth rate of 13.72% in the same year. The country’s economy experienced a sharp decline in 2020 but has shown signs of robust recovery.
Drinking Water Source
Most of the population in The Bahamas has access to improved drinking water sources. As of 2017, about 98.9% of the population had access to improved water sources.
Population, Median Age, Migration, and Citizenship
The median age in The Bahamas is approximately 30.2 years as of 2023. The country has a positive net migration rate, indicating more people moving into the country than leaving. Citizenship in The Bahamas is primarily acquired by descent, with stringent residency requirements for naturalization.
Average Number of Childbirths
The total fertility rate in The Bahamas is relatively low, with an estimated 1.44 children born per woman as of 2023. This rate reflects the country’s developing economy and changing social norms regarding family size.
Is this country a Safe Destination?
The Bahamas is generally considered a safe destination for travelers. However, visitors are advised to remain vigilant, especially in areas popular with tourists, and to be aware of the country’s laws and customs to ensure a safe and enjoyable visit.
Healthcare and Infectious Diseases
The healthcare system in The Bahamas is evolving, with efforts to improve medical infrastructure and services. Infectious diseases are relatively controlled, but standard vaccinations are recommended for travelers.
Natural Hazards
The Bahamas is prone to hurricanes and other tropical storms, which can cause significant flood and wind damage. Being an island nation, it is particularly vulnerable to these natural hazards.
The Flag and Other Symbols
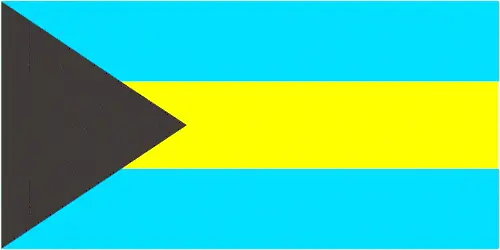
The Bahamas flag features three equal horizontal bands of aquamarine, gold, and aquamarine, with a black equilateral triangle on the hoist. The blue marlin, flamingo, and Yellow Elder flower are national symbols representing the Bahamian people’s natural beauty and resilience.
Constitution
The Constitution of The Bahamas, adopted in 1973, establishes the framework for a parliamentary democracy under a constitutional monarchy. It has been amended several times, with the most recent changes in 2016.
Legal System
The Bahamas follows a common law system based on the English model. The legal system is upheld by a hierarchy of courts, including the Court of Appeal and the Supreme Court.
About the Unemployment Rate, Labor Force, and Poverty Line
The unemployment rate in The Bahamas was estimated at 13.24% in 2021. The labor force is diversified, with significant contributions from agriculture, industry, services, and tourism. Approximately 9.3% of the population is below the poverty line.
About the Budget and Central Government Debt
The national budget of The Bahamas shows a deficit, with public debt reaching 84.45% of GDP in 2020. Fiscal management and debt reduction are ongoing challenges for the government.
Inflation Rate and Prime Lending Rate
The inflation rate in The Bahamas was estimated at 2.9% in 2021. Market conditions and the central bank’s monetary policy determine the prime lending rate.
Export/Import Partners and Data
The Bahamas’ major export partners include the United States, Germany, and Singapore. Key export commodities are refined petroleum, ships, and seafood. The country primarily imports from the United States, South Korea, and Germany, with refined petroleum and ships being significant import items.
Renewable Energies Used
Renewable energy development in The Bahamas is at a nascent stage, with the majority of electricity generation still reliant on fossil fuels. Efforts are underway to increase the use of solar and other renewable energy sources.
Telecommunication Data, Calling Code
The Bahamas’s telecommunications sector is evolving, focusing on expanding broadband and mobile services. The international calling code for The Bahamas is +1-242.
Transport Infrastructure
The Bahamas has a well-developed transport infrastructure, including numerous airports with paved and unpaved runways, a significant merchant marine fleet, and several major seaports. These facilities are crucial in supporting the nation’s tourism and trade.
More Interesting Facts
The Bahamas is famous for its vibrant culture, beautiful beaches, and unique biodiversity. The nation’s music, cuisine, and festivals reflect a rich cultural heritage influenced by African, British, and American traditions. Additionally, The Bahamas is home to the world’s third-largest barrier reef and offers some of the best diving and snorkeling experiences in the Caribbean.
Did you know?
Did you know that the Bahamas, with its stunning archipelago of islands and cays, is a treasure trove of fascinating facts? Here are some intriguing insights into this captivating country:
- Underwater Caves: The Bahamas is home to one of the world’s largest networks of underwater caves, known as blue holes. These natural wonders are a source of fascination for geologists and divers alike.
- Pink Sands: One of the Bahamas’ most unique natural features is the pink sand beaches found on Harbour Island. The pink hue comes from foraminifera, a microscopic organism with a bright pink or red shell.
- The Flamingo Sanctuary: Inagua National Park in the Bahamas is one of the world’s largest breeding colonies for West Indian flamingos. This sanctuary is vital for the conservation of these vibrant birds.
- Historical Significance in Exploration: Christopher Columbus landed in the New World on the Bahamian island of San Salvador in 1492. This event marked the beginning of the European exploration and colonization of the Americas.
- A Nation of Islands: Out of the 700 islands and more than 2,000 cays, only about 30 are inhabited. This makes the Bahamas an archipelago with many untouched and pristine islands.
- The Third Richest Country in the Americas: Based on GDP per capita, the Bahamas is one of the wealthiest countries in the Americas, thanks to its thriving tourism and finance sectors.
- Pirate History: In the early 18th century, Nassau in the Bahamas was known as a pirate’s paradise, home to the infamous Blackbeard (Edward Teach) and Calico Jack.
- The Island of Pigs: Big Major Cay, an uninhabited island in the Bahamas, is famously known as “Pig Beach” for its population of swimming pigs. The origin of these pigs is still a mystery, and they have become a significant tourist attraction.
- Queen Conch: The Bahamas is known for its queen conch, a large, edible sea snail. Conch is a staple in Bahamian cuisine and integral to the country’s cultural identity.
- World’s Deepest Blue Hole: Dean’s Blue Hole near Long Island is the world’s second-deepest known saltwater blue hole. It plunges 202 meters (663 feet) into the ocean floor, making it a popular spot for freedivers.
These fascinating facts highlight the Bahamas’ unique blend of natural wonders, rich history, and vibrant culture, making it an endlessly intriguing destination.
Many thanks for visiting and sharing this map & country information site!