Google Maps and Detailed Facts of Barbados (BB). This page lets you explore Barbados and its border countries (Country Location: the Caribbean, an island in the North Atlantic Ocean, northeast of Venezuela) through detailed Satellite imagery – fast and easy as never before Google Maps.
Find comprehensive information about this country’s diversity below: Google Maps, geography, economy, science, people, culture, environment, government, and history – All in One Wiki page.
There is also a Street View and free Driving Directions at your service. Your Google Satellite Map Sightseeing in Barbados, Central America, and the Caribbean starts at Driving Directions and Maps.com.
About Barbados in detail
Table of contents
- Background
- Overview
- Google Maps
- Climate
- Geography
- Resources and Land Use
- Population Data
- Economic Data
- Drinking Water Source
- Population, Median Age, Migration, and Citizenship
- Average Number of Childbirths
- Is this country a Safe Destination?
- Healthcare and Infectious Diseases
- Natural Hazards
- The Flag and Other Symbols
- Constitution
- Legal System
- About the Unemployment Rate, Labor Force, and Poverty Line
- About the Budget and Central Government Debt
- Inflation Rate and Prime Lending Rate
- Export/Import Partners and Data
- Renewable Energies Used
- Telecommunication Data, Calling Code
- Transport Infrastructure
- More Interesting Facts
Background
Barbados, first settled by the British in 1627, witnessed the establishment of sugar plantations worked by African slaves. By the early 18th century, its dominance in the sugar industry waned in favor of the Leeward Islands and Jamaica. The abolition of slavery in 1834 didn’t end the economic reliance on sugar, rum, and molasses production, which persisted into the 20th century. Political and social reforms in the mid-20th century paved the way for complete independence from the UK in 1966. Since the 1990s, tourism and manufacturing have overtaken sugar as economic drivers. Barbados transitioned to a republic in November 2021, with Sandra Mason elected as the first president, and plans for a new constitution were announced for 2022.
Overview
Barbados, an island nation in the North Atlantic, thrives primarily on tourism and manufacturing. The shift from its historical sugar industry roots has diversified its economy. As the easternmost island in the Caribbean, its tropical climate and picturesque beaches make it a popular tourist destination. Despite its small size, Barbados maintains a significant cultural influence in the region and beyond.
Official Name: Barbados
Date of Formation: 30 November 1966 (from the UK)
Capital: Bridgetown
Population: 303,431 (2023 estimate)
Total Area: 166 Sq. Miles / 430 Sq. Km
Population Density: N/A
Languages: English (official), Bajan (English-based creole language, widely spoken in informal settings)
Religions: Protestant 66.4%, Roman Catholic 3.8%, other Christian 5.4%, Rastafarian 1%, other 1.5%, none 20.6%, unspecified 1.2% (2010 est.)
Ethnic Origin: African descent 92.4%, mixed 3.1%, White 2.7%, East Indian 1.3%, other 0.2%, unspecified 0.3% (2010 est.)
Government: Parliamentary republic; a Commonwealth realm
Currency: Barbadian dollar (BBD)
Literacy Rate: 99.6% (2014)
Calorie Consumption: N/A
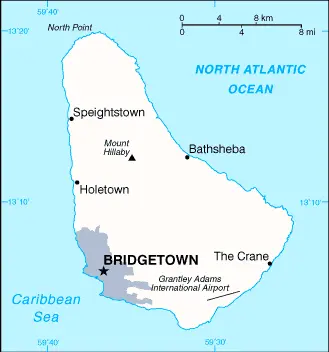
Barbados Google Maps
Google Maps provides comprehensive coverage of Barbados, offering detailed views of its varied landscape, from the urban expanse of Bridgetown to the serene beaches. This tool is invaluable for both visitors planning their travels and locals navigating daily life.
Barbados is the most easterly of the Caribbean islands. Once solely inhabited by the native Arawak, British settlers first colonized Barbados in the 1620s. Encircled by coral reefs. Fertile and predominantly flat, with a few gentle hills to the north.
The map below shows Barbados’s cities, towns, highways, main roads, streets, and Street Views. To find a location, use the form below, type any city or place, view a simple map, and click the “show map” button.
The Google Maps above shows Barbados with its location: Central America and the Caribbean (geographic coordinates: 13 10 N, 59 32 W) and the international borders of Barbados; 0 km; furthermore, its inland counties boundaries.
The map of Barbados, Central America, and the Caribbean is for informational use only. No representation is made or warrantied given any map or content by the Driving Directions and Maps site. The user assumes all risks of using this Barbados Google Maps and facts/wiki.
Climate
Barbados, nestled in the eastern Caribbean, experiences a predominantly tropical climate, which significantly shapes the island’s natural environment and influences the lifestyle of its inhabitants.
Tropical Climate with Distinct Seasons: The climate in Barbados is marked by two distinct seasons: the wet season and the dry season. The wet season, typically from June to October, coincides with the Atlantic hurricane season. During this period, the island experiences higher humidity and increased rainfall. Average rainfall during these months ranges from 100mm to 150mm (about 4 to 6 inches) per month. The rain usually comes in quick, heavy showers, followed by sunshine.
Dry Season: The dry season spans from December to May. In these months, the island enjoys lower humidity and less frequent rainfall, making it the peak season for tourism. The average temperature in the dry season ranges from 21°C to 31°C (70°F to 88°F), providing ideal conditions for outdoor activities and beach-going.
Geographical Location and Storms: Geographically, Barbados is situated in the Lesser Antilles, at the eastern edge of the Caribbean Sea, near the boundary of the Atlantic Ocean. This location plays a crucial role in the island’s weather patterns. Barbados occasionally follows the path of tropical storms and hurricanes developing in the Atlantic; however, it is generally less susceptible to direct hurricane hits than other Caribbean islands. This is partly due to its easterly location, which often places it outside the principal hurricane belt.
Moderating Influence of the Sea: The surrounding ocean exerts a moderating influence on the island’s climate. The sea breezes help temper the sun’s heat, making the warm temperatures more comfortable. The average sea temperature is consistently warm, ranging from 26°C to 29°C (79°F to 84°F) throughout the year, which is ideal for swimming and water sports.
Impact on Agriculture and Daily Life: Barbados’ climate significantly impacts agriculture, particularly the cultivation of sugarcane, which has historically been a key crop. The wet season provides essential water for these crops, but excessive rainfall can lead to challenges such as flooding and soil erosion. In daily life, the climate dictates much of the social and cultural activities, with many events and festivals planned around the favorable weather conditions of the dry season.
In summary, Barbados enjoys a warm, tropical climate with a distinct wet and dry season moderated by the surrounding sea. While it is prone to tropical storms and hurricanes, its geographical location tends to shield it somewhat from the most severe impacts experienced by other Caribbean islands. This climate not only influences the natural environment and agriculture but also plays a central role in the daily life and culture of the island.
Geography
Barbados, an island nation in the Caribbean, is situated in a unique geographical position northeast of Venezuela in the North Atlantic Ocean. Its location and topographical features present a distinctive landscape compared to other Caribbean islands.
Terrain and Topography: Barbados is primarily a coral island contributing to its relatively flat terrain. The island gently rises into rolling hills in the central highland region, culminating in the highest point, Mount Hillaby, at an elevation of 336 meters (1,102 feet). This central highland region starkly contrasts the otherwise flat coastal areas that are more common on the island.
Geographical Size: The island extends approximately 34 kilometers (21 miles) in length and up to 23 kilometers (14 miles) in width, covering a total land area of about 430 square kilometers (166 square miles). Despite its small size, Barbados boasts a diverse landscape, including long stretches of sandy beaches, rugged cliffs, and lush, hilly interiors.
Surrounding Waters and Marine Life: The waters surrounding Barbados are part of the Atlantic Ocean, with the Caribbean Sea located to the west of the island. These waters are known for their rich marine biodiversity, including vibrant coral reefs, which are crucial for the island’s fishing industry and attract numerous tourists for snorkeling and diving.
Proximity to Other Countries: Barbados is the easternmost island in the Caribbean island chain, creating a buffer against the Atlantic Ocean for the rest of the Caribbean. Its nearest neighbors are Saint Lucia and Saint Vincent and the Grenadines to the west, with both located over 160 kilometers (100 miles) away. Further to the south, the coast of Venezuela in South America is approximately 400 kilometers (about 250 miles) away, making it one of the closest continental landmasses.
Environmental Challenges: Barbados’ geography makes it vulnerable to certain environmental challenges, particularly the effects of climate change. Rising sea levels and increased frequency of severe weather events, such as hurricanes and tropical storms, pose risks to its low-lying coastal areas. Additionally, the health of its coral reefs is a concern, as they are vital to both the ecosystem and the economy.
Impact on Economy and Culture: The geographical features of Barbados, including its beaches and coral reefs, have a significant impact on the island’s economy, particularly the tourism sector, which is a major contributor to its GDP. The flat terrain of the island also facilitates agriculture, especially sugarcane cultivation, which has historically been an important industry.
In summary, Barbados’ geography, characterized by its flat terrain, central highlands, and location in the North Atlantic Ocean, plays a pivotal role in shaping its environment, economy, and culture. The island’s position as the easternmost in the Caribbean also bestows it with unique environmental and geopolitical significance.
Resources and Land Use
The island’s natural resources include petroleum, fish, and natural gas. Land use is predominantly agricultural (32.6%), with arable land making up 25.6% of the total area, supporting crops like sugar cane and vegetables.
Population Data
Barbados has a population of approximately 303,431 as of 2023, making it one of the most densely populated countries in the eastern Caribbean. The urban population accounts for about one-third of the total.
Economic Data
The economy of Barbados is the largest in the Eastern Caribbean and is heavily dependent on the US for imports and currency strength. Tourism and financial services are key sectors, with public debt and cost of living presenting ongoing challenges.
Drinking Water Source
Access to improved drinking water is nearly universal in Barbados, with 98.8% of the population having access to such sources as of 2020.
Population, Median Age, Migration, and Citizenship
The median age in Barbados is 41 years as of 2023. A slight net outflow characterizes migration patterns, and the country recognizes dual citizenship.
Average Number of Childbirths
The total fertility rate in Barbados stands at 1.7 children born per woman as of 2023, indicating a moderate birth rate.
Is this country a Safe Destination?
Barbados is generally considered safe for tourists, with low crime rates. Visitors should nevertheless remain aware of their surroundings and take standard safety precautions.
Healthcare and Infectious Diseases
The healthcare system in Barbados is relatively well-developed, with a high physician density and adequate hospital bed capacity. The country has made significant strides in public health, though it faces challenges like chronic non-communicable diseases.
Natural Hazards
Barbados is vulnerable to natural hazards such as hurricanes, tropical storms, and periodic landslides.
The Flag and Other Symbols
The flag of Barbados consists of three vertical bands of ultramarine blue and gold, with a black trident head centered on the gold band. National symbols include Neptune’s trident, the pelican, and the Red Bird of Paradise flower.
Constitution
Barbados’ constitution, adopted in 1966 and amended in 2021, established it as a parliamentary republic and a Commonwealth realm. The transition to a republic in 2021 marked a significant constitutional change.
Legal System
The legal system of Barbados is based on English common law. There is no judicial review of legislative acts, but the country participates in international law organizations.
About the Unemployment Rate, Labor Force, and Poverty Line
The unemployment rate in Barbados was approximately 10.41% in 2021. The economy is characterized by a high dependency on tourism and the external sector, posing employment and income distribution challenges.
About the Budget and Central Government Debt
Barbados faces a significant public debt of 146.93% of GDP in 2016. Managing fiscal balance and debt sustainability is a key economic challenge for the government.
Inflation Rate and Prime Lending Rate
The inflation rate was estimated at 4.1% in 2019. The country’s currency, the Barbadian dollar, is pegged to the US dollar, influencing its lending rates and monetary policy.
Export/Import Partners and Data
The main export partners are the United States, Jamaica, and Guyana, with key exports including rums, liquors, and ships. Imports mainly come from the United States, Guyana, and China, with refined petroleum and cars being significant import items.
Renewable Energies Used
Barbados is actively pursuing renewable energy sources, with solar energy being a primary focus to reduce dependence on imported fossil fuels.
Telecommunication Data, Calling Code
The telecommunication sector in Barbados is well-developed, with a high mobile-cellular and internet penetration rate. The country’s international calling code is +1-246.
Transport Infrastructure
Barbados boasts a comprehensive transport network, including a well-developed road system and a major seaport in Bridgetown, which are crucial for its tourism-driven economy.
More Interesting Facts
Barbados is known for its vibrant culture, including music, cuisine, and the Crop Over festival. It is also home to historic Bridgetown and its Garrison, a UNESCO World Heritage Site. The island’s commitment to environmental protection and sustainable tourism is noteworthy in the Caribbean region.
Did you know?
Did you know that Barbados, a jewel in the Caribbean, is not just a picturesque island but also a land rich in history and unique features? Here are some fascinating facts about Barbados:
- Oldest Rum in the World: Barbados is considered the birthplace of rum, and it is home to Mount Gay Rum, established in 1703, which is reputed to be the oldest rum distillery in the world.
- Flying Fish: Barbados is often associated with flying fish, a species that glides over the water and is a national symbol. Flying fish is also a staple in the Bajan diet, commonly served as ‘Flying Fish and Cou-Cou,’ the national dish of Barbados.
- George Washington’s Only Trip Outside the US: The only country ever visited by George Washington, the first President of the United States, outside the continental United States was Barbados in 1751.
- A Rare Natural Phenomenon: The “Cherry Tree Hill” offers a rare natural phenomenon where the trade winds off the Atlantic Ocean sweep through the island’s east coast, causing trees to lean westward.
- Coral Island: Unlike many other volcanic Caribbean islands, Barbados is made entirely of coral. This makes for some of the finest white-sand beaches and clear, turquoise waters.
- Historic Bridgetown and Garrison: The capital city, Bridgetown, and its Garrison are designated as UNESCO World Heritage Sites, rich in colonial architecture and historical significance.
- Land of the Bearded Ones: The name ‘Barbados’ is derived from ‘Los Barbados’ (the bearded ones), which Portuguese explorers named the island in the 16th century due to the island’s fig trees, which have a beard-like appearance.
- Home to a Rare Species of Snake: Barbados is home to the rarest species of snake in the world, the Barbados Threadsnake, which is about as wide as a spaghetti noodle and shorter than a pencil.
- High Literacy Rate: Barbados boasts one of the highest literacy rates in the world, estimated to be over 98%.
- Concorde Experience: Barbados was one of the only destinations outside of Europe to receive Concorde flights regularly, and today, it houses one of the retired aircraft, which is part of the Barbados Concorde Experience for visitors.
These interesting facts about Barbados reveal the island’s rich and diverse culture, history, and natural wonders, making it a unique and enchanting destination in the Caribbean.
Many thanks for visiting and sharing this map & country information site!