Google Maps and Detailed Facts of Bermuda (BM). This page lets you explore Bermuda and its border countries (Country Location: North America, group of islands in the North Atlantic Ocean, east of South Carolina (US)) through detailed Satellite imagery – fast and easy as never before Google Maps.
Find comprehensive information about this country’s diversity below: Google Maps, geography, economy, science, people, culture, environment, government, and history – All in One Wiki page.
There is also a Street View and free Driving Directions at your service. Your Google Satellite Map Sightseeing in Bermuda starts at Driving Directions and Maps.com in North America.
About Bermuda in detail
Table of contents
- Background
- Overview
- Google Maps
- Climate
- Geography
- Resources and Land Use
- Population Data
- Economic Data
- Drinking Water Source
- Population, Median Age, Migration, and Citizenship
- Average Number of Childbirths
- Is this country a Safe Destination?
- Healthcare and Infectious Diseases
- Natural Hazards
- The Flag and Other Symbols
- Constitution
- Legal System
- About the Unemployment Rate, Labor Force, and Poverty Line
- About the Budget and Central Government Debt
- Inflation Rate and Prime Lending Rate
- Export/Import Partners and Data
- Renewable Energies Used
- Telecommunication Data, Calling Code
- Transport Infrastructure
- More Interesting Facts
Background
Bermuda, first settled in 1609 by shipwrecked English colonists headed for Virginia, is the oldest and most populous of the British overseas territories. Self-governing since 1620, Bermuda has developed a unique cultural identity. The island became a popular destination for North American tourists escaping cold winters during Victorian times. Its economy has traditionally been driven by tourism, but in recent years, international business and offshore financial services have grown in importance. A 1995 referendum on independence from the UK was soundly defeated, reflecting the island’s strong ties with Britain.
Overview
Located in North America, Bermuda is a group of islands in the North Atlantic Ocean, east of South Carolina. The territory covers a total area of 54 sq km, about one-third the size of Washington, DC. Bermuda’s climate is subtropical, mild, and humid, with frequent gales and strong winds in winter. The terrain features low hills separated by fertile depressions. With a population of 72,576 (2023 estimate), Bermuda boasts a diverse society, with a majority of African descent, followed by White, mixed, Asian, and other ethnic groups.
Official Name: Bermuda
Date of Formation: N/A
Capital: Hamilton
Population: 72,576 (2023 estimate)
Total Area: 20.8 Sq. Miles / 54 Sq. Km
Population Density: N/A
Languages: English (official), Portuguese
Religions: Protestant 46.2% (includes Anglican 15.8%, African Methodist Episcopal 8.6%, Seventh Day Adventist 6.7, Pentecostal 3.5%, Methodist 2.7%, Presbyterian 2.0%, Church of God 1.6%, Baptist 1.2%, Salvation Army 1.1%, Brethren 1.0%, other Protestant 2.0%), Roman Catholic 14.5%, Jehovah’s Witness 1.3%, other Christian 9.1%, Muslim 1%, other 3.9%, none 17.8%, unspecified 6.2% (2010 estimate)
Ethnic Origin: African descent 52%, White 31%, mixed 9%, Asian 4%, other 4% (2010 estimate)
Government: Overseas Territory of the UK with limited self-government; parliamentary democracy
Currency: Bermudian dollar (BMD)
Literacy Rate: N/A
Calorie Consumption: N/A
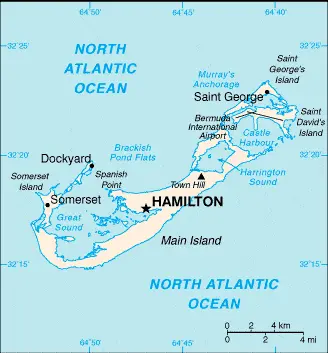
Bermuda Google Maps
Google Maps provides detailed and interactive maps of Bermuda, crucial for exploring its scenic beauty and navigating its roadways and maritime areas. Whether for tourists or residents, Google Maps is a key resource for experiencing Bermuda’s unique blend of British and American culture.
The map below shows Bermuda’s cities, towns, highways, main roads, streets, and Street Views. To find a location, use the form below, type any city or place, view a simple map, and click the “show map” button.
The Google Maps above shows Bermuda with its location: North America (geographic coordinates: 32 20 N, 64 45 W) and the international borders of Bermuda; 0 km; furthermore, its inland counties boundaries.
The map of Bermuda, North America, is for informational use only. No representation is made or warranted given any map or its content by the Driving Directions and Maps site. The user assumes all risks of using this Bermuda Google Maps and facts/wiki.
Climate
Bermuda, a picturesque archipelago located in the North Atlantic Ocean, is known for its stunning subtropical climate. This climate significantly shapes the island’s natural environment, lifestyle, and activities for both residents and visitors.
- Mild and Humid Conditions: Bermuda’s climate is generally mild and humid. The temperatures in Bermuda are moderated by the warm waters of the Gulf Stream, resulting in a climate that is neither excessively hot in summer nor too cold in winter. Average temperatures range from around 18°C to 24°C (64°F to 75°F) in the winter months (December to March) and 25°C to 30°C (77°F to 86°F) in the summer months (April to November).
- Winter Winds and Gales: During winter, Bermuda experiences strong winds and occasional gales, predominantly from the northwest. These winds can influence sea conditions, making them rougher, which is particularly relevant for marine activities and transportation.
- Rainfall Patterns: Bermuda receives ample rainfall throughout the year, with no distinct dry season. The average annual rainfall is approximately 1,500 millimeters (59 inches). Rain tends to be fairly evenly distributed throughout the year, although the summer months can occasionally see heavier showers and thunderstorms.
- Hurricane Season: Bermuda lies within the Atlantic hurricane belt, and thus, the island can be affected by hurricanes and tropical storms, particularly between June and November. While direct hits are rare, the proximity of these systems can result in high winds and heavy rainfall. Bermuda’s infrastructure, however, is notably well-prepared for such weather events, with stringent building codes and effective disaster preparedness strategies.
- Influence on Flora and Fauna: The subtropical climate of Bermuda contributes to a rich and diverse range of flora and fauna. The island is famous for its lush, verdant landscapes and vibrant gardens. Bermuda’s cedar, an endemic species, is a key component of the local ecosystem. The mild climate also allows for various exotic plants, originally imported, to thrive.
- Impact on Lifestyle and Activities: The climate plays a vital role in Bermudians’ lifestyle and visitors’ experiences. Outdoor activities such as golf, tennis, cricket, and water sports like sailing, snorkeling, and diving are popular and can be enjoyed for most of the year. The mild winters make Bermuda an attractive destination for tourists seeking a warm, but not excessively hot, climate.
- Environmental Concerns: Climate change poses a significant threat to Bermuda, as rising sea levels and increased intensity of hurricanes can have profound impacts on the island’s geography and ecosystems. Sustainability and environmental protection efforts are key priorities for the local government and communities.
In summary, Bermuda’s subtropical climate, characterized by mild temperatures, humidity, and ample rainfall, is crucial in defining the island’s natural beauty, biodiversity, and way of life. While the climate offers ideal conditions for various outdoor activities and supports a rich natural environment, the island also faces challenges such as hurricane threats and the long-term impacts of climate change.
Geography
Bermuda’s unique geographical features, comprising approximately 138 coral islands and islets, create a distinctive and picturesque landscape that plays a significant role in the island’s ecosystem and lifestyle.
- Archipelago Structure and Formation: Bermuda is not a single island but an archipelago, primarily formed from volcanic activity and shaped significantly by coral growth. These coral islands are the visible parts of an underwater plateau rising up from the ocean floor. The islands are connected by bridges and causeways, creating a network facilitating movement across the archipelago.
- Lack of Freshwater Sources: One of Bermuda’s most notable geographic features is the complete absence of rivers or freshwater lakes. This fact significantly influences how the island manages its water resources. The highest point, Town Hill, stands at just 79 meters (259 feet) above sea level, offering little in terms of natural freshwater collection.
- Water Collection and Conservation: Bermuda relies heavily on rainfall for its water supply due to the lack of natural freshwater sources. The ample rainfall the island receives is critical for meeting the water needs of its population. Historically and even today, Bermudians collect rainwater through rooftop catchments, which leads to storage tanks. This water collection and conservation method is a distinctive feature of Bermudian architecture and lifestyle.
- Coral Reefs and Marine Biodiversity: The surrounding coral reefs are integral to Bermuda’s geography. These reefs add to the island’s natural beauty and play a vital role in protecting the shoreline from erosion and providing habitats for diverse marine life. Bermuda’s coral reefs are among the northernmost in the Atlantic Ocean and are renowned for their health and biodiversity.
- Climate Influence: Bermuda’s subtropical climate influences its geographical features. The warm temperatures and ample rainfall support a lush, green landscape and have led to the development of unique ecosystems on land and in the surrounding waters.
- Isolation and Nearest Landmasses: Bermuda is notably isolated in terms of geography. It is located in the North Atlantic Ocean, approximately 1,030 kilometers (640 miles) east-southeast of Cape Hatteras, North Carolina, USA, and about 1,550 kilometers (960 miles) northeast of Miami, Florida. The closest landmass is the Cape Hatteras area of the Outer Banks of the United States, making Bermuda one of the most isolated inhabited islands in the world.
- Environmental Concerns and Conservation: Bermuda’s unique geography brings with it specific environmental concerns. The lack of natural freshwater resources, the vulnerability of coral reefs to climate change and human activity, and the challenges of waste management on a small island are ongoing issues. Conservation efforts are critical to preserving Bermuda’s natural beauty and ecological health.
In summary, Bermuda’s geography, characterized by its coral islands and islets, lack of freshwater sources, and reliance on rainfall for water supply, shape its environment and way of life. The surrounding coral reefs contribute significantly to Bermuda’s marine biodiversity and play a crucial role in protecting the island’s shores. Bermuda’s isolated location in the North Atlantic Ocean adds to its uniqueness as a geographic entity. The island’s unique challenges, such as water resource management and environmental conservation, are pivotal to its geographical identity.
Resources and Land Use
Bermuda’s natural resources are limited to limestone and its pleasant climate, which fosters tourism. Land use is predominantly for agriculture (14.8%) and forests (20%). The absence of significant natural resources has led Bermuda to develop a strong service-oriented economy.
Population Data
With a population of 72,576 in 2023, Bermuda has a relatively even population distribution. The entire population is urbanized, with significant concentrations in Hamilton, the capital city.
Economic Data
Bermuda’s economy is primarily driven by international business and tourism, with a growing importance in offshore banking. Its GDP (PPP) was $5.127 billion in 2021, and the economy is known for its high GDP per capita, indicating a high standard of living.
Drinking Water Source
Nearly 100% of Bermuda’s urban population has access to improved drinking water sources, a testament to the island’s developed infrastructure and commitment to public health.
Population, Median Age, Migration, and Citizenship
The median age in Bermuda is 43.7 years. The net migration rate is 1.4 migrants/1,000 population, reflecting a stable population with moderate migration.
Average Number of Childbirths
The total fertility rate in Bermuda is 1.89 children born per woman, aligning with trends in developed nations where birth rates are relatively low.
Is this country a Safe Destination?
Bermuda is generally a safe destination for travelers. The main natural hazard is hurricanes, which occur from June to November.
Healthcare and Infectious Diseases
Bermuda has a well-developed healthcare system, though data on healthcare expenditures and physician density are unavailable. The island’s isolation and developed public health infrastructure help manage infectious diseases effectively.
Natural Hazards
Hurricanes are the primary natural hazard in Bermuda, particularly from June to November. The island’s infrastructure is designed to withstand hurricane impacts.
The Flag and Other Symbols
Bermuda’s flag is red, with the UK flag in the upper quadrant and the Bermudian coat of arms. The coat of arms features a red lion and a depiction of the shipwreck of the Sea Venture in 1609, an event central to Bermuda’s history.
Constitution
Bermuda’s constitution, dating back to 1684 with the latest version from 1968, provides the legal framework for its status as a British Overseas Territory with limited self-government.
Legal System
Bermuda follows the English common law system. It participates in various international legal organizations but has not declared jurisdiction for the International Court of Justice.
About the Unemployment Rate, Labor Force, and Poverty Line
The unemployment rate in Bermuda was 7% as of 2017. About 11% of the population lived below the poverty line in 2008, indicating challenges in income distribution.
About the Budget and Central Government Debt
Bermuda’s budget had revenues of $999.2 million and expenditures of $1.176 billion in 2017, leading to a budget deficit. Managing this deficit is crucial for maintaining fiscal stability.
Inflation Rate and Prime Lending Rate
The inflation rate was 1.9% in 2017. Bermuda’s economy, heavily reliant on services, particularly financial services and tourism, requires careful inflation and lending rates management.
Export/Import Partners and Data
Bermuda’s main export partners include Jamaica and Luxembourg, with primary exports being recreational boats and ships. Major imports, including ships and refined petroleum, come from the United States, South Korea, and Germany.
Renewable Energies Used
Bermuda’s electricity generation is entirely from fossil fuels. No significant use of renewable energy sources indicates an area for potential development.
Telecommunication Data, Calling Code
Bermuda has a developed telecommunications system with high teledensity. The country code is +1-441. The focus remains on improving LTE coverage rather than investing in 5G.
Transport Infrastructure
Bermuda’s transport infrastructure includes a well-maintained network of roads and a single airport with a paved runway. The island relies heavily on marine transport, with several major seaports.
More Interesting Facts
Bermuda, a small archipelago with a rich history and unique natural features, holds a trove of fascinating facts that many may not know. Here are some intriguing “Did you know” facts about Bermuda:
Did you know?
- Bermuda Triangle: Did you know that Bermuda is one corner of the infamous Bermuda Triangle? This loosely defined region in the North Atlantic Ocean is famous for the mysterious disappearances of ships and aircraft. While largely considered a product of folklore and sensationalist writing, it has captured the public imagination for decades.
- Named After a Spanish Explorer: Bermuda was named after Juan de Bermúdez, a Spanish explorer who first sighted the uninhabited islands in 1505. Despite its discovery, Bermuda was not immediately colonized due to its lack of gold and the perceived danger of its surrounding reefs.
- The Oldest British Overseas Territory: Bermuda is the oldest and most populous remaining British Overseas Territory. English settlement began in Bermuda when the Sea Venture shipwrecked on the islands in 1609. The survivors stayed and established a colony.
- Pink Sand Beaches: One of Bermuda’s most famous natural attractions is its pink sand beaches. The pink hue comes from tiny red organisms that live in the coral reef and mix with the white sand and crushed coral.
- Bermuda Shorts: Bermuda is known for popularizing ‘Bermuda shorts,’ a form of short trousers that end about 1 inch above the knee. They are considered formal in Bermuda and often worn with a jacket and tie.
- A Significant Role in World War II: During World War II, Bermuda was a significant base for the Royal Navy and the Royal Air Force. The island was also a rendezvous point for trans-Atlantic convoys.
- No Rivers or Lakes: Interestingly, Bermuda has no rivers or freshwater lakes. Residents rely on rainwater collected on their roofs and stored in tanks for their freshwater supply, supplemented by desalination plants.
- A Hub for Offshore Finance: Bermuda is a tourist destination and one of the world’s largest offshore finance centers, known for its insurance and reinsurance industries.
- Bermuda Onion: In the 19th century, Bermuda was famous for exporting Bermuda onions, often called “onions” in the United States. They were a significant agricultural product until after World War I when competition from the American South and Texas reduced their profitability.
- Unique Wildlife: The Bermuda petrel, or “Cahow,” a bird thought to be extinct for over 300 years, was rediscovered in 1951. This rediscovery is one of the great “Lazarus” stories of ornithology and a symbol of hope for conservationists.
These facts about Bermuda highlight its intriguing blend of natural beauty, cultural heritage, and economic significance. From its role in maritime lore to its distinct fashion contributions, Bermuda remains an island full of surprises and unique characteristics.
Many thanks for visiting and sharing this map & country information site!