Google Maps and Detailed Facts of Burkina Faso (BF). This page lets you explore Burkina Faso and its border countries (Country Location: Western Africa, north of Ghana) through detailed Satellite imagery – fast and easy as never before Google Maps.
Find comprehensive information about this country’s diversity below: Google Maps, geography, economy, science, people, culture, environment, government, and history – All in One Wiki page.
There is also a Street View and free Driving Directions at your service. Your Google Satellite Map Sightseeing in Burkina Faso, Africa, starts here at Driving Directions and Maps.com.
About Burkina Faso in detail
| Borderline map of Burkina Faso | Location map of Burkina Faso | Flag of Burkina Faso |
|---|---|---|
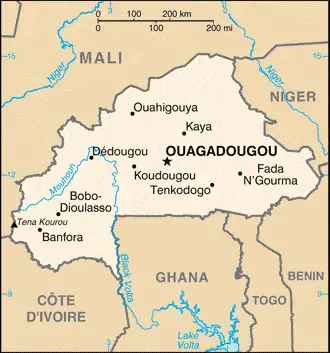 |  |  |
Table of contents
- Background
- Overview
- Google Maps
- Climate
- Geography
- Resources and Land Use
- Population Data
- Economic Data
- Drinking Water Source
- Population, Median Age, Migration, and Citizenship
- Average Number of Childbirths
- Is this country a Safe Destination?
- Healthcare and Infectious Diseases
- Natural Hazards
- The Flag and Other Symbols
- Constitution
- Legal System
- About the Unemployment Rate, Labor Force, and Poverty Line
- About the Budget and Central Government Debt
- Inflation Rate and Prime Lending Rate
- Export/Import Partners and Data
- Renewable Energies Used
- Telecommunication Data, Calling Code
- Transport Infrastructure
- More Interesting Facts
Background
Burkina Faso’s diverse ethnic composition stems from several groups arriving between the 12th and 15th centuries, including the Gurma and Mossi peoples. The Mossi kingdoms, notably Ouagadougou and Yatenga, were significant regional powers. The late 19th century saw European competition for control, with France eventually establishing a protectorate. Independence was achieved in 1960, and the country’s name changed to Burkina Faso in 1984. A history of military coups and political instability followed, with recent challenges including terrorist attacks and internal displacement.
Overview
Burkina Faso is a country in West Africa that has a complex history. Many ethnic groups in Burkina Faso arrived in the region between the 12th and 15th centuries. The Gurma and Mossi peoples established powerful kingdoms, with the Mossi kingdoms of Ouagadougou and Yatenga being the most significant. In the late 19th century, European states, notably France, vied for regional control. Eventually, France conquered Burkina Faso and established it as a French protectorate. However, the country gained independence from France in 1960 and changed its name to Burkina Faso in 1984. Following independence, Burkina Faso experienced a turbulent political landscape with several military coups. In 1987, Blaise Compaoré ousted the former president, established his government, and ruled for 27 years. In 2014, protests against Compaoré’s attempts to amend the constitution led to his resignation. An interim administration supervised a transition period, which culminated in the election of Roch Marc Christian Kaboré as president in 2015. However, instability continued in Burkina Faso. In 2022, the country witnessed two military coups. First, Colonel Paul Henri Damiba overthrew President Kaboré in January 2022, and then Army Captain Ibrahim Traoré deposed Damiba in September of the same year, becoming the transition president. The transition government initially planned to hold democratic elections by July 2024 but might face delays due to security concerns. Burkina Faso has also been plagued by terrorist groups affiliated with Al-Qaeda and the Islamic State since 2016. These groups have carried out attacks, particularly in the capital city. By early 2023, the insecurity caused by terrorism had resulted in the displacement of over 2 million people and increased humanitarian needs and food insecurity. Moreover, Burkina Faso grapples with other challenges, including a high population growth rate, recurring droughts, widespread food insecurity, and limited natural resources. As a result, it is considered one of the world’s poorest countries.
Official Name: Burkina Faso
Capital: Ouagadougou
Population: 22,489,126 (2023 estimate)
Total Area: 274,200 sq km
Languages: Mossi, Fula, Gourmantche, Dyula, French (official)
Religions: Muslim 63.8%, Roman Catholic 20.1%, Animist 9%, Protestant 6.2%
Ethnic Groups: Mossi 52%, Fulani (Peuhl) 8.4%, Gurma 7%, Bobo 4.9%
Government: Presidential republic
GDP (Purchasing Power Parity): $48.175 billion (2021 estimate)
Burkina Faso Google Maps
Burkina Faso, located in Western Africa, is landlocked and shares borders with six countries. Google Maps offers an insightful view of its varied landscapes, from the Sahel region in the north to more fertile areas in the south. This platform easily explores key cities like the capital, Ouagadougou, and Bobo-Dioulasso.
Burkina Faso was known as Upper Volta until 1984. It became a multiparty state in 1991, though former military ruler Blaise Compaoré remains in power. The Sahara covers the north of the country. The south is largely savanna. The three main rivers are the Black, White, and Red Voltas.
The map below shows Burkina Faso’s cities, towns, highways, main roads, streets, and Street Views. To find a location, use the form below, type any city or place, view a simple map, and click the “show map” button.
The Google Maps above shows Burkina Faso’s location: Africa (geographic coordinates: 13 00 N, 2 00 W) and the international borders of Burkina Faso; total: 3,611 km. Border countries (total: 6): Benin 386 km, Cote d’Ivoire 545 km, Ghana 602 km, Mali 1,325 km, Niger 622 km, Togo 131 km; furthermore, it’s inland counties boundaries.
The map of Burkina Faso, Africa, is for informational use only. No representation is made or warrantied given any map or content by the Driving Directions and Maps site. The user assumes all risks of using this Burkina Faso Google Maps and facts/wiki.
Climate
Burkina Faso’s climate, characterized by its variation across different zones, significantly shapes the country’s agriculture, population distribution, and economy. Let’s delve into the details of each climate zone and their implications:
Tropical Savanna in the South:
- This region experiences a tropical savanna climate with distinct wet and dry seasons.
- The rainy season typically runs from May to October, with annual rainfall ranging from 900 to 1,200 mm.
- The south is the most agriculturally productive region of Burkina Faso, supporting crops like sorghum, millet, maize, peanuts, and cotton.
- The availability of water and fertile soil also supports denser population settlements in this area.
Semi-Arid Sahel Region in the North:
- The Sahel region is characterized by a semi-arid climate, with a shorter rainy season and less frequent precipitation than the south.
- Rainfall in the Sahel varies from 300 to 600 mm annually and is highly variable, often leading to drought conditions.
- This region is predominantly used for pastoralism and some rain-fed agriculture, with crops like millet and sorghum being cultivated.
- The harsher climate conditions in the Sahel contribute to lower population densities and greater challenges in sustaining livelihoods.
Hot Desert Area in the Far North:
- Far north of Burkina Faso borders the Sahara Desert, which features a hot desert climate.
- This area receives less than 250 mm of rainfall annually, making it one of the least hospitable regions for agriculture and human settlements.
- The extreme temperatures and water scarcity limit economic activities to mostly nomadic pastoralism.
Impact on Economy and Agriculture:
- Agriculture is the backbone of Burkina Faso’s economy, employing a significant portion of the population. The varying climatic zones influence the types of crops that can be grown and the agricultural practices employed.
- Climate variability, especially in the Sahel region, poses challenges such as droughts, leading to food insecurity and impacting the economy.
Climate Change Implications:
- Burkina Faso is increasingly vulnerable to the effects of climate change, with rising temperatures and changing rainfall patterns exacerbating water availability, agriculture, and food security challenges.
- The Sahel region, in particular, faces the threat of desertification, which could impact livelihoods and lead to migration.
Biodiversity and Ecosystems:
- The different climatic zones support a variety of ecosystems and biodiversity. The southern savanna zone is home to a range of flora and fauna, while the Sahel and desert regions have adapted species that can withstand more arid conditions.
Water Resources:
- The availability and management of water resources are critical issues, particularly in the Sahel and desert regions. Seasonal rivers and underground aquifers are vital for sustaining both human populations and agriculture.
Burkina Faso’s climatic zones, ranging from tropical savanna to the semi-arid Sahel and a hot desert area, significantly influence the country’s agricultural practices, population distribution, and overall economic activities. The varying climate also poses challenges that are intensified by the ongoing impacts of climate change, particularly regarding water availability and agricultural productivity.
Geography
Burkina Faso’s geography is characterized by its varied terrain and ecological zones, reflecting the transition from the Sahara Desert in the north to the more verdant regions in the south. Here’s an extended look at the country’s geographical features, along with information on its neighboring countries:
- Plateau and Plains: Much of Burkina Faso is situated on a vast plateau, which is generally flat but includes areas of dissected, undulating plains. The average elevation of the plateau is around 200-300 meters above sea level.
- Hilly Regions: The west and southeast of the country are more hilly. The Banfora Hills in the southwest are particularly notable. These regions provide a contrast to the otherwise predominantly flat terrain of the country.
- Ecological Transition: There is a clear ecological transition from north to south. The northern part of the country, closer to the Sahara, consists of a grassy savanna, which gradually changes into more dense vegetation and sparse forests in the south. The varying climate across the country influences this transition.
- Major Rivers: Burkina Faso is a landlocked country with several significant rivers. The Mouhoun (Black Volta), Nakambé (White Volta), and Nazinon (Red Volta) are the main rivers contributing to the country’s agriculture and are vital for irrigation and fishing.
- Natural Resources: The country has various natural resources, including gold, manganese, limestone, marble, phosphates, pumice, and salt. However, limited rainfall and water supply are challenges for agriculture, which is a major part of the economy.
- Surrounding Countries:
- Mali to the north and west,
- Niger to the east,
- Benin to the southeast,
- Togo and Ghana to the south,
- Côte d’Ivoire to the southwest.
- Agricultural Land: Most of Burkina Faso’s population relies on subsistence agriculture. The most fertile areas are in the south and west, where rainfall is more abundant.
- Climate Impact on Geography: The varying climate across Burkina Faso, from semi-arid in the north to more humid in the south, directly impacts its geographical features, influencing soil types, vegetation, and the ability to engage in different types of agriculture.
- Environmental Challenges: The country faces environmental challenges, including desertification, soil degradation, and deforestation. These issues are exacerbated by overgrazing, over-farming, and deforestation.
- Biodiversity and Protected Areas: Burkina Faso has several national parks and reserves, such as W National Park (part of a transnational park shared with Benin and Niger) and Arly National Park. These areas are crucial for preserving the country’s biodiversity, including various species of mammals, birds, and plants.
In summary, Burkina Faso’s geography, characterized by its plateau, plains, hills, and ecological diversity, shapes the livelihoods of its population and the country’s economic activities. The geographic diversity from north to south, along with climate and environmental management challenges, plays a significant role in the nation’s development and sustainability efforts.
Resources and Land Use
Key natural resources include gold, manganese, zinc, and limestone. Agricultural land constitutes 44.2% of the land use, focused on crops like sorghum, maize, millet, and cotton.
Population Data
Most of the population is concentrated in the center and south, with about one-third living in cities. Ouagadougou, the capital, is the largest city with a population of 1.8 million.
Economic Data
Burkina Faso’s economy is primarily agricultural and low-income, with widespread poverty. Key industries include cotton lint, beverages, and gold mining.
Drinking Water Source
Improved drinking water sources are available to 78.5% of the population, with a higher accessibility rate in urban areas (94.7%) compared to rural areas (71.3%).
Population, Median Age, Migration, and Citizenship
The median age is 18.5 years. The country experiences net migration of -0.6 migrants/1,000 population, indicating more people leaving than entering.
Average Number of Childbirths
The total fertility rate is high at 4.14 children born/woman.
Is this country a Safe Destination?
Burkina Faso faces security challenges due to terrorist activities. Travelers are advised to exercise caution, especially in areas prone to attacks.
Healthcare and Infectious Diseases
Healthcare facilities are limited, with common diseases including malaria, dengue fever, and hepatitis A.
Natural Hazards
The country is prone to recurring droughts, impacting agriculture and living conditions.
The Flag and Other Symbols
The flag has two horizontal bands of red and green with a yellow star in the center. National symbols include the white stallion and the colors red, yellow, and green.
Constitution
The constitution, adopted in 1991, has undergone several amendments. A transition charter was adopted in March 2022, allowing military authorities to rule for three years.
Legal System
Burkina Faso’s legal system combines civil law based on the French model and customary law.
About the Unemployment Rate, Labor Force, and Poverty Line
The unemployment rate is estimated at 4.76%. However, 41.4% of the population lives below the poverty line.
About the Budget and Central Government Debt
Public debt is 72.53% of GDP (2020 est.), with the government focusing on managing expenditures and revenues.
Inflation Rate and Prime Lending Rate
The inflation rate is 3.65% (2021 est.), indicative of the country’s economic situation.
Export/Import Partners and Data
Key exports include gold and cotton, primarily to Switzerland and India. Major imports from Cote d’Ivoire and China include refined petroleum and delivery trucks.
Renewable Energies Used
Renewable energy sources are limited, with a focus on expanding solar energy capacity.
Telecommunication Data, Calling Code
The country’s telecommunications infrastructure is developing, focusing on increasing mobile cellular subscriptions and internet access. The country code is +226.
Transport Infrastructure
Transport infrastructure includes a network of roads, with a total of 15,304 km, and railways extending 622 km.
More Interesting Facts
Burkina Faso is known for its vibrant cultural festivals, rich musical heritage, and diverse ethnic groups. The country also faces challenges related to food insecurity and internal displacement due to ongoing conflicts and environmental issues.
Did You Know?
- Name Meaning: “Burkina Faso” translates to “Land of Honest Men” or “Land of Upright People.” The name was adopted in 1984, reflecting the country’s pride in integrity and values.
- Cultural Diversity: Burkina Faso is home to over 60 different ethnic groups, each with its own language and culture. The Mossi is the largest ethnic group, making up about half of the population.
- Famous for Music and Film: The country hosts one of Africa’s most important film festivals, FESPACO (Panafrican Film and Television Festival of Ouagadougou), held every two years in the capital, Ouagadougou. Burkina Faso is also known for its vibrant music scene, blending traditional and modern styles.
- Unique Geography: Despite being landlocked, Burkina Faso features significant natural beauty, including the Sindou Peaks – remarkable rock formations created by wind erosion over centuries.
- Agricultural Society: Agriculture is a key part of life in Burkina Faso, with most of the population engaged in subsistence farming. The country is one of the world’s largest cotton producers.
- Mask Festivals: Traditional masks are important to Burkina Faso’s cultural heritage, especially among the Bwa and Nuna communities. Elaborate mask festivals featuring dancing and rituals are significant cultural attractions.
- Rich Handicraft Tradition: The country is renowned for its art and handicrafts, particularly in areas like weaving, bronze casting, and wood carving. The market in Ouagadougou is famous for its range of artisanal products.
- Unique Architecture: Burkina Faso is noted for its distinctive mud-brick architecture, particularly in the Kassena village of Tiébélé. These houses are decorated with intricate geometric patterns.
- Important Bird Area: Burkina Faso has several Important Bird Areas (IBAs) that are designated for the conservation of bird populations. These areas are vital for protecting numerous species, including some that are globally threatened.
- Environmental Initiatives: The country has been involved in innovative environmental projects, including reforestation and the use of sustainable farming techniques to combat desertification and soil degradation.
These intriguing facts about Burkina Faso reveal its rich cultural tapestry, diverse natural landscapes, and commitment to environmental and cultural preservation, making it a unique and fascinating country in West Africa.
Many thanks for visiting and sharing this map & country information site!
