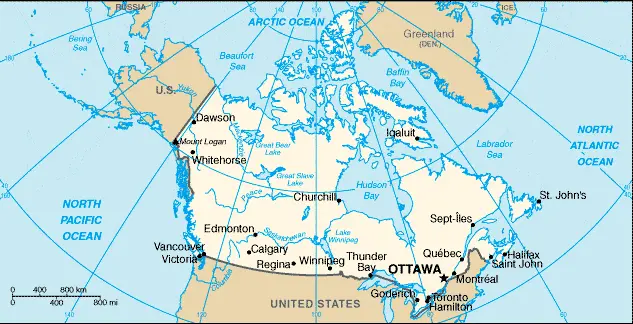
Google Maps and Detailed Facts of Canada (CA). This page lets you explore Canada and its border countries (Country Location: Northern North America, bordering the North Atlantic Ocean on the east, North Pacific Ocean on the west, and the Arctic Ocean on the north, north of the conterminous US) through detailed Satellite imagery – fast and easy as never before Google Maps.
Find comprehensive information about this country’s diversity below: Google Maps, geography, economy, science, people, culture, environment, government, and history – All in One Wiki page.
There is also a Street View and free Driving Directions at your service. Your Google Satellite Map Sightseeing in Canada in North America, starts here at Driving Directions and Maps.com.
About Canada in detail
Table of contents
- Background
- Overview
- Google Maps
- Climate
- Geography
- Resources and Land Use
- Population Data
- Economic Data
- Drinking Water Source
- Population, Median Age, Migration, and Citizenship
- Average Number of Childbirths
- Is this country a Safe Destination?
- Healthcare and Infectious Diseases
- Natural Hazards
- The Flag and Other Symbols
- Constitution
- Legal System
- About the Unemployment Rate, Labor Force, and Poverty Line
- About the Budget and Central Government Debt
- Inflation Rate and Prime Lending Rate
- Export/Import Partners and Data
- Renewable Energies Used
- Telecommunication Data, Calling Code
- Transport Infrastructure
- More Interesting Facts
Background
Canada, a nation known for its vast distances and rich natural resources, evolved into a self-governing dominion in 1867 while maintaining ties to the British crown. Gaining legislative independence from Britain in 1931 and constitutional independence with the Canada Act in 1982, Canada has developed in parallel with the US. It faces challenges in improving public services like healthcare and education and responding to Quebec’s francophone concerns. Additionally, Canada focuses on developing its diverse energy resources while committing to environmental conservation.
Overview
Located in Northern North America, Canada is the world’s second-largest country by total area. It’s a federal parliamentary democracy under a constitutional monarchy and a Commonwealth realm. The country is known for its multicultural society and robust economy, driven by industries like transportation equipment, chemicals, minerals, and forestry products.
Official Name: Canada
Date of Formation: Became a self-governing dominion in 1867
Capital: Ottawa
Population: Approximately 38.52 million (2023 estimate)
Total Area: 9,984,670 square kilometers (3,854,083 square miles)
Population Density: N/A
Languages: English and French (official), along with several Indigenous languages
Religions: Diverse, including Christianity, Islam, Hinduism, Sikhism, Buddhism, and others
Ethnic Origin: A mix of Indigenous peoples and various immigrant groups
Government: Federal parliamentary democracy under a constitutional monarchy
Currency: Canadian Dollar (CAD)
Literacy Rate: N/A
Calorie Consumption: N/A
Canada Google Maps
Google Maps is a useful tool for navigating Canada’s extensive landscapes, ranging from the Atlantic Ocean in the east to the Pacific and Arctic Oceans in the north and west. It helps explore Canada’s major cities, vast wilderness, and diverse ecosystems.
Canada extends from the Arctic to its US border along the 49th parallel. Unified under British rule from 1763, its development and expansion attracted large-scale immigration. The world’s second-largest country, stretching north to Cape Colombia on Ellesmere Island, south to Lake Erie, and across five time zones from the Pacific seaboard to Newfoundland. Arctic tundra and islands in the far north give way southward to forests, interspersed with lakes and rivers, and then the vast Canadian Shield, which covers over half the area of Canada. The Rocky Mountains in the west, beyond which are the Coast Mountains, islands, and fjords. Fertile lowlands in the east.
The map below shows Canada’s cities, towns, highways, main roads, streets, and Street Views. To find a location, use the form below, type any city or place, view a simple map, and click the “show map” button.
The Google Maps above shows Canada with its location: North America (geographic coordinates: 60 00 N, 95 00 W) and the international borders of Canada; total: 8,893 km. Border countries (total: 1): United States 8,893 km (includes 2,477 km with Alaska). Note: Canada is the world’s largest country that borders only one country: The United States of America.
The map of Canada and North America is for informational use only. No representation is made or warrantied given any map or its content by Driving Directions and Maps site. The user assumes all risks of using this Canada Google Maps and facts/wiki.
Climate
Canada’s climatic diversity is as vast as its geography, encompassing a range from temperate in the south to subarctic and arctic in the north. Each region presents unique weather patterns and climatic characteristics:
- Temperate Climate in the South: This region, including southern Ontario, Quebec, and the Atlantic provinces, typically experiences four distinct seasons. Summers are warm, with temperatures often reaching up to 30°C (86°F), particularly in the interior areas, while winters are cold and snowy, with temperatures often dropping below freezing. The Great Lakes and Atlantic Ocean influence the climate, leading to moderate temperatures and higher humidity levels.
- Prairie Climate: The central provinces, primarily Saskatchewan, Manitoba, and parts of Alberta, experience a continental climate. Here, temperature extremes are more pronounced. Winters are very cold, with temperatures often plummeting to -20 °C (- 4°F) or lower, accompanied by heavy snowfall. Summers, conversely, can be very hot, with temperatures occasionally exceeding 35°C (95°F). This region is also known for its dramatic thunderstorms and tornadoes in the summer.
- West Coast Climate: British Columbia’s coastal areas, particularly Vancouver and Victoria, enjoy the mildest climate in Canada. Influenced by the Pacific Ocean, this region rarely sees extreme temperatures. Winters are generally wet and mild, with snow being a rarity in lower elevations, while summers are relatively dry and pleasant, with temperatures rarely exceeding 25°C (77°F).
- Subarctic and Arctic Climate: Northern regions of Canada, including the Yukon, Northwest Territories, and Nunavut, experience long, extremely cold winters with limited daylight hours and short, cool summers. In the high Arctic, temperatures can plummet to -40 °C (- 40°F) in winter. The phenomenon of the “Midnight Sun” (where the sun is visible at midnight during the summer) and “Polar Night” (when the sun does not rise during the winter) are observed in these regions.
- Mountainous Climate: The Rocky Mountains and other ranges exhibit an alpine climate. Here, weather can change rapidly, and temperatures vary significantly with altitude. Winters are snowy and cold, making it a popular destination for skiing and winter sports.
The climatic variation across Canada has significant implications for its natural environment, agriculture, and daily life. For instance, the lengthy growing season in the south supports a variety of crops, while the colder northern climates limit agricultural activities but are critical for Canada’s extensive forestry industry. The diverse weather conditions also contribute to Canada’s rich biodiversity, from temperate rainforests in British Columbia to tundra in the Arctic.
Geography
Canada’s geography is remarkably diverse, encompassing a vast array of landscapes, each with its distinct features and statistics:
- Plains: The Canadian Prairies, stretching across Manitoba, Saskatchewan, and Alberta, are characterized by their vast, flat landscapes. These plains are among the world’s most fertile agricultural lands, producing a significant portion of Canada’s grains and oilseeds. The prairies also house important oil and natural gas fields, particularly in Alberta.
- Mountains: The western part of Canada is dominated by the Rocky Mountains and other ranges such as the Coast Mountains, the Columbia Mountains, and the Cassiar Mountains. The Canadian Rockies stretch over 1,200 kilometers (745 miles) from the northern tip of British Columbia to the southern border with the United States. They are renowned for their stunning natural parks like Banff and Jasper. Besides Mount Logan (5,959 meters or 19,551 feet, the highest peak in Canada), other significant peaks include Mount Saint Elias (5,489 meters or 18,009 feet) and Mount Lucania (5,226 meters or 17,146 feet).
- Lowlands: The southeastern regions, particularly along the Great Lakes and the Saint Lawrence River, are characterized by lower land elevations. The Great Lakes-St. Lawrence Lowlands are the smallest but most populous of the landform regions in Canada, housing major cities like Toronto and Montreal. This area is characterized by rich soil and a relatively mild climate, making it Canada’s primary agricultural region.
- Coastline: Canada has the world’s longest coastline, stretching over 202,080 kilometers (125,567 miles). It borders three major oceans: the Atlantic Ocean to the east, the Pacific Ocean to the west, and the Arctic Ocean to the north. This extensive coastline is home to many marine ecosystems and is vital for Canada’s fishing industry.
- Surrounding Countries: Canada shares the world’s longest undefended border with the United States to the south and the northwest, spanning 8,891 kilometers (5,525 miles), including the border with Alaska. It also shares maritime borders with Greenland (an autonomous territory of Denmark) to the northeast and France’s overseas collectivity of Saint Pierre and Miquelon to the east.
- Other Geographical Features: Canada is also home to over 2 million lakes, covering approximately 7.6% of its landmass. These include some of the largest freshwater lakes in the world, such as the Great Lakes and Lake Winnipeg. The country also features several major river systems, such as the Mackenzie, the Yukon, and the Saint Lawrence River.
This geographical diversity contributes to Canada’s unique environment, supporting many ecosystems, from temperate rainforests on the west coast to the Arctic tundra in the north. It also plays a crucial role in Canada’s economy, influencing agriculture, forestry, mining, and tourism industries.
Resources and Land Use
The country is endowed with natural resources like bauxite, iron ore, nickel, zinc, copper, gold, lead, uranium, rare earth elements, molybdenum, potash, diamonds, silver, fish, timber, wildlife, coal, petroleum, natural gas, and hydropower.
Population Data
As of 2023, Canada’s population is approximately 38.52 million, with a majority living within 300 km of the southern border with the United States.
Economic Data
Canada’s real GDP is $1.832 trillion (2021 estimate), reflecting a growth rate of 4.54% in 2021. The economy is highly diversified, with key sectors including transportation equipment, chemicals, minerals, and forestry products.
Drinking Water Source
Approximately 99.2% of Canadians have access to improved drinking water sources.
Population, Median Age, Migration, and Citizenship
The median age in Canada is 42.4 years. The country has a net migration rate of 5.4 migrants/1,000 population (estimated for 2023).
Average Number of Childbirths
The total fertility rate in Canada is 1.57 children born per woman (estimated for 2023).
Is this country a Safe Destination?
Canada is generally considered safe, with relatively low crime rates and a well-established law enforcement system.
Healthcare and Infectious Diseases
Canada spends 12.9% of its GDP on healthcare (2020 estimate) and has a physician density of 2.44 physicians/1,000 population (2019).
Natural Hazards
Canada faces natural hazards like permafrost in the north, cyclonic storms east of the Rocky Mountains, and occasional volcanic activity in Western Canada’s Coast Mountains.
The Flag and Other Symbols
Canada’s flag is red with a white square and a red maple leaf in the center. The national symbols are the maple leaf and the beaver.
Constitution
Canada’s constitution consists of unwritten and written acts, customs, judicial decisions, and traditions dating from 1763. The latest constitutional amendment was in 2011.
Legal System
Canada’s legal system is a common law system, except in Quebec, where civil law based on the French civil code prevails.
About the Unemployment Rate, Labor Force, and Poverty Line
The unemployment rate was 7.51% in 2021, and approximately 9.4% of the population lived below the poverty line in 2008.
About the Budget and Central Government Debt
Canada’s public debt was 72.09% of GDP in 2020, with budget revenues of $686.718 billion and expenditures of $861.955 billion in 2020.
Inflation Rate and Prime Lending Rate
The inflation rate in Canada was 3.4% in 2021.
Export/Import Partners and Data
The United States is Canada’s primary export partner, constituting 73% of exports in 2019. Major exports include crude petroleum, cars, and natural gas. Imports mainly come from the United States, China, and Mexico.
Renewable Energies Used
Canada increasingly utilizes renewable energy sources, including hydroelectricity, wind, and solar power.
Telecommunication Data, Calling Code
Canada has an advanced telecommunications system with a country code of +1. It has made significant advancements in 5G technologies.
Transport Infrastructure
Canada boasts a comprehensive transport infrastructure, including numerous airports, a vast network of railways, and major ports like Halifax, Saint John, and Vancouver.
More Interesting Facts
Did You Know?
- World’s Longest Coastline: Canada has the longest coastline of any country in the world, stretching over 202,080 kilometers (125,567 miles). This vast coastline touches three different oceans: the Atlantic, Pacific, and Arctic.
- Largest Number of Lakes: Canada has the largest number of lakes globally, with over 2 million lakes covering about 7.6% of its landmass. This includes some of the largest freshwater lakes in the world, such as the Great Lakes.
- Polar Bear Capital: Churchill, Manitoba, in Canada, is known as the “Polar Bear Capital of the World”. Polar bears migrate directly through Churchill every fall, making it one of the few human settlements where you can observe polar bears in the wild.
- Officially Bilingual: Canada is officially bilingual, with both English and French recognized as official languages at the federal level. This reflects the country’s historical ties to both Britain and France.
- Longest Undefended Border: Canada shares the world’s longest undefended border with the United States. This border stretches for 8,891 kilometers (5,525 miles), including the boundary with Alaska.
- Inventor of Basketball: Dr. James Naismith, a Canadian, invented the sport of basketball in 1891. Interestingly, he developed this game to keep his students active during winter.
- Snack Inventor: Canada is the birthplace of the beloved Hawaiian pizza, which was actually created by a Greek immigrant in Ontario in 1962.
- World’s Smallest Jail: Rodney, Ontario, Canada, boasts the world’s smallest jail, measuring only 24.3 square meters (262 square feet).
- First UFO Landing Pad: The world’s first one was built in 1967 in St. Paul, Alberta. It was built as a landmark for the town’s centennial and as a symbol of keeping space free from human warfare.
- Third-Largest Oil Reserves: Canada has the third-largest oil reserves in the world, behind Venezuela and Saudi Arabia. The majority of these reserves are found in the oil sands of Alberta.
- Canadian Inventions: Canada has contributed many significant inventions, including the electric wheelchair, the telephone (by Scottish-born Canadian Alexander Graham Bell), and insulin treatment for diabetes.
- Narwhal Tusk Discovery: Canada’s Arctic waters are home to the narwhal, often called the ‘unicorn of the sea’. Their long, spiral tusk is a tooth, a unique feature in the animal kingdom.
These interesting facts highlight Canada’s geographical and ecological diversity and its contributions to global culture, science, and technology.
Many thanks for visiting and sharing this map & country information site!