 |
 |
 |
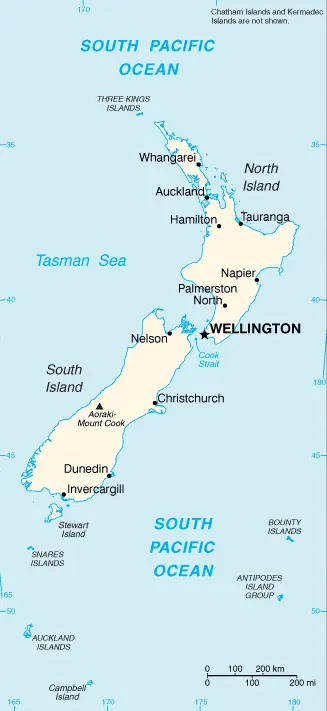
| Borderline map of New Zealand | Location map of New Zealand | Flag of New Zealand |
Google Maps and Detailed Facts of New Zealand (NZ). This page lets you explore New Zealand and its border countries (Country Location: Oceania, islands in the South Pacific Ocean, southeast of Australia) through detailed Satellite imagery – fast and easy as never before Google Maps.
Find comprehensive information about this country’s diversity below: Google Maps, geography, economy, science, people, culture, environment, government, and history – All in One Wiki page.
There is also a Street View and free Driving Directions at your service. Your Google Satellite Map Sightseeing in New Zealand, in Oceania, starts here at Driving Directions and Maps.com.
New Zealand Google Maps & Satellite Maps
The map below shows New Zealand with its cities, towns, highways, main roads, streets, and Street Views. To find a location, use the form below, type any city or place, view a simple map, and click the “show map” button.
The Google Maps above shows New Zealand with its location: Oceania (geographic coordinates: 41 00 S, 174 00 E) and the international borders of New Zealand; 0 km; furthermore, it’s inland counties boundaries.
Hint: Look at the Street view in New Zealand or Oceania. All you have to do is drag and pull the little yellow man (named: Pegman) on the Google Maps above the desired location. After that, whenever it is available (more than 50 countries globally), blue stripes will appear to show the photos and details from Google’s regularly updated data image base. In case if you have signed in to your Google account currently, you may have a look at the satellite map of this country/area as well.
The map of New Zealand, Oceania, is for informational use only. No representation is made or warrantied given any map or its content by Driving Directions and Maps site. The user assumes all risks of using this New Zealand Google Maps and facts/wiki.
About New Zealand in detail
Where is New Zealand?
New Zealand is looking on the map under the Coordinates 41 18 S 174 47 E otherwise in Oceania, in Oceania, islands in the South Pacific Ocean, southeast of Australia.
What is the capital city of New Zealand?
The capital city of New Zealand is Wellington.
What is the time in Wellington?
It is 17 hours ahead of Washington, D.C., during Standard Time. The timezone of Wellington is UTC+12.
What is the Internet code for New Zealand?
The Top Level Domain (TLD) for New Zealand is: .nz
What is the size of New Zealand?
The territory of New Zealand is total: 268,838 sq km; land: 264,537 sq km, water: 4,301 sq km.
If we want to describe the size of the territory of New Zealand is almost twice the size of North Carolina, about the size of Colorado.
If we would like to walk around and discover New Zealand, we can cover 0 km.
What is the water coverage of New Zealand?
We have already mentioned what percentage of New Zealand is covered by water (see below), including a 15,134 km coastline.
What is the climate like in New Zealand?
The climate of New Zealand is temperate with sharp regional contrasts.
Geographical data of New Zealand
New Zealand; mean elevation: 388 m, elevation extremes; lowest point: Pacific Ocean 0 m, highest point: Aoraki-Mount Cook 3,754 m.
The specific geographical details of New Zealand include predominately mountainous with vast coastal plains.
Suppose we would like to describe the countries location from a different perspective. In that case, it is safe to say, and easy to read from a map, New Zealand is almost 90% of the population lives in cities; Wellington is the southernmost national capital in the world.
Resources and land use of New Zealand
The country’s main mined products are natural gas, iron ore, sand, coal, timber, hydropower, gold, limestone. The population partly uses the earlier highlighted land territory and partly left in its natural state: agricultural land: 43.2%; arable land 1.8%; permanent crops 0.3%; permanent pasture 41.1%; forest: 31.4%; other: 25.4% (2011 estimate).
Population data of New Zealand
The number of inhabitants of New Zealand is 4,474,549 (July 2016 estimate).
If we examine the proportion of population distribution, it is safe to say that N/A.
If we look at the proportion of the urbanized and barely populated areas, these are the figures: urban population: 86.3% of the total population (2015).
Most of the New Zealand population concentrated in Auckland 1.344 million, WELLINGTON (capital) 383,000 (2015).
Ethnicity in New Zealand
According to ethnicity details, the ethnic groups are European 71.2%, Maori 14.1%, Asian 11.3%, Pacific peoples 7.6%, Middle Eastern, Latin American, African 1.1%, other 1.6%, not stated or unidentified 5.4%note: based on the 2013 census of the usually resident population; percentages add up to more than 100% because respondents were able to identify more than one ethnic group (2013 estimate).
Spoken languages in New Zealand
The spoken languages in New Zealand are the following: English (de facto official language) 89.8%, Maori (de jure official language) 3.5%, Samoan 2%, Hindi 1.6%, French 1.2%, Northern Chinese 1.2%, Yue 1%, other or not stated 20.5%, New Zealand Sign Language (de jure official language). Note shares sum to 120.8% due to multiple responses on the census (2013 estimate).
What are the most important religions in New Zealand?
During the general census, researchers examine the churches, according to this: Christian 44.3% (Catholic 11.6%, Anglican 10.8%, Presbyterian and Congregational 7.8%, Methodist, 2.4%, Pentecostal 1.8%, other 9.9%), Hindu 2.1%, Buddhist 1.4%, Maori Christian 1.3%, Islam 1.1%, other religion 1.4% (includes Judaism, Spiritualism, and New Age religions, Baha’i, Asian religions other than Buddhism), no religion 38.5%, not stated or unidentified 8.2%, objected to answering 4.1%note: based on the 2013 census of the usually resident population; percentages add up to more than 100% because people were able to identify more than one religion (2013 estimate).
Further population data of New Zealand
The proportion of gender and age tells a lot about the society as follows 0-14 years: 19.76% (male 452,810 / female 431,198) 15-24 years: 13.56% (male 312,032 / female 294,662) 25-54 years: 40.05% (male 897,549 / female 894,394) 55-64 years: 11.7% (male 255,381 / female 268,012) 65 years and over: 14.94% (male 308,949 / female 359,562) (2016 estimate). It also a significant factor in a society the population growth rate, which in the case of New Zealand is 0.8% (2016 estimate).
The population growth rate is based on two elements, the birth and the death rate. In New Zealand the birth rate is 13.3 births / 1,000 population (2016 estimate), the death rate 7.4 deaths / 1,000 population (2016 estimate).
In this day and age in developed societies, the first child borns later compared to the previous centuries and decades, so childbearing is extended. In New Zealand, the average age of mothers at the first childbirth is N/A.
Although the children’s birth is postponed in the best-case scenario, the parents can still see their kids grow as life expectancy also extended. In the case of New Zealand, these figures are. With the introduction of modern medicine, vaccinations, and the proper hygienic conditions, the infant mortality rate is in a steep decline. The infant mortality statistics in New Zealand are the following: 3,8/1000. Relevant data is the budget of healthcare, which is in the case of this country is 11% of GDP (2014).
Economic data of New Zealand
Suppose we would like to describe a country. We also have to mention its economy; Over the past 30 years, the government has transformed New Zealand from an agrarian economy, dependent on concessionary British market access more industrialized, free-market economy that can compete globally. This dynamic growth has boosted real in Per capita income rose for ten consecutive years until 2007 in purchasing power parity terms but fell in 2008-09. Debt-driven consumer spending drove robust growth in the first half of the decade, fueling a large balance of payments deficit that posed aThe economy fell into recession before starting the global financial crisis and contracted for five consecutive quarters 2008-09. In line with global peers, the central bank cut interest rates aggressively, and the government developed a fiscal stimulus.
GDP is a prominent figure, as all the relevant calculations and statistics are based on it. GDP in New Zealand is $179.4 billion (2015 estimate).
Another important indicator is the rate of GDP growth, which in New Zealand is 2.8% (2016 estimate), 3% (2015 estimate) 3% (2014 estimate).
These statistics affect the world economy; remember, in 2015, the Chinese real GDP growth rate was worse than expected; The world markets fall, and the Chinese stock exchange is temporally suspended.
A further major factor of a country’s economy, the GDP per capita. In New Zealand this is $37,100 (2016 estimate) $36,600 (2015 estimate) $36,300 (2014 estimate).
In the economy, the Trinity is in common places, such as agriculture, industry, and services.
What are the agricultural products New Zealand produces?
The main agricultural products of New Zealand are dairy products, sheep, beef, poultry, fruit, vegetables, wine, seafood, wheat, and barley.
The important segments are agriculture, forestry, fishing, logs and wood articles, manufacturing, mining, construction, financial services, real estate services, and tourism. The crucial and regularly mentioned GDP is based on agriculture, forestry, fishing, logs and wood articles, manufacturing, mining, construction, financial services, real estate services, tourism.
Drinking water source in New Zealand
It is essential to mention that – thanks to the development of the infrastructure -, the rate of potable water improved: urban: 100% of the population, rural: 100% of the population, total: 100% of the population. Unimproved: urban: 0% of population, rural: 0% of population, total: 0% of population (2015 estimate).
The average number of childbirth in New Zealand
In New Zealand, the average delivery number is 2.03 children born / woman (2016 estimate).
Population, median age, migration, and citizenship in New Zealand
The population’s average age is 37.8 years; male: 36.9 years, female: 38.7 years (2016 estimate). The age of adulthood varies in every country of the world. In New Zealand, it is 18 years of age, universal.
When we are experiencing an unprecedented scale of migration and globalization, it is an important factor in the number of new immigrants. In New Zealand is 2.2 migrant(s) / 1,000 population (2016 estimate). It is important to know how to apply for citizenship: citizenship by birth: no. Citizenship by descent only: at least one parent must be a citizen of New Zealand. Dual citizenship recognized: yes, the residency requirement for naturalization: 3 years.
Is New Zealand a safe destination? Healthcare services and contagious diseases in New Zealand
Many of the travelers are looking into the healthcare services and infectious diseases of their destinations. In New Zealand, the hospital beds’ density is 2.3 beds / 1,000 population (2011).
According to the WHO rating regarding contagious diseases in New Zealand: N/A.
However, HIV is not curable but maintainable. Let’s do not forget when the disease surfaced; it was a world threatening condition. Unfortunately, in some countries, it is still very high the number of infected patients and fatalities due to the disease.
In New Zealand, the number of HIV/AIDS deaths: N/A.
Regarding tourism obesity, not an important issue, but we have to mention health statistics, as it is the plague of the 20th and the 21st century. The rate of obese adults in New Zealand is 30.6% (2014).
What are the natural hazards in New Zealand? Is there any?
The most known natural risk in New Zealand are earthquakes are common, though usually not severe; volcanic activity: significant volcanism on North Island; Ruapehu (elevation 2,797 m), which last erupted in 2007, has a history of substantial eruptions in the past century; Taranaki has the potential to produce dangerous avalanches and lahars; other historically active volcanoes include Okataina, Raoul Island, Tongariro, and White Island.
More interesting facts about New Zealand
Like every country and society, a few words about the past are connected to its history; The Polynesian Maori reached New Zealand in about A.D. 800. In 1840, their chieftains entered into a compact with Britain, the Treaty of Waitangi, in which they ceded sovereignty to Queen Victoria while retaining territorial rights. That same year, the British began the first organized colonial settlement. A series of land wars between 1843 and 1872 ended with the defeat of the native peoples. The British colony of New Zealand became an independent dominion in 1907 and supported the U.K. militarily in both world wars. New Zealand’s full participation in several defense alliances lapsed by the 1980s. In recent years, the government has sought to address longstanding Maori grievances. New Zealand assumed a nonpermanent seat on the U.N. Security Council for the 2015-16 term.
In every nation’s memory, some cornerstones placed the country on the timeline of history. The date of declaration of independence of New Zealand: 26 September 1907 (from the U.K.).
The flag and other symbols of New Zealand
The colors, symbols, and animals on the flag usually have a historical background or an important milestone or memory of the nation.
This case is not an exception either; blue with the UK’s flag in the upper hoist-side quadrant with four red five-pointed stars edged in white centered in the outer half of the flag; the stars represent the Southern Cross constellation.
Apart from the flag, the symbol of national unity is the national anthem. The anthem’s primary purpose is to share the nation’s core values, endeavors, and patriotic feelings.
National symbols of New Zealand: Southern Cross constellation (four, five-pointed stars), kiwi (bird), silver fern; national colors: black, white, red (ochre).
Constitution of New Zealand
The existence of the nation is based on the constitution. Some constitutions knew worldwide, like the U.S. Constitution that was accepted on the 17th of September 1787, in Philadelphia, the United States of America’s Constitution.
It is not related to the declaration of independence that was stolen by Nicolas Cage in the movie National Treasure 🙂
What is the legal system of New Zealand?
Most of the time, the legal system of a country is the focus of lawyers. It is a common fact that there are two main approaches in the world, “the law in books” and “the law in action.”
In the Anglo-Saxon world, the practice is the “law in action,” while in the rest of the world, the law is based on Roman law, the “law in books.”
The legal system of New Zealand is a common law system based on the English model, with special legislation and land courts for the Maori.
It was Aristotle who founded the Theory of 3 separations of powers. In his view, these are the council of public affairs, the magistrates, and the justice system. The age of enlightenment was the time when terminologies have defined the way we still use them. In most democratic countries, the three authorities separated from each other. In dictatorships, the rules usually interweaved in one hand.
About the legislative branch of New Zealand, we can highlight the following structures unicameral House of Representatives – commonly called Parliament (usually 120 seats; 70 members directly elected in single-seat constituencies, including 7 Maori constituencies, by simple majority vote and 50 directly elected by proportional representation vote; members serve 3-year terms).
About the unemployment rate, labor force, and poverty line in New Zealand
One of the major problems of the 21st-century economy is unemployment. Governments are struggling to maintain a low level of the unemployment rate. Still, as a result of automation, the cheap 3rd world labor, and the outsourcing of workflow, these attempts fail. In New Zealand, the labor force is 2.562 million (2016 estimate). Please bear in mind that the population in New Zealand is total: 4.5 deaths / 1,000 live births; male: 5 deaths / 1,000 live births, female: 3.9 deaths / 1,000 live births (2016 estimate) – as we already mentioned above.
The rate of unemployment in New Zealand is 5.1% (2016 estimate).
Widely known that the gap between the rich and poor is widening on an enormous scale.
According to the 2017 shocking Oxfam report, the most affluent eight people’s fortune is equal to the wealth of the poorest half of the world’s population.
In New Zealand, the households’ income and consumption compared to the entire population: lowest 10%: N/A% highest 10%: N/A%.
Another widely used indicator is the so-called GINI index, which measures the inequalities of statistical dispersion, but is mainly used for measuring the sharing of income and fortune.
The GINI index was named after its founder Corrado Gini, an Italian economist. Gini index has grades between 0-1, but often it is used on a percentage basis. It is 0 if the examined criteria territorial distribution is equal. It is one of the criteria concentrated on the territory. In New Zealand, the GINI index is .36,2 (1997).
The states usually set up a poverty line, which is more or less, is a subjective measure. It varies by country; its base is often the minimum pension, the most insufficient 20 percent incomes, and the X percent of income per capita.
In New Zealand, the poverty line people are the lowest 10%: N/A% highest 10%: N/A%.
About the budget and central governments debt of New Zealand
The available budget mainly defines the state’s economy. The budget of New Zealand is; revenues: $67.61 billion, expenditures: $67.01 billion (2016 estimate). Taxes and other revenues are 37.7% of GDP (2016 estimate).
The budget deficit (Budget surplus (+) or deficit (-)) is N/A.
The fiscal year in New Zealand is 1 April – 31 March. Note: this is the fiscal year for tax purposes.
In the country’s economy, we have to consider the public debt. Public debt is the consolidated sum of the state’s local, federal, and central government debt.
Inflation rate and prime lending rate in New Zealand
A few further interesting and relevant economic data are the following; Inflation rate: 0.6% (2016 estimate), 0.3% (2015 estimate), and the rate of the Commercial bank prime lending rate: 5% (31 December 2016 estimate).
Export/import partners and data of New Zealand
New Zealand, with the export of products, industrial tools, and other services, generates revenue. The export value in New Zealand is $31.96 billion (2016 estimate), $34.41 billion (2015 estimate). The total revenue of these activities: dairy products, meat, and edible offal, logs and wood articles, fruit, crude oil, wine.
The most important export partners of New Zealand are China 17.5%, Australia 16.9%, the US 11.8%, Japan 6% (2015).
The most important imported products are petroleum and products, mechanical machinery, vehicles and parts, electrical machinery, textiles, and the countries from where the import is coming: China 19.4%, Australia 11.8%, US 11.7%, Japan 6.6%, Germany 4.7%, Thailand 4.2% (2015).
Renewable energies used in New Zealand
To suppress the pollution of the environment, renewable energies have to replace the fossil energy. The more the proportion of renewable energies in a country means more effort against pollution. New Zealand indicates how much of the country’s produced energy comes from the hydroelectric source, 55.2% of total installed capacity (2012 estimate).
To indicate how much another renewable energy produced is 15.8% of total installed capacity (2012 estimate).
Telecommunication data of New Zealand, calling code
To maintain the economy, the development of a reliable and modern telecommunications infrastructure is crucial. We can say the following about New Zealand; excellent domestic and international systems domestic: combined fixed-line and mobile-cellular telephone subscribership exceed 160 per 100 persons. International: country code – 64; the Southern Cross submarine cable system provides links to Australia, Fiji, and the US; satellite earth stations – 8 (1 Inmarsat – Pacific Ocean, seven other) (2015).
Transport infrastructure in New Zealand
In the 21st century, we often say that the world has become small and there are no distances anymore. With extensive air travel when (sometimes) there are no visa restrictions, it is easy to reach other countries, but if the distance is not too long, we can also use railway or water transportation.
The number of airports in New Zealand: 123 (2013), and the number of heliports: N/A.
The total length of the roadways in New Zealand: 94,902 km, paved: 62,759 km (includes 199 km of expressways), unpaved: 32,143 km (2012).
The total length of the waterways in New Zealand: N/A.
Are you traveling to New Zealand?
If you plan to travel by plane to New Zealand, try our air ticket comparison site, where you can choose from hundreds of carriers and offers. Our application is scanning the market and shows you the best and the cheapest deals without any extra charge or commission.
Are you looking for a hotel, apartment another kind of accommodation in New Zealand, Oceania? We are here to help you to find your accommodation from budget to luxury. Our search engine is scanning, regularly updating data from hundreds of accommodation websites and more than a million offers. You can quickly and easily find your hotel stay anywhere in the world, without any extra charge or commission.
Facts & data about New Zealand
Name of the country: conventional long way: none, traditional short form: New Zealand abbreviation: NZ, etymology: Dutch explorer Abel TASMAN was the first European to reach New Zealand in 1642; he named it Staten Landt, but Dutch cartographers renamed it Nova Zeelandia in 1645 after the Dutch province of Zeeland; British explorer Captain James COOK subsequently anglicized the name to New Zealand when he mapped the islands in 1769.
| Abbreviation: New Zealand | Geographic coordinates: 41 00 S, 174 00 E |
Country Location: Oceania |
| Capital of New Zealand: Wellington | GPS of the Capital: 41 18 S 174 47 E |
Position: Oceania, islands in the South Pacific Ocean, southeast of Australia |
| Land area: total: 268,838 sq km; land: 264,537 sq km, water: 4,301 sq km | Terrain: predominately mountainous with vast coastal plains |
Area comparative: almost twice the size of North Carolina; about the size of Colorado |
| Population: 4,474,549 (July 2016 estimate) | Population grow rate: 0.8% (2016 estimate) | Sex ratio: at birth: 1.05 male(s) / female, 0-14 years: 1.05 male(s) / female, 15-24 years: 1.06 male(s) / female, 25-54 years: 1 male(s) / female, 55-64 years: 0.95 male(s) / female, 65 years and over: 0.86 male(s) / female, total population: 0.99 male(s) / female (2016 estimate) |
| Exports: $31.96 billion (2016 estimate), $34.41 billion (2015 estimate) | Imports: $34.83 billion (2016 estimate), $35.8 billion (2015 estimate) | Import partners: China 19.4%, Australia 11.8%, US 11.7%, Japan 6.6%, Germany 4.7%, Thailand 4.2% (2015) |
| Urbanization: urban population: 86.3% of the total population (2015) | Major urban area(s): Auckland 1.344 million; WELLINGTON (capital) 383,000 (2015) | Median age: total: 37.8 years; male: 36.9 years, female: 38.7 years (2016 estimate) |
| Internet users: total: 3.916 million. Percent of population: 88.2% (July 2015 estimate) | Telephones (fixed-lines): total subscriptions: 1.85 million. Subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 42 (July 2015 estimate) | Telephones (mobile, cellular): total: 5.6 million. Subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 126 (July 2015 estimate) |
| Unemployment rate: 5.1% (2016 estimate) | Nationality: New Zealander(s) adjective: New Zealand | National holidays: Waitangi Day (Treaty of Waitangi established British sovereignty over New Zealand), 6 February (1840); ANZAC Day (commemorated as the anniversary of the landing of troops of the Australian and New Zealand Army Corps during World War I at Gallipoli, Turkey), 25 April (1915) |
| Life expectancy at birth: total population: 81.2 years. Male: 79.1 years, female: 83.3 years (2016 estimate) | Total fertility rate: 2.03 children born / woman (2016 estimate) | Birthrate: 13.3 births / 1,000 population (2016 estimate) |
| Literacy: N/A | Legal system: common law system, based on English model, with special legislation and land courts for the Maori | Suffrage: 18 years of age, universal |
| Industries: agriculture, forestry, fishing, logs and wood articles, manufacturing, mining, construction, financial services, real estate services, tourism | Industrial production growth rate: 2.6% (2016 estimate) | GDP real growth rate: 2.8% (2016 estimate) 3% (2015 estimate) 3% (2014 estimate) |
Do you like this New Zealand Google Maps & information page?
Please do us a favor: Share or like this page using the icons at the top of the page. We also do encourage you to visit our Facebook page for more travel and country related information.
Thank you for visiting and sharing this map & country information page.
