 |
 |
 |
| Borderline map of Russia | Location map of Russia | Flag of Russia |
Google Maps and Detailed Facts of Russia (RU). This page lets you explore Russia and its border countries (Country Location: North Asia bordering the Arctic Ocean, extending from Europe (the portion west of the Urals) to the North Pacific Ocean) through detailed Satellite imagery – fast and easy as never before Google Maps.
Find comprehensive information about this country’s diversity below: Google Maps, geography, economy, science, people, culture, environment, government, and history – All in One Wiki page.
There is also a Street View and free Driving Directions at your service. Your Google Satellite Map Sightseeing in Russia in Asia starts here at Driving Directions and Maps.com.
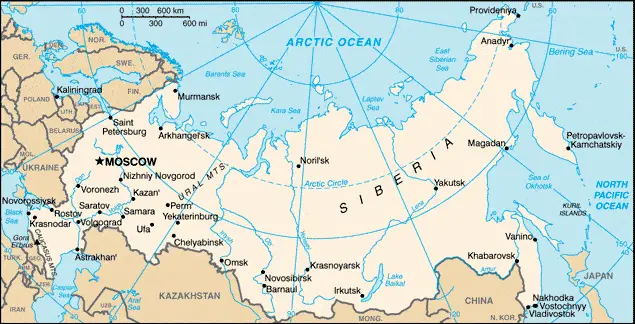
Russia Google Maps & Satellite Maps
The map below shows Russia with its cities, towns, highways, main roads, streets, and Street Views. To find a location, use the form below, type any city or place, view a simple map, and click the “show map” button.
The Google Maps above shows Russia with its location: Asia (geographic coordinates: 60 00 N, 100 00 E) and the international borders of Russia; total: 22,408 km. Border countries (14): Azerbaijan 338 km, Belarus 1,312 km, China (southeast) 4,133 km, China (south) 46 km, Estonia 324 km, Finland 1,309 km, Georgia 894 km, Kazakhstan 7,644 km, North Korea 18 km, Latvia 332 km, Lithuania (Kaliningrad Oblast) 261 km, Mongolia 3,452 km, Norway 191 km, Poland (Kaliningrad Oblast) 210 km, Ukraine 1,944 km; furthermore, it’s inland counties boundaries.
Hint: Look at the Street view in Russia or Asia. All you have to do is drag and pull the little yellow man (named: Pegman) on the Google Maps above the desired location. After that, whenever it is available (more than 50 countries globally), blue stripes will appear to show the photos and details from Google’s regularly updated data image base. In case if you have signed in to your Google account currently, you may have a look at the satellite map of this country/area as well.
The map of Russia, Asia is for informational use only. No representation is made or warrantied given any map or its content by Driving Directions and Maps site. The user assumes all risks of using this Russia Google Maps and facts/wiki.
About Russia in detail
Where is Russia?
Russia, in case, if you are looking on the map under the Coordinates 55 45 N 37 36 E otherwise in Asia, in North Asia bordering the Arctic Ocean, extending from Europe (the portion west of the Urals) to the North Pacific Ocean.
What is the capital city of Russia?
The capital city of Russia is Moscow.
What is the time in Moscow?
It is 8 hours ahead of Washington, D.C. during Standard Time. Moscow’s timezone is UTC+3.
What is the Internet code for Russia?
The Top Level Domain (TLD) for Russia is: .ru
What is the size of Russia?
The territory of Russia is total: 17,098,242 sq km; land: 16,377,742 sq km, water: 720,500 sq km.
If we want to describe Russia’s territory’s size is approximately 1.8 times the US’s size.
If we would like to walk around and discover Russia, we can cover a total distance: 22,408 km.
What is the water coverage of Russia?
We have already mentioned what percentage of Russia is covered by water (see below), including a 37,653 km coastline.
What is the climate like in Russia?
The climate of Russia ranges from steppes in the south through humid continental in much of European Russia: subarctic in Siberia to tundra climate in the polar north: winters vary from cool along Black Sea coast to frigid in Siberia: summers vary from warm in the steppes to cool along Arctic coast.
Geographical data of Russia
Russia’s elevation includes 600 m, elevation extremes; lowest point: the Caspian Sea -28 m, highest point: Gora El’brus 5,633 m.
Russia’s specific geographical details include a broad plain with low hills west of Urals; vast coniferous forest and tundra in Siberia; uplands and mountains along southern border regions.
If we would like to describe the countries location from a different perspective, it is safe to say, and easy to read from a map, Russia is the largest country in the world in terms of area but unfavorably located to major sea lanes of the world; despite its size, much of the country lacks proper soils and climates (either too cold or too dry) for agriculture; Mount El’brus is Europe’s tallest peak; Lake Baikal, the deepest lake in the world, is estimated to hold one-fifth of the world’s freshwater.
Resources and land use of Russia
The country’s main mined products are a wide natural resource base, including major deposits of oil, natural gas, coal, and many strategic minerals, reserves of rare earth elements, timber. Note: formidable obstacles of climate, terrain, and distance hinder exploitation of natural resources. The population partly uses the earlier highlighted land territory and partly left in its natural state: agricultural land: 13.1%; arable land 7.3%; permanent crops 0.1%; permanent pasture 5.7%; forest: 49.4%; other: 37.5% (2011 estimate).
Population data of Russia
The number of inhabitants of Russia is 142,355,415 (July 2016 estimate).
Let’s examine the proportion of the population distribution. It is safe to say that the population is heavily concentrated in the westernmost fifth of the country, extending from the Baltic Sea, south to the Caspian Sea, and eastward parallel to the Kazakh border. Sizeable pockets are isolated and generally found in the south.
If we look at the proportion of the urbanized and barely populated areas, these are the figures: urban population: 74% of the total population (2015).
Most of Russia’s population is concentrated in MOSCOW (capital) 12.166 million; Saint Petersburg 4.993 million; Novosibirsk 1.497 million; Yekaterinburg 1.379 million; Nizhniy Novgorod 1.212 million; Samara 1.164 million (2015).
Ethnicity in Russia
According to ethnicity details, the ethnic groups are Russian 77.7%, Tatar 3.7%, Ukrainian 1.4%, Bashkir 1.1%, Chuvash 1%, Chechen 1%, other 10.2%, unspecified 3.9%note: nearly 200 national and ethnic groups are represented in Russia’s 2010 census (2010 estimate).
The spoken languages in Russia are the following: Russian (official language) 85.7%, Tatar 3.2%, Chechen 1%, other 10.1%. Note: data represent native language spoken (2010 estimate).
What are the most important religions in Russia?
According to this general census, researchers examine the churches: Russian Orthodox 15-20%, Muslim 10-15%, other Christian 2% (2006 estimate). Note: estimates are of practicing worshipers; Russia has large populations of non-practicing believers and non-believers, a legacy of over seven decades of Soviet rule; Russia officially recognizes Orthodox Christianity, Islam, Judaism, and Buddhism traditional religions.
Further population data of Russia
The proportion of gender and age tells a lot about the society as follows 0-14 years: 16.94% (male 12,385,281 / female 11,726,473) 15-24 years: 9.71% (male 7,071,489 / female 6,754,928) 25-54 years: 45.16% (male 31,528,258 / female 32,753,350) 55-64 years: 14.27% (male 8,727,233 / female 11,591,221) 65 years and over: 13.92% (male 6,152,252 / female 13,664,930) (2016 estimate). It also a significant factor in a society the population growth rate, which in the case of Russia is -0.06% (2016 estimate).
The population growth rate is based on two elements, the birth and the death rate. In Russia the birth rate is 11.3 births / 1,000 population (2016 estimate), the death rate 13.6 deaths / 1,000 population (2016 estimate).
In this day and age in developed societies, the first child borns later compared to the previous centuries and decades, so childbearing is extended. In Russia, the average age of mothers at the first childbirth is N/A.
Although the children’s birth is postponed in the best-case scenario, the parents can still see their kids grow as life expectancy also extended. In the case of Russia, these figures are. With the introduction of modern medicine, vaccinations, and the proper hygienic conditions, the infant mortality rate is in a steep decline. The infant mortality statistics in Russia are the following: N/A. Relevant data is the budget of healthcare, which is in the case of this country is 7.1% of GDP (2014).
Economic data of Russia
If we would like to describe a country, we also have to mention its economy; Russia has undergone significant changes since the collapse of the Soviet Union, moving from a centrally planned economy towards a more market-based system. Economic growth and reform have stalled in recent years; however, Russia remains a prom; Russia is one of the world’s leading oil and natural gas producers. It is also a top exporter of metals such as steel and primary aluminum. The economy, which had averaged 7% growth during 1998-2008 as oil prices rose rapidly, has seen diminishing growth rates since then due to Russia’s commodity-based growth model’s exhaustion. A combination of falling oil prices, international sanctions, and structural limitations pushed Russia into a deep recession in 2015, with the GDP falling by close to 4%. The downturn continued through 2016.
GDP is a prominent figure, as all the relevant calculations and statistics are based on it. GDP in Russia is $1.268 trillion (2015 estimate).
Another important indicator is the rate of GDP growth, which in Russia is -0.8% (2016 estimate) -3.7% (2015 estimate) 0.7% (2014 estimate).
These statistics affect the world economy; remember, in 2015, the Chinese real GDP growth rate was worse than expected; The world markets fall, and the Chinese stock exchange is temporally suspended.
A further major factor of a country’s economy, the GDP per capita. In Russia this is $26,100 (2016 estimate) $26,300 (2015 estimate) $27,300 (2014 estimate).
In the economy, the Trinity is in common places, such as agriculture, industry, and services.
What are the agricultural products Russia produces?
Russia’s main agricultural products are grain, sugar beets, sunflower seeds, vegetables, fruits, beef, milk.
The essential segments are a complete range of mining and extractive industries producing coal, oil, gas, chemicals, and metals; all forms of machine building from rolling mills to high-performance aircraft and space vehicles; defense industries (including radar, missile production. The crucial and regularly mentioned GDP is based on a complete range of mining and extractive industries producing coal, oil, gas, chemicals, and metals; all forms of machine building from rolling mills to high-performance aircraft and space vehicles; defense industries (including radar, missile production.
Drinking water source in Russia
It is essential to mention that – thanks to the development of the infrastructure -, the rate of potable water improved: urban: 98.9% of the population, rural: 91.2% of the population, total: 96.9% of the community. Unimproved: urban: 1.1% of the people, rural: 8.8% of the people, total: 3.1% of the population (2015 estimate).
The average number of childbirth in Russia
In Russia, the average delivery number is 1.61 children born / woman (2016 estimate).
Population, median age, migration, and citizenship in Russia
The population’s average age is 39.3 years; male: 36.4 years, female: 42.3 years (2016 estimate). The age of adulthood varies in every country of the world. In Russia, it is 18 years of age, universal.
When we are experiencing an unprecedented scale of migration and globalization, it is an important factor in the number of new immigrants. In Russia is 1.7 migrant(s) / 1,000 population (2016 estimate). It is important to know how to apply for citizenship: citizenship by birth: no. Citizenship by descent only: at least one parent must be a citizen of Russia. Dual citizenship recognized: yes, the residency requirement for naturalization: 3-5 years.
Is Russia a safe destination? Healthcare services and infectious diseases in Russia
Many of the travelers are looking into the healthcare services and infectious diseases of their destinations. In Russia, the hospital beds’ density is 9.7 beds / 1,000 population (2006).
According to the WHO rating regarding contagious diseases in Russia, the degree of risk: intermediate food or waterborne diseases: bacterial diarrhea vectorborne disease: tickborne encephalitis (2016).
However, HIV is not curable but maintainable. Let’s do not forget when the disease surfaced; it was a world threatening condition. Unfortunately, in some countries, it is still very high the number of infected patients and fatalities due to the disease.
In Russia, the number of HIV/AIDS deaths: N/A.
Regarding tourism obesity, not an important issue, but we have to mention health statistics, as it is the plague of the 20th and the 21st century. The rate of obese adults in Russia is 26.2% (2014).
What are the natural hazards in Russia? Is there any?
The most known natural risk in Russia are permafrost over much of Siberia is a significant impediment to development; volcanic activity in the Kuril Islands; volcanoes and earthquakes on the Kamchatka Peninsula; spring floods and summer/autumn forest fires throughout Siberia and parts of European Russiavolcanism: significant volcanic activity on the Kamchatka Peninsula and Kuril Islands; the peninsula alone is home to some 29 historically active volcanoes, with dozens more in the Kuril Islands; Kliuchevskoi (elevation 4,835 m), which erupted in 2007 and 2010, is Kamchatka’s most active volcano; Avachinsky and Koryaksky volcanoes, which pose a threat to the city of Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky, have been deemed Decade Volcanoes by the International Association of Volcanology and Chemistry of the Earth’s Interior, worthy of study due to their explosive history and close proximity to human populations; other notable historically active volcanoes include Bezymianny, Chikurachki, Ebeko, Gorely, Grozny, Karymsky, Ketoi, Kronotsky, Ksudach, Medvezhia, Mutnovsky, Sarychev Peak, Shiveluch, Tiatia, Tolbachik, and Zheltovsky.
More interesting facts about Russia
A few words about the past, as every country and society, are connected to its history; Founded in the 12th century, Muscovy’s Principality was able to emerge from over 200 years of Mongol domination (13th-15th centuries) and to conquer and absorb surrounding principalities gradually. In the early 17th century, a new ROMANOV Dynasty continued this expansion policy across Siberia to the Pacific. Under PETER I (ruled 1682-1725), hegemony was extended to the Baltic Sea, and the country was renamed the Russian Empire. During the 19th century, more territorial acquisitions were made in Europe and Asia. Defeat in the Russo-Japanese War of 1904-05 contributed to the Revolution of 1905, which resulted in a parliament and other reforms. The Russian army’s repeated devastating defeats in World War I led to widespread rioting in the Russian Empire’s major cities and the overthrow in 1917 of the imperial household.
The communists under Vladimir LENIN seized power soon after and formed the USSR. Iosif STALIN (1928-53) ‘s brutal rule strengthened communist rule and Russian dominance of the Soviet Union at the cost of tens of millions of lives. After defeating Germany in World War II as part of an alliance with the US (1939-1945), the USSR expanded its territory and influence in Eastern Europe and emerged as a global power. The USSR was the principal adversary of the US during the Cold War (1947-1991). The Soviet economy and society stagnated in the decades following Stalin’s rule, until General Secretary Mikhail GORBACHEV (1985-91) introduced glasnost (openness) and perestroika (restructuring) in an attempt to modernize communism. Still, his initiatives inadvertently released forces that by December 1991 splintered the USSR into Russia and 14 other independent republics.
Following economic and political turmoil during President Boris YELTSIN’s term (1991-99), Russia shifted toward a centralized authoritarian state under the leadership of President Vladimir PUTIN (2000-2008, 2012-present) in which the regime seeks to legitimize its rule through managed elections, populist appeals, a foreign policy focused on enhancing the country’s geopolitical influence, and commodity-based economic growth. Russia faces a mostly subdued rebel movement in Chechnya and some other surrounding regions, although violence still occurs throughout the North Caucasus.
In every nation’s memory, some cornerstones placed the country on the timeline of history. The date of declaration of independence of Russia: 24 August 1991 (from the Soviet Union); notable earlier dates: 1157 (Principality of Vladimir-Suzdal created); 16 January 1547 (Tsardom of Muscovy established); 22 October 1721 (Russian Empire proclaimed); 30 December 1922 (the Soviet Union established).
The flag and other symbols of Russia
The colors, symbols, and animals on the flag usually have a historical background or an important milestone or memory of the nation.
This case is not an exception: three equal horizontal bands of white (top), blue, and red. Note: the colors may have been based on those of the Dutch flag; despite many popular interpretations, there is no official meaning assigned to the colors of the Russian flag; this flag inspired several other Slav countries to adopt horizontal tricolors of the same colors but in different arrangements, and so red, blue, and white became the Pan-Slav colors.
Apart from the flag, the symbol of national unity is the national anthem. The anthem’s primary purpose is to share the nation’s core values, endeavors, and patriotic feelings.
National symbols of Russia: bear, double-headed eagle; national colors: white, blue, red.
Constitution of Russia
The existence of the nation is based on the constitution. Some constitutions knew worldwide, like the U.S. Constitution that was accepted on the 17th of September 1787, in Philadelphia, the United States of America’s Constitution.
It is not related to the declaration of independence that was stolen by Nicolas Cage in the movie National Treasure 🙂
What is the legal system of Russia?
Most of the time, the legal system of a country is the focus of lawyers. It is a common fact that there are two main approaches in the world, “the law in books” and “the law in action.”
In the Anglo-Saxon world, the practice is the “law in action,” while in the rest of the world, the law is based on Roman law, the “law in books.”
The legal system of Russia is a civil law system; judicial review of legislative acts.
It was Aristotle who founded the Theory of 3 separations of powers. In his view, these are the council of public affairs, the magistrates, and the justice system. The age of enlightenment was the time when terminologies have defined the way we still use them. In most democratic countries, the three authorities separated from each other. In dictatorships, the rules usually interweaved in one hand.
About the legislative branch of Russia, we can highlight the following structures bicameral Federal Assembly or Federalnoye Sobraniye consists of the Federation Council or Sovet Federatsii (166 seats; 2 members in each of the 83 federal administrative units – oblasts, krays, republics, autonomous okrugs and oblasts, and the federal cities of Moscow and Saint Petersburg – appointed by the top executive and legislative officials; members serve 4-year terms) and the State Duma or Gosudarstvennaya Duma (450 seats; as of February 2014, the electoral system reverted to a mixed electoral system for the 2016 election in which one-half of the members are directly elected by simple majority vote and one-half directly elected by proportional representation vote; members serve 5-year terms).
About the unemployment rate, labor force, and poverty line in Russia
One of the major problems of the 21st-century economy is unemployment. Governments are struggling to maintain a low level of the unemployment rate. Still, as a result of automation, the cheap 3rd world labor, and the outsourcing of workflow, these attempts fail. In Russia, the labor force is 77.41 million (2016 estimate). Please bear in mind that the population in Russia is total: 6.9 deaths / 1,000 live births; male: 7.7 deaths / 1,000 live births, female: 6 deaths / 1,000 live births (2016 estimate) – as we already mentioned above.
The rate of unemployment in Russia is 8.2% (2016 estimate).
Widely known that the gap between the rich and poor is widening on an enormous scale.
According to the 2017 shocking Oxfam report, the most affluent eight people’s fortune is equal to the wealth of the poorest half of the world’s population.
In Russia, the households’ income and consumption compared to the entire population: lowest 10%: 5.7% highest 10%: 42.4% (2011 estimate).
Another widely used indicator is the so-called GINI index, which measures the inequalities of statistical dispersion, but is mainly used for measuring the sharing of income and fortune.
The GINI index was named after its founder Corrado Gini, an Italian economist. Gini index has grades between 0-1, but often it is used on a percentage basis. It is 0 if the examined criteria territorial distribution is equal. It is one of the criteria concentrated on the territory. In Russia, the GINI index is .42 (2014).
The states usually set up a poverty line, which is more or less, is a subjective measure. It varies by country; its base is often the minimum pension, the incomes of the most deficient 20 percent, the X percent of income per capita Etc.
In Russia, the poverty line people are the lowest 10%: 5.7% highest 10%: 42.4% (2011 estimate).
About the budget and central governments debt of Russia
The available budget mainly defines the state’s economy. Russia’s budget is; revenues: $186.5 billion, expenditures: $236.6 billion (2016 estimate). Taxes and other revenues are 14.7% of GDP (2016 estimate).
The budget deficit (Budget surplus (+) or deficit (-)) is N/A.
The fiscal year in Russia is the calendar year.
In the country’s economy, we have to consider the public debt. Public debt is the consolidated sum of the state’s local, federal, and central government debt.
Inflation rate and prime lending rate in Russia
A few further interesting and relevant economic data are the following; Inflation rate: 7.2% (2016 estimate), 15.5% (2015 estimate), and the rate of the Commercial bank prime lending rate: 12.7% (31 December 2016 estimate).
Export/import partners and data of Russia
Russia, with the export of products, industrial tools, and other services, generates revenue. The export value in Russia is: $259.3 billion (2016 estimate), $341.5 billion (2015 estimate). The total revenue of these activities: petroleum and petroleum products, natural gas, metals, wood and wood products, chemicals, and a wide variety of civilian and military manufactures.
Russia’s most important export partners are the Netherlands, 11.9%, China 8.3%, Germany 7.4%, Italy 6.5%, Turkey 5.6%, Belarus 4.4%, Japan 4.2% (2015).
The most important imported products are machinery, vehicles, pharmaceutical products, plastic, semi-finished metal products, meat, fruits and nuts, optical and medical instruments, iron, steel, and the countries from where the import is coming: China 19.2%, Germany 11.2%, US 6.4%, Belarus 4.8%, Italy 4.6% (2015).
Renewable energies used in Russia
To suppress the pollution of the environment, renewable energies have to replace the fossil energy. The more the proportion of renewable energies in a country means more effort against pollution. Russia, the indicator of how much of the country’s produced energy is coming from the hydroelectric source, is 20.2% of total installed capacity (2012 estimate).
To indicate how much another renewable energy produced is 0.4% of total installed capacity (2012 estimate).
Telecommunication data of Russia, calling code
To maintain the economy, the development of a reliable and modern telecommunications infrastructure is crucial. We can say the following about Russia; the telephone system is experiencing significant changes; more than 1,000 companies licensed to offer communication services; access to digital lines has improved, particularly in urban centers; progress made toward building the telecommunications infrastructure domestic: cross-country digital trunk lines run from Saint Petersburg to Khabarovsk, and from Moscow to Novorossiysk; the telephone systems in 60 regional capitals have modern digital infrastructures; cellular services, both analog and digital, are available in many international: country code – 7; connected internationally by undersea fiber -optic cables; satellite earth stations provide access to Intelsat, Intersputnik, Eutelsat, Inmarsat, and Orbita systems (2011).
Transport infrastructure in Russia
In the 21st century, we often say that the world has become small and there are no distances anymore. With widespread air travel when (sometimes) there are no visa restrictions, it is easy to reach other countries, but if the distance is not too long, we can also use railway or water transportation.
The number of airports in Russia: 1,218 (2013), and the number of heliports: 49 (2013).
The total length of the roadways in Russia: total: 1,283,387 km, paved: 927,721 km (includes 39,143 km of expressways), unpaved: 355,666 km (2012).
The total length of the waterways in Russia: 102,000 km (including 48,000 km with guaranteed depth; the 72,000-km system in European Russia links Baltic Sea, White Sea, Caspian Sea, Sea of Azov, and the Black Sea) (2009).
Are you traveling to Russia?
If you plan to travel by plane to Russia, try our air ticket comparison site, where you can choose from hundreds of carriers and offers. Our application is scanning the market and shows you the best and the cheapest deals without any extra charge or commission.
Are you looking for a hotel, apartment another kind of accommodation in Russia, Asia? We are here to help you to find your accommodation from budget to luxury. Our search engine is scanning, regularly updating data from hundreds of accommodation websites and more than a million offers. You can quickly and easily find your hotel stay anywhere in the world, without any extra charge or commission.
Facts & data about Russia
Name of the country: conventional long way: Russian Federation, traditional short form: Russia, local long form: Rossiyskaya Federatsiya, local short state: Rossiya, former: Russian Empire, Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic, etymology: Russian lands were generally referred to as Muscovy until PETER I officially declared the Russian Empire in 1721; the new name sought to invoke the patrimony of the medieval eastern European Rus state centered on Kyiv in present-day Ukraine; the Rus were a Varangian (eastern Viking) elite that imposed their rule and eventually their name on their Slavic subjects.
| Abbreviation: Russia | Geographic coordinates: 60 00 N, 100 00 E |
Country Location: Asia |
| Capital of Russia: Moscow | GPS of the Capital: 55 45 N 37 36 E |
Position: North Asia bordering the Arctic Ocean, extending from Europe (the portion west of the Urals) to the North Pacific Ocean |
| Land area: total: 17,098,242 sq km; land: 16,377,742 sq km, water: 720,500 sq km | Terrain: broad plain with low hills west of Urals; vast coniferous forest and tundra in Siberia; uplands and mountains along southern border regions |
Area comparative: approximately 1.8 times the size of the US |
| Population: 142,355,415 (July 2016 estimate) | Population grow rate: -0.06% (2016 estimate) | Sex ratio: at birth: 1.06 male(s) / female, 0-14 years: 1.06 male(s) / female, 15-24 years: 1.05 male(s) / female, 25-54 years: 0.96 male(s) / female, 55-64 years: 0.75 male(s) / female, 65 years and over: 0.45 male(s) / female, total population: 0.86 male(s) / female (2016 estimate) |
| Exports: $259.3 billion (2016 estimate), $341.5 billion (2015 estimate) | Imports: $165.1 billion (2016 estimate), $193 billion (2015 estimate) | Import partners: China 19.2%, Germany 11.2%, US 6.4%, Belarus 4.8%, Italy 4.6% (2015) |
| Urbanization: urban population: 74% of the total population (2015) | Major urban area(s): MOSCOW (capital) 12.166 million; Saint Petersburg 4.993 million; Novosibirsk 1.497 million; Yekaterinburg 1.379 million; Nizhniy Novgorod 1.212 million; Samara 1.164 million (2015) | Median age: total: 39.3 years; male: 36.4 years, female: 42.3 years (2016 estimate) |
| Internet users: total: 104.553 million. Percent of the population: 73.4% (July 2015 estimate) | Telephones (fixed-lines): total subscriptions: 36,524,978. Subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 26 (July 2015 estimate) | Telephones (mobile, cellular): total: 227.288 million. Subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 160 (July 2015 estimate) |
| Unemployment rate: 8.2% (2016 estimate) | Nationality: Russian(s) adjective: Russian | National holidays: Russia Day, 12 June (1990) |
| Life expectancy at birth: total population: 70.8 years. Male: 65 years, female: 76.8 years (2016 estimate) | Total fertility rate: 1.61 children born / woman (2016 estimate) | Birthrate: 11.3 births / 1,000 population (2016 estimate) |
| Literacy: age 15 and over can read and write. Total population: 99.7%; male: 99.7%, female: 99.6% (2015 estimate) | Legal system: civil law system; judicial review of legislative acts | Suffrage: 18 years of age, universal |
| Industries: complete range of mining and extractive industries producing coal, oil, gas, chemicals, and metals; all forms of machine building from rolling mills to high-performance aircraft and space vehicles; defense industries (including radar, missile production, | Industrial production growth rate: 0.7% (2016 estimate) | GDP real growth rate: -0.8% (2016 estimate) -3.7% (2015 estimate) 0.7% (2014 estimate) |
Do you like this Russia Google Maps & country information page?
Please do us a favor: Share or like this page using the icons at the top of the page. We also do encourage you to visit our Facebook page for more travel and country related information.
Many thanks for visiting and sharing this map & country information site!
