The United States (USA) Google Maps
Google Maps and detailed facts about the United States (US). This page lets you explore the United States (USA) and its border countries (Country Location: North America, bordering both the North Atlantic Ocean and the North Pacific Ocean, between Canada and Mexico) through detailed Satellite imagery – fast and easy as never before Google Maps.
Find comprehensive information about this country’s diversity below: Google Maps, geography, economy, science, people, culture, environment, government, and history – All in One Wiki page.
There is also a Street View and free Driving Directions at your service. Your Google Satellite Map Sightseeing in the United States (USA) in North America starts here at Driving Directions and Maps.com.
 |  |  |
| Borderline map of the United States (USA) | Location map of the United States (USA) | Flag of the United States (USA) |
Table of contents
- Background
- Overview
- Google Maps
- Climate
- Geography
- Resources and Land Use
- Population Data
- Economic Data
- Drinking Water Source
- Population, Median Age, Migration, and Citizenship
- Average Number of Childbirths
- Is this country a Safe Destination?
- Healthcare and Infectious Diseases
- Natural Hazards
- The Flag and Other Symbols
- Constitution
- Legal System
- About the Unemployment Rate, Labor Force, and Poverty Line
- About the Budget and Central Government Debt
- Inflation Rate and Prime Lending Rate
- Export/Import Partners and Data
- Renewable Energies Used
- Telecommunication Data, Calling Code
- Transport Infrastructure
- More Interesting Facts
Background
The United States of America, formed from Britain’s American colonies breaking away in 1776, has a history of significant expansion and growth. Following the Treaty of Paris in 1783, the nation expanded across the North American continent, adding 37 new states to the original 13. The United States has faced pivotal historical moments, including the Civil War and the Great Depression. The US remains a leading global power, emerging victorious in both World Wars and the end of the Cold War in 1991. Since World War II, the nation has seen steady economic growth, low unemployment and inflation rates, and significant technological advancements.
Overview
The United States, located in North America and bordering both the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans, is the third-largest country by size and population. It’s a constitutional federal republic comprising 50 states and the District of Columbia. The US economy is diverse and highly developed, being the world’s largest importer and the second-largest exporter.
Official Name: United States of America
Date of Formation: 1776
Capital: Washington, D.C.
Population: Approximately 339.7 million (2023 estimate)
Total Area: 9,833,517 square kilometers (3,796,742 square miles)
Population Density: N/A
Languages: English (predominant), Spanish, and numerous other languages
Religions: Predominantly Christian, with a diversity of other religious affiliations
Ethnic Origin: Diverse, including White, African American, Hispanic, Asian, Native American, and others
Government: Federal presidential constitutional republic
Currency: United States Dollar (USD)
Literacy Rate: N/A
Calorie Consumption: N/A
The United States (USA) Google Maps
Google Maps offers an extensive view of the United States’ vast geography, including its major cities, national parks, and diverse landscapes. It’s an essential tool for exploring the country’s various regions, from the bustling streets of New York City to the serene landscapes of the Grand Canyon.
The map below shows the United States (USA) with its cities, towns, highways, main roads, streets, and Street Views. To find a location, use the form below, type any city or place, view a simple map, and click the “show map” button.
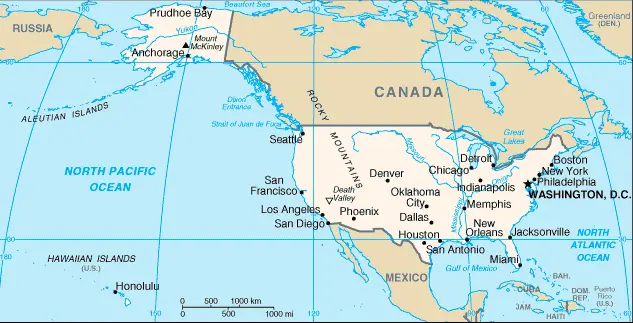
The Google Maps above shows the United States (USA) with its location: North America (geographic coordinates: 38 00 N, 97 00 W) and the international borders of the United States (USA); total: 12,048 km. Border countries (total: 2): Canada 8,893 km (including 2,477 km with Alaska), Mexico 3,155 km.
Note: The US Naval Base at Guantanamo Bay, Cuba, is leased by the US and is part of Cuba; the base boundary is 28.5 km; furthermore, it has inland counties’ boundaries.
The United States (USA) and North American maps are for informational use only. No representation is made or warrantied given any map or content by Driving Directions and Maps site. The user assumes all risks of using the United States (USA) Google Maps and Facts/wiki.
Climate
The United States, due to its vast size and diverse topography, experiences a wide range of climatic conditions. Here’s an extended overview of the various climate zones and weather phenomena across different regions of the U.S.:
- Tropical Climate in Hawaii and Florida: Hawaii, being in the central Pacific, and southern Florida have a tropical climate. These areas experience warm temperatures year-round, with a wet season in the summer and a dry season in the winter. The average temperature in these regions is typically above 18°C (64°F).
- Arctic Climate in Alaska: Northern parts of Alaska experience an arctic climate, characterized by long, very cold winters and short, cool summers. In the Arctic regions, temperatures can drop below -30°C (-22°F) during winter. The warmest month has an average temperature below 10°C (50°F).
- Semiarid and Arid Climates in the Great Plains and Southwest: The Great Plains, stretching from Texas to North Dakota, have a semiarid climate, with relatively low annual rainfall, hot summers, and cold winters. The Great Basin and parts of the Southwest, including large areas of Nevada and Arizona, experience an arid or desert climate characterized by very low rainfall and high temperatures, especially in the summer.
- Humid Continental Climate in the Northeast and Midwest: The Northeast and Midwest regions generally experience a humid continental climate. This climate features warm to hot summers and cold winters, with a significant temperature variation between seasons. Precipitation is fairly evenly distributed throughout the year.
- Mediterranean Climate in Coastal California: Coastal California, particularly its central and southern parts, experiences a Mediterranean climate characterized by dry summers and mild, wet winters. This climate is ideal for agriculture, supporting a variety of crops, including grapes, olives, and citrus fruits.
- Marine West Coast Climate in the Pacific Northwest: The Pacific Northwest, including western Washington and Oregon, has a marine west coast climate. This region experiences mild, wet winters and relatively dry, mild summers. The proximity to the ocean moderates temperature extremes.
- Diverse Weather Phenomena:
- Hurricanes: The U.S. Gulf Coast and East Coast are susceptible to hurricanes, particularly from June to November. These powerful storms can cause significant damage due to high winds, heavy rainfall, and storm surges.
- Tornadoes: The U.S. experiences more tornadoes than any other country, particularly in the central part, known as “Tornado Alley,” which includes states like Oklahoma, Kansas, and Texas. Tornado season typically peaks in the spring and early summer.
- Blizzards: Northern states, particularly those in the Midwest and Northeast, often experience blizzards in the winter. These severe snowstorms are accompanied by strong winds and low visibility, creating hazardous conditions.
- Climate Change Impact: The U.S. is experiencing various impacts from climate change, including increased temperatures, changes in precipitation patterns, more frequent and intense heat waves, rising sea levels, and an increase in the severity of extreme weather events.
- Regional Variations: Within these broad climate zones, there are significant regional variations. For example, the Appalachian Mountains, the Rocky Mountains, and other ranges have their microclimates, with generally cooler temperatures and more precipitation at higher elevations.
The climate of the United States, with its vast array of conditions, plays a significant role in shaping the country’s natural landscapes, agriculture, and lifestyle. Understanding these climatic conditions is crucial for environmental planning and agriculture and for addressing the challenges of climate change.
Geography
The United States’ geography is incredibly diverse, encompassing many physical features across its vast expanse. Here’s an extended overview of the U.S. geographical features, including more detailed statistics and information about its neighboring countries:
- Central Plains: The Great Plains stretch across the central part of the country, from Texas in the south to the Canadian border in the north. This region is characterized by its flat to gently rolling terrain and is a major agricultural area, often referred to as the “breadbasket” of the U.S.
- Mountain Ranges in the West: The western United States is known for its rugged mountain ranges. The Rocky Mountains, extending from New Mexico to the northern U.S. border, are a prominent feature. Other significant ranges include the Sierra Nevada and the Cascades. These mountains are known for their scenic beauty and are home to several national parks.
- Low Mountains in the East: The eastern U.S. features lower, older mountain ranges such as the Appalachian Mountains, which extend from Alabama to the northeastern states and into Canada. These mountains are characterized by their rolling appearance and rich biodiversity.
- Volcanic Topography in Hawaii: The Hawaiian Islands, located in the central Pacific Ocean, are volcanic in origin. The islands feature a range of volcanic landscapes, including active volcanoes like Kīlauea and Mauna Loa on the Big Island.
- Highest Point – Denali: Denali, formerly known as Mount McKinley, is the highest peak in North America, standing at 6,190 meters (20,310 feet). It is located in Alaska and is a prominent feature of Denali National Park and Preserve.
- Lowest Point – Death Valley: The lowest point in the U.S. is Death Valley, California, at -86 meters (-282 feet) below sea level. Death Valley is one of the hottest and driest places in North America.
- Total Area: The total area of the United States is approximately 9.8 million square kilometers (3.8 million square miles), making it the third or fourth largest country by total area, depending on the measurement method.
- Coastline: The U.S. has a vast and varied coastline along both the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans, including the Gulf of Mexico. The total length of the nation’s coastline is about 133,312 kilometers (82,931 miles), including Alaska and Hawaii.
- Surrounding Countries:
- Canada: To the north, the U.S. shares a long border with Canada, extending about 8,891 kilometers (5,525 miles). This border is the longest international border globally, not patrolled by military forces.
- Mexico: To the south, the U.S. shares a border with Mexico, which is approximately 3,145 kilometers (1,954 miles) long. This border traverses a variety of terrains, including deserts, mountains, and rivers.
- Alaska and Arctic Region: Alaska, the largest state in the U.S., extends into the Arctic Circle and has a diverse geography, including coastlines, mountains, forests, and tundra.
- Diverse Ecosystems: The U.S. encompasses many ecosystems, from the tropical rainforests of Hawaii and the Everglades in Florida to the arid deserts of the Southwest and the vast forests of the Pacific Northwest and the Northeast.
The geography of the United States, with its vast plains, multiple mountain ranges, diverse coastlines, and unique island territories, not only defines its natural beauty and resources but also influences its climate, biodiversity, and human activities. The country’s position in North America and its borders with Canada and Mexico are important for understanding its geopolitical and environmental context.
Resources and Land Use
The United States is indeed endowed with a wealth of natural resources, which have played a significant role in its economic development. Here’s an extended overview of the U.S.’s natural resources, including more detailed statistics and some interesting facts:
- Coal Reserves: The U.S. has the world’s largest coal reserves, with about 23% of the world’s total. These reserves are primarily located in the Appalachian, Illinois Basin, and western regions, including Wyoming, Montana, and North Dakota. Coal has historically been a major energy source, though its use has declined in recent years due to environmental concerns and competition from natural gas and renewable energy sources.
- Copper: The U.S. is one of the world’s largest producers of copper. Major copper mines are located in Utah, Arizona, New Mexico, Nevada, and Montana. Copper is essential for electrical wiring, plumbing, and the production of industrial machinery.
- Lead and Zinc: The U.S. also has significant lead and zinc resources, with major mines in Alaska, Missouri, and Idaho. These metals are used in batteries, construction materials, and alloys.
- Phosphates: The U.S. is a major producer of phosphates, primarily used in fertilizer. The largest phosphate rock deposits are found in Florida, North Carolina, Idaho, and Utah.
- Rare Earth Elements (REEs): The U.S. has significant deposits of REEs, which are critical for manufacturing high-tech devices, including smartphones, electric vehicles, and various defense applications. The Mountain Pass mine in California is one of the richest REE deposits in the world.
- Uranium: Uranium mining in the U.S. has historically been concentrated in states like Wyoming, Texas, and Nebraska. Uranium is critical for nuclear power generation and military uses.
- Bauxite and Aluminum: While the U.S. has bauxite reserves, particularly in Arkansas, it relies heavily on imports for aluminum (processed from bauxite), mainly due to the high energy costs associated with aluminum production.
- Gold: The U.S. is one of the top gold-producing countries, with significant mining operations in Nevada, Alaska, and Colorado. Gold is used in jewelry and electronics and as an investment.
- Iron Ore: The U.S. has large iron ore deposits, particularly in the Great Lakes region. Minnesota and Michigan have large iron ore reserves, a key component in steel production.
- Timber: The U.S. has extensive forested areas, especially in the Pacific Northwest, the South, and the eastern U.S. Timber is a significant natural resource used for construction, paper products, and furniture.
- Reliance on Imports for Certain Resources: Despite its vast natural resources, the U.S. relies on imports for certain strategic minerals, including some REEs, tin, and chromium. This reliance is due to a combination of factors, including the economics of domestic production and the availability of resources abroad.
- Energy Production: The U.S. is a leading producer of natural gas and oil, largely due to the development of hydraulic fracturing and horizontal drilling technologies. Texas, Pennsylvania, Oklahoma, and North Dakota are among the top oil and gas-producing states.
These natural resources have been crucial for the U.S. economy and play a significant role in global markets. The management and development of these resources continue to be a key aspect of U.S. economic and environmental policy.
Population Data
As of 2023, the US population is approximately 339.7 million. The population is concentrated in urban clusters throughout the eastern half and along the western states.
Economic Data
The real GDP of the US is $21.132 trillion, with a growth rate of 5.95% as of 2021. The economy is characterized by low-interest rates, rising socioeconomic inequalities, and the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic.
Drinking Water Source
About 99.9% of the US population can access improved drinking water sources.
Population, Median Age, Migration, and Citizenship
The median age in the US is 38.5 years. The country experiences a net migration rate of 3 migrants/1,000 population.
Average Number of Childbirths
The total fertility rate in the US is 1.84 children born per woman.
Is this country a Safe Destination?
The United States is generally considered safe for travel; however, crime rates can vary significantly between urban and rural areas.
Healthcare and Infectious Diseases
The US spends 18.8% of its GDP on healthcare, with a physician density of 2.61 physicians/1,000 population.
Natural Hazards
The US faces various natural hazards, including tsunamis, earthquakes, hurricanes, tornadoes, and wildfires, particularly in certain geographic regions.
The Flag and Other Symbols
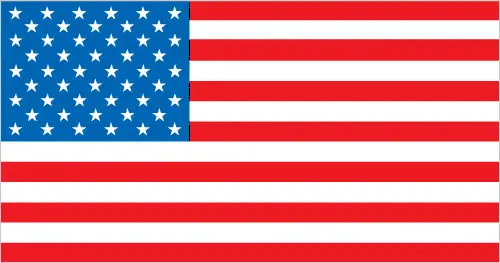
The US flag, known as “Old Glory,” has 13 stripes and 50 stars, representing the original colonies and the states. The national symbol is the bald eagle.
Constitution
The US Constitution, the world’s oldest written national constitution still in use, was ratified in 1788 and has been amended 27 times.
Legal System
The US legal system is based on English common law, with a unique blend of federal and state laws.
About the Unemployment Rate, Labor Force, and Poverty Line
The unemployment rate was 5.46% in 2021, and approximately 15.1% of the population lived below the poverty line in 2010.
About the Budget and Central Government Debt
The public debt of the US stood at 126.39% of GDP in 2020, with budget revenues of $6.429 trillion against expenditures of $7.647 trillion in 2019.
Inflation Rate and Prime Lending Rate
The inflation rate was 4.7% in 2021.
Export/Import Partners and Data
Major export partners include Canada, Mexico, and China, with key exports being refined petroleum, natural gas, and cars. Major imports, including cars and crude petroleum, come from China, Mexico, and Canada.
Renewable Energies Used
The US is gradually increasing its renewable energy sources, including solar, wind, and hydroelectric power.
Telecommunication Data, Calling Code
The US has an advanced telecommunication system with a country code of +1. It’s a global leader in internet and mobile technologies.
Transport Infrastructure
The US boasts an extensive transport infrastructure, including the world’s largest number of airports, a vast network of highways, and extensive railroads.
More Interesting Facts
The US is known for its diverse culture, technological innovation, and influential role in global affairs. It has numerous world-renowned landmarks, national parks, and cultural institutions.
Did You Know?
- Diverse Landscape: The United States is one of the world’s most geographically diverse countries. It includes a variety of landscapes, from the Arctic wilderness of Alaska to the tropical beaches of Hawaii, the vast Great Plains, the world’s largest cave system at Mammoth Cave National Park, and the majestic Grand Canyon.
- Tallest Mountain: While Denali in Alaska is the highest peak in North America at 6,190 meters (20,310 feet), when measured from base to summit, Hawaii’s Mauna Kea is the tallest mountain on Earth, exceeding Everest. Most of Mauna Kea is underwater, with its total height from base to summit being about 10,210 meters (33,500 feet).
- Largest Volcano: The Yellowstone Caldera in Yellowstone National Park is one of the largest active volcanic systems in the world. The park is also famous for its geothermal features, such as the Old Faithful geyser.
- Invention Hub: The U.S. is known for its spirit of innovation and has been the birthplace of many modern technologies, including the Internet, the airplane, the light bulb, and the mobile phone.
- Cultural Influence: American music, movies, and television shows have significant global influence. Hollywood is considered the world’s movie capital, and American music genres like jazz, blues, rock, and hip-hop have worldwide popularity.
- National Parks System: The U.S. established the first national park in the world, Yellowstone National Park, in 1872. The country now has 63 national parks, attracting millions of visitors annually.
- Diverse Climate: The U.S. experiences many climatic conditions, from the tropical climate in Florida and Hawaii to the polar climate in Alaska. The country also sees a range of weather phenomena, including hurricanes, tornadoes, and blizzards.
- Multicultural Society: The U.S. is often called a “melting pot” because of its diverse population, composed of people from virtually every nation and culture in the world. This diversity is reflected in the country’s cuisine, traditions, and languages spoken.
- Space Exploration: The United States was the first country to land a man on the Moon in 1969. NASA, the U.S. space agency, has been a global leader in space exploration for decades.
- Largest Economy: The U.S. has the world’s largest economy by nominal GDP. It is also a global leader in science and technology research and development.
- National Symbol: The bald eagle is the national bird and symbol of the United States, chosen for its long life, great strength, and majestic looks.
- Sporting Culture: Sports are an integral part of American culture, with American football, baseball, basketball, and ice hockey being the most popular sports in the country.
These facts about the United States highlight its vast geographical diversity, cultural influence, technological innovation, and unique natural wonders, making it a country of significant global importance and interest.
Thank you for visiting & supporting us!
